It just so happened that the Voskhod-2 engine, the repair of which will be discussed in this article, was given to me for repair in a non-working condition. And to be more precise, half disassembled. According to the owner of this miracle, after a major overhaul the engine started poorly and was consuming oil from the gearbox.
Naturally, the owner was not satisfied with such a repair, and after a long and tedious discussion, he and I agreed that the engine needed to be disassembled again - to assess the scale of the technical problems and, based on this and the availability of the necessary spare parts for sale, make a decision on the advisability of further repairs.
I don't know if this engine had clutch problems or not. Who knows?.. Maybe they were, maybe not. In any case, since the owner and I have agreed on a major overhaul, we will disassemble the clutch, like other components, check the parts for acceptable wear, and after a major overhaul of the engine, we will put everything back together.
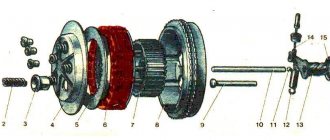
Voskhod clutch device
A motorcycle clutch is a mechanism designed to temporarily disconnect the rotation transmission from the crankshaft to the gearbox and further along the chain to the wheel. By squeezing the lever on the left half of the steering wheel, we break the connection of this chain. By releasing, the reverse action of connection occurs. It is desirable that the work be carried out without sudden jerks. This helps to start the movement smoothly. It is also necessary for changing gears, braking, and stopping the motorcycle.
Return to content☝
Motorcycle clutch Minsk
The design of the clutch mechanism of Minsk motorcycles.
The clutch mechanism is designed to transmit torque from the engine to the gearbox, disconnect the Engine from the gearbox during gear changes and during emergency braking of the motorcycle (so that the engine does not stall when the motorcycle stops). The clutch ensures smooth starting of the motorcycle, protects transmission and engine parts from damage when there is a sudden change in the speed of the engine or the drive wheel of the motorcycle. The clutch is multi-plate and operates in an oil bath. Minsk motorcycles are equipped with four cork drive clutch discs (you can also install six plastic discs from the Voskhod motorcycle).
To control the activation mechanism, use a lever mounted on the left side of the steering wheel. When the control lever is released, the clutch is engaged. When you press the clutch control lever, the discs move apart and friction between them stops. In this case, the clutch is disengaged. Use the clutch control lever when starting, changing gears, stopping and braking. Do not change the speed by slipping the clutch; this will lead to accelerated wear of the clutch discs.
How to adjust the clutch?
Clutch adjustment is carried out using an adjusting screw, when turning it out, the free play of the clutch lever increases, and when screwing it in, it decreases. Carry out work on adjusting the clutch in the following sequence: remove the plug of the right crankcase cover and, having released the lock nut, unscrew and then tighten the screw until the fungus rests on the clamping disk (this moment is determined by a noticeable increase in the resistance to tightening). Then loosen the screw 1/4 turn and tighten the locknut, holding the screw from turning with a screwdriver. In a correctly adjusted clutch, the free play at the end of the lever (on the motorcycle handlebar) should be 5.10 mm. Why does the clutch “drive” or “slip”?
Clutch slipping is expressed by a discrepancy (slow increase) between the speed of the motorcycle and the engine crankshaft rotation speed, which is especially noticeable during acceleration, when starting from a stop and moving uphill.
If the clutch adjustment is carried out correctly, then one of the reasons for slipping may be weakening of the pressure springs. They should be screwed in deeper (1 turn), and the protruding ends of the springs (more than 4.5 mm from the end of the drum) should be ground off. Slipping can also occur due to jamming of the worm and clutch cable, as well as a bent rod in the hole of the input shaft. The worm and cable should be washed and lubricated, and the bent rod should be straightened. The clutch also “slips” if the cork liners of the drive discs are worn. In this case, you should increase the thickness of the disk package by adding one driven and one driving disk (the driving disk can also be plastic from the Voskhod motorcycle), adding two or three driven disks, or replacing the entire worn package.
The reason for slipping of the clutch discs can be significant wear (the appearance of holes) in the grooves of the drive drum, in which the discs “hang” when the clutch is engaged. To eliminate the malfunction, you should disassemble the clutch mechanism and use a needle file or a small file to clean out the irregularities at the ends of the grooves.
A sign that the clutch is “driving” is difficulty shifting gears, as well as the motorcycle’s tendency to move with the clutch lever fully depressed.
The clutch “drives” for one of the following reasons: incorrect adjustment; misalignment of the pressure plate due to uneven tension of the springs; bending of the fungus stem or as a result of non-perpendicularity of the supporting plane of the fungus head to its stem, as well as due to the increased viscosity of the oil in the gearbox crankcase. When the oil is not warmed up, a serviceable clutch with a correctly adjusted drive also “drives”, so clutch operation should be assessed on a warm engine.
Kickstarter Sunrise
This unit performs another important job - starting the engine. By pressing the kickstarter to start the engine, the sector engages with a gear mounted on the drum on the side of the box. The gear, in turn, begins to rotate the drum and then the chain transmits force to the crankshaft. The engine starts.
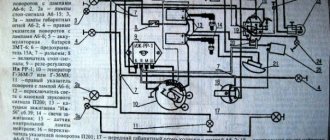
The location of the clutch is in the left half of the engine crankcase, on the input shaft of the box. It is closed with a lid with holes for fastening bolts.
At the top of the cover there is a threaded hole and a plug - a dipstick for filling and monitoring the oil level. In the center of the lid there is a threaded plug for adjustment.
Return to content☝
Photo report: Repair of the clutch of the Voskhod and Minsk motorcycles
It just so happened that the Voskhod-2 engine, the repair of which will be discussed in this article, was given to me for repair in a non-working condition. And to be more precise, half disassembled. According to the owner of this miracle, after a major overhaul the engine started poorly and was consuming oil from the gearbox.
Naturally, the owner was not satisfied with such a repair, and after a long and tedious discussion, he and I agreed that the engine needed to be disassembled again - to assess the scale of the technical problems and, based on this and the availability of the necessary spare parts for sale, make a decision on the advisability of further repairs.
Disassembling the clutch and kickstarter Voskhod
We repeat all removal work exactly as described below: - remove the ends of the spring from engagement with the pressure plate; — dismantle the pressure disk with the adjusting bolt and lock nut, driven and driven; - remove the squeeze fungus; — bend the lock washer securing the inner drum, use a 22 by 17 socket wrench to unscrew the nut and remove the inner drum.
It is easier and more convenient to unscrew the fastening nut by fixing the drum using a homemade device as in the photo. Don't forget the thread is left-handed.
— Unscrew the nut securing the crankshaft sprocket, remove the washer; - pull off the drive gear from the crankshaft along with the chain and outer drum; — remove the key from the groove of the left crankshaft journal; — remove the spacer sleeve with the washer from the input shaft; — remove the trigger mechanism.
Why put the trigger lever on the splined end of the roller? Slowly turning it clockwise, lift the trigger mechanism upward so that it goes beyond the plane of the crankcase. Then, slowly releasing it, take it out.
Return to content☝
Photo report: Disassembling the engine of the Voskhod-3M motorcycle
The engine that we will be disassembling today had some problem with gear shifting. The owner seemed to start disassembling it, removed the generator, clutch basket, cylinder, and then something went wrong with him. In general, he took it, threw it into a bag and brought it to me with all the “gibles” for repairs.
Remove the kickstarter shaft.
Using round-nose pliers, remove the retaining ring from the piston pin boss, push it out and remove the piston from the connecting rod.
We take out the separator from the upper head of the connecting rod and hide it somewhere further.
We unscrew all the bolts holding the crankcase halves together and knock out the guide bushings (if any). Typically, guide bushings are pressed into holes through which the engine is attached to the frame.
We take a mallet and strike the crankcase halves evenly from all sides (“pricking the engine”).
Before disassembling the engine, do not forget to put the drive sprocket on the output (secondary) shaft of the gearbox. If this is not done, then during disassembly, the secondary shaft jumps out of the cage and all the bearing rollers scatter in different directions. The videos are then very difficult to find. It is better to remove the secondary shaft over some kind of pallet or container, so that if something happens, the rollers will not disappear from you.
The crank chamber contained sea sand mixed with some kind of dirt. The main bearings from such “super synthetics” became completely unusable.
The condition of the main bearings, as I wrote above: “is beyond doubt”...
For ease of operation, we place the engine on some planks.
Unbend the lock washers of the gearshift bracket and remove the bolts.
Remove the bracket.
We unbend the lock washers on the bolts of the gear shift mechanism sector and unscrew the bolts in the same way.
We take out the intermediate shaft of the gearbox.
Using a screwdriver, press the sector lock of the gear shift mechanism inward.
We remove the gear shift mechanism sector from the crankcase.
The gear shift section was found to be in very good condition. Small abrasions on the gearshift forks are well within the permissible standard of 0.5 mm; I did not find any increased play or deformation. The gearbox, too, turned out to be in perfect condition, all the teeth are normal without damage, the cams are not “fidgeted”, the angles correspond to their values, in general the condition of the gearbox is simply perfect, which seemed very strange to me after what I saw in the crank chamber. The bearings, however, turned out to be very worn out, but this is nonsense.
We take out the shaft of the gear shift mechanism.
Remove the retaining ring and then remove the cap along with the spring.
So the reason (broken spring) for the problems with the gearbox was found.
Turn the engine over and use a mallet to knock out the gearbox input shaft.
We take the second half of the crankcase, place it on the planks so that the crankshaft hangs in the air, hold the crankshaft from the bottom with one hand, and use a mallet to knock it out of the crankcase half with the other hand.
After everything has been done, remove all the seals and retaining rings from the crankcase. We knock out worn bearings (if necessary).
There are adjusting washers under the gearbox bearings; try to remember their location so that when reassembling the gearbox you don’t have to re-adjust the axial play of the gearbox shafts.
After thoroughly washing all the parts, we carefully inspect the crankcase for damage, deformations, check the integrity of the threaded connections, and if any malfunctions are found, we eliminate them. You will find all the answers to crankcase repair in the article: Scooter crankcase repair
The final assembly of the Voskhod-3M motorcycle engine is shown in detail in the article: Repair of the Voskhod-3M motorcycle engine
Tips for assembling the Voskhod clutch
This work should be carried out in the reverse order, and the following tips should be taken into account: - the tension of the trigger spring should be such that the pedal freely returns to its original position; — under the screws securing the crankcase cover, except for the rear point, it is necessary to place copper-asbestos gaskets; — securely fasten the start and shift control levers to the rollers (without rolling), ensuring their free rotation relative to each other and the crankcase cover; — fill 500 cm3 of motor-tractor oil (the lower oil level in the crankcase should be 1.5 mm above the end of the dipstick, and the upper oil level in the crankcase should be at the dipstick mark).
After installing the coupling, we check its functionality. If during inspection it turns out that the clutch does not engage or disengage properly, adjustment must be made.
Return to content☝
Ignition and carburetor
It is these two components that, as a rule, determine the stability of the engine. Often, interruptions in the crankshaft rotation speed, loss of traction, and difficulties starting the engine are associated precisely with their malfunctions. Repairing the ignition and carburetor usually comes down to adjusting them. Setting the ignition includes setting the gap between the coil core and the sensor magnet within 0.295...0.305 mm. The piston ignition timing should be 3.5-5 mm to top dead center. Adjusting the carburetor is somewhat more difficult. If you are repairing a Voskhod-3M motorcycle, then you will have to deal with the K65V carburetor, and the main tools will be the quality and quantity screws included in its design. Using the first, you can lean or enrich the mixture - change the proportion of fuel and air entering the cylinder. The second determines its volume per working cycle. With the standard setting, the quality screw is screwed in completely and then unscrewed half a turn. Then the rotation of the quantity screw achieves the minimum stable speed and the quality of the mixture is re-adjusted. Finding the optimal adjustment balance is a search for maximum traction and stability with minimum fuel consumption.