The scooter's ignition system is needed to ignite the gasoline entering the cylinders. It is very important that the moment of fire is chosen accurately, otherwise the scooter will not move. Ignition is provided by a powerful electrical discharge issued by the spark plug. This requires a voltage of at least 15,000 volts, which can only be obtained thanks to the ignition coil, which converts the voltage supplied by the battery. Older models were equipped with contact cam ignition; modern ones are equipped with contactless ignition, which proves to be better and more practical.
DC CDI switch
One of the most famous switches due to the ease of connection. The most common one has only 4 contacts for the following wires:
- Plus (12V)
- Minus
- Hall Sensor
- Ignition coil
Despite its simplicity, there are many switches of this type. It is available with and without a maximum speed limiter, with variable ignition timing, and with additional contacts for a wide variety of needs. In particular, you can “hook” a side stand to some switches, so that when opened, the engine will not spin up to the speed at which the clutch engages. This is done in order to insure the driver against dangerous rash actions.
Scooter electronic ignition device
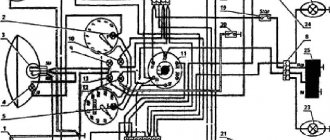
The modern ignition system of a 4t scooter is designed as follows: the switch and coil, which are its main elements, supply high voltage to the spark plug, which generates an electrical discharge that can ignite the fuel. The coil generates high voltage due to electromagnetic induction. The switch is needed to distribute its interruption voltage at the right time. Inside there is an electronic circuit, a thyristor and three outputs for wires. At the right moment, the switch supplies voltage or turns it off.
The principle of operation of the scooter ignition system is as follows: the battery supplies voltage to the coil, which is often connected to a switch in one unit, the switch supplies voltage to the spark plug, and decides when to interrupt it. The mixture in the cylinders lights up at the right time. The correct operation of the engine and whether it will start at all depends on how the ignition is configured and set.
Switch
In many scooter models, the commutator is combined with a coil, so if one of the devices fails, the entire unit has to be replaced. Such spare parts are inexpensive.
Externally, the switch looks like a plastic box. Inside there is a microcircuit, a variety of electronics that cannot be repaired. In addition, there is a thyristor. The task of this element is to interrupt the electrical impulse at the right moment; for this purpose it has three outputs. When current enters one of them, the thyristor turns into a conductor, and the current moves from the input contact to the output. When a certain voltage is reached and the current drops, the pulse is interrupted, after which the Hall sensor returns the thyristor to its original position so that the signal arrives again at the third output. The process is repeated every time the voltage is applied again.
AC switch
It differs from DC switches in the ability to do without a stable 12V current. It is designed a little differently, because, despite having a more conventional design, it has a more complex connection to the electrical circuit. Unlike DC switches, AC switches are mostly without a speed limiter due to their small size and fairly simple design; they can boast of the ability to operate perfectly in the absence of a number of nodes, without which a DC switch cannot work in principle. Even if you remove the battery, relay-regulator, ignition switch, keep only the high-voltage generator coil and the Hall sensor, and the scooter will still start and drive. There are quite cleverly organized switches of the provided type that can compete with the DC type, but this is rare. Despite the lack of need for direct current, speakers are very dependent on alternating current and the relationship between the engine block and the frame, and if you burnt or damaged one coil in the generator, which produces high voltage, then the scooter will not start under any circumstances.
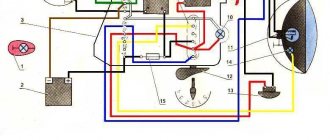
Ignition coil on a scooter: what is it for and how to diagnose its malfunction
The ignition on a scooter consists of many elements, but the basic unit of the entire system is the ignition coil. Without it, the operation of a moped or scooter will simply be impossible.
The main function of the ignition coil is to increase the operating voltage to a level at which the spark plug can create a spark and ignite the air-fuel mixture. If the ignition on the scooter is installed incorrectly, then without the appropriate voltage, a spark will not occur, and the motor vehicle simply will not move.
The ignition coil on a scooter is located immediately after the switch, so it is not difficult to find.
The ignition on a scooter works as follows. At a certain moment, the switching unit generates and supplies pulses of a special frequency to the ignition coil. This happens in a clearly defined time period when there is a corresponding engine stroke. By creating a spark in the spark plug, ignition is transmitted to the scooter through the system. The voltage, immediately after leaving the ignition coil, is applied to the spark plug, and its value is 10,000 volts or even more. Given such a high indicator, it is necessary to hold the spark plug cap extremely carefully and carefully when checking and diagnosing the spark. Especially when the electrode is shorted to the engine. At this moment it is strictly forbidden to touch him.
The ignition on scooters of different models and different manufacturers may differ in their design features, but the principle of operation will be the same everywhere. So, Suzuki and some Chinese models have an ignition coil built into the switch. Such a unit is considered non-separable, and it was first used at Suzuki factories. And Chinese factories simply copied a ready-made motorcycle part and did not invent anything new. This is even for the better, since this design of ignition on a scooter has already proven itself to be excellent among motorcyclists of all categories.
The model lines of other manufacturers (Yamaha and Honda) are fundamentally different. The scooter ignition installed on their motor vehicles is characterized by a separate design of the switch and ignition coil. And this can rightfully be considered the most rational option. As soon as one element fails, it is enough to replace it, rather than buy the entire complete unit. So, to replace the ignition coil, you will have to spend a little more than 5 US dollars, which is incommensurately little with the purchase of a switch.
Diagnosis of ignition coil malfunction
The ignition on a scooter often does not work due to a failed coil. Since the “culprit” is a transformer that produces high currents, its windings may burn out from time to time. The same thing often happens as a result of an interturn short circuit. Both the first case and the second lead to complete failure of the motorcycle part, after which the scooter stops starting.
Considering the importance of the coil, it is necessary to start checking the ignition on a scooter with it. This is the “golden” rule, compliance with which will help save a lot of time and money. You shouldn’t immediately rush to the motorcycle parts store and buy every possible ignition for your scooter; perhaps it’s just a matter of the coil.
To independently diagnose a faulty ignition coil, you will need a very ordinary multimeter that can measure the resistance value. The best option for the inexperienced would be a digital device, but for experienced motorcyclists there is not much difference. A digital multimeter is very important, since the values of the measured resistance may differ very slightly, and without proper experience, the fluctuations of the needle may simply not be detected.
There are 2 terminals on each ignition coil. Voltage is applied to them. There is also 1 output for high voltage voltage. It is to this that the spark plug is connected.
The ignition coil consists of two layers of winding - primary and secondary. Each one needs to be checked. To check the primary winding, you need to connect the multimeter probes to the terminals of the ignition coil, and then apply voltage. A range from 0.5 to 5 Ohms will be considered a normal indicator, but it is best to find your exact numbers in the manual for your scooter model.
If the readings are in the required range, then there may be problems with the secondary winding. To check, connect one probe to the power supply to the coil, and the other to the spark plug cap (high-voltage output). The reading range should be between 2 and 3 ohms.
Stock switch for scooter
A stock or original switch is the one that is installed on the vehicle from the factory. Its main advantage over others is that it is already designed for the equipment with which it operates; it is often equipped with a limiter so that the engine does not develop speeds that are dangerous to the life and life of the main bearings, the entire crank mechanism, cylinder-piston groups and other structures and assemblies. The stock commutator is the main source of a well thought out engine's longevity, efficiency and durability. Those who take the risk of replacing a factory switch with a sports (tuning) one are risking a lot. Those who do not fully understand what they intend to do risk even more. Inept installation of such parts and their subsequent use with a conventional engine often lead to a decrease in service life and the death of the engine, sometimes on the same day.
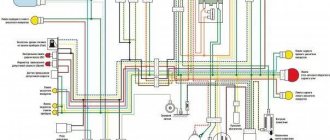
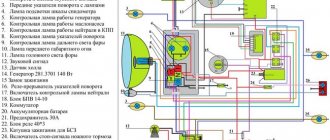
Ignition circuit components
The ignition circuit is an important part of the scooter's electrical system, without which it simply will not work without proper assembly. The circuit includes a coil, a spark plug, a switch, a generator, and a CDI ignition module. The latter looks like a small block, on one side it is plastic, on the other it is filled with compound. It is for this reason that when a unit fails, it is completely replaced without trying to disassemble it.
The CDI module has outputs for connecting five conductors. It is usually located quite close to the battery, can be mounted on the scooter frame or have a special cell. Most often, the CDI unit is located closer to the bottom of the vehicle, so it is not easy to reach. Without this element the system will not work.
Relay regulator
The relay regulator is colloquially called a stabilizer. This element is needed in order to rectify the voltage and stabilize it to the required level, which is suitable for the operation of the scooter’s electrical appliances. In Chinese and many Japanese models you need to look for it in the front of the vehicle, usually under the fairing. During operation, the radiator of the part becomes very hot, so it is placed where it can receive air cooling.
During operation, the generator produces alternating current, which is supplied first to the relay-regulator, and then moves on. The relay converts alternating voltage to direct voltage, in addition, it stabilizes the voltage to 13.5-14.8 Volts. If the voltage is less, the battery will not be able to charge; if it is more, there is a high risk of failure of the electrical system.
The regulator usually has 4 wires. They differ in color; in a standard diagram, the green wire is always ground. Red is under constant voltage. White supplies the regulator relay with the voltage supplied by the generator: this is alternating current. The yellow wire also goes from the generator to the relay regulator. The relay converts the voltage, turning it into a pulsating one. After this, the voltage goes to lighting fixtures, which are the most powerful consumers. Some models have an illuminated dashboard, additional lighting, running lights or other types of suspension. All this is powered by the same wire.