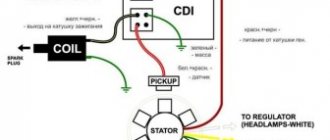
Hi all! In this article I will write about the most common problem - why there is no spark on the Alpha moped. And I will write the reasons for her disappearance.
You can check for a spark at the spark plug as follows. We unscrew the spark plug from the cylinder, put a high-voltage cap on it, turn on the ignition, lean the spark plug against the cylinder head and turn the kickstarter foot.
If a spark does not jump at the spark plug electrode, then we begin to look for the reason for its absence.
The first reason for the lack of a spark is a faulty spark plug.
The spark plug is faulty.
To do this, you must have a spare spark plug in stock. We put the high-voltage cap on the spare spark plug and repeat the procedure again. If there is no spark, then we look for the reason further.
If the spark on the spark plug electrode jumps in different directions, then it is better to replace it.
You should know that three things are responsible for a spark on a moped:
- Ignition coil (Bobbin);
- Switch;
- Generator.
We will now examine these three reasons.
Fork repair and disassembly process
Manipulations for complete replacement of oil, seals or oil seals and elimination of breakdowns require complete or selective disassembly of the front fork. This procedure is performed as follows:
- set the bike with the saddle down, loosen the brake, remove the front wheel, handlebars with stem and pipe;
- remove the fork, being careful not to lose the bearing balls. To remove the rod ring, you should use some sharp object.
Using a spring-elastomer design, we will try to understand in what sequence the fork needs to be disassembled:
- Unscrew the lower mounting bolts using hexagons.
- Unscrew the bolt that coordinates the force of the spring, remembering its stroke.
- Pull out the elastomer and, if necessary, change its size by simply cutting off the excess.
- Unscrew the bolts and remove the “pants”, from which, using a screwdriver, remove the anthers and bushings, rotating them clockwise.
Then all elements should be examined for the presence of defects and washed in kerosene. Parts that require lubrication must be treated with a suitable product. Experts recommend lubricating the spring with a thick product - this will make the fork work more efficiently. The assembly procedure is exactly the opposite and does not require additional explanation. Replacing a shock-absorbing bicycle fork should be entrusted to a person specializing in such work, or this procedure should be carried out in full accordance with his recommendations.
Experienced cyclists can repair the fork with their own hands, because during the process of use, a person who is interested in the structure of his vehicle gradually remembers the names and functions of the elements, and therefore it will not be difficult for him to detect the problem and fix it. Those who have recently become the owner of this type of transport and have not yet acquired the necessary skills and knowledge should turn to a bicycle workshop for help.
The second reason if there is no spark on the Alpha moped is the ignition coil, or switch
Checking the switch
The switch is in an accessible location. You just need to remove the right side decorative cover on the moped. Disconnect the switch from the wires and check with a multimeter. If such a device is not available, then we go to the store and buy a new switch. Fortunately, it costs a couple of hundred rubles.
Similar actions with the ignition coil.
Ignition coil (Bobbin)
Adjusting the shock absorber rebound speed
The rebound of the shock absorber characterizes the speed at which the fork returns to its original position under load. The response speed of the breaker mechanism must be such that the shock absorber does not shoot out immediately and can absorb the shock from the next obstacle.
How to determine the rebound efficiency of a bicycle fork? When driving over uneven surfaces, impacts are absorbed before they hit the steering wheel - the rebound is well tuned. The shock absorber does not work on small obstacles - minor adjustments are required. And finally, an advanced case when the end call is very late.
Rebound adjustment bolt: hare - increase speed, tortoise - slow down rebound
Adjusting rebound on the fly:
- Find a road or path with uneven surfaces.
- Set the regulator to the fastest rebound.
- Accelerate, feel how hard it hits the steering wheel.
- Tighten the adjuster until the beating stops.
It's important to set up the Rebound so that the shocks don't hit the wheel, but still maintain a soft ride. If the rebound is set to the correct value but the shock behaves unpredictably, the fork travel and compression may need to be readjusted. It is recommended to adjust the front fork not immediately, but in the sequence “Preload – Compression – Rebound”
Individual selection of each parameter will improve the performance of the shock absorber and provide comfortable trips
It is recommended to adjust the front fork not immediately, but in the sequence “Preload – Compression – Rebound”. Individual selection of each parameter will improve the performance of the shock absorber and provide comfortable trips.
The third reason is the generator
If after replacing the ignition coil and switch the spark does not appear, then we check the generator. Here we need a multimeter. We set the device to the diode position, remove the generator chip and begin the test. Two wires are responsible for the spark:
- blue with a white stripe is a hall sensor;
- black with a red stripe is the coil on the generator.
Generator chip
Check the hall sensor. We connect the probe from the device to the blue wire with a white stripe. And we connect the other probe to engine ground. Numbers should appear on the device, indicating that the hall sensor is working.
We do the same work with the coil on the generator. If the numbers are displayed on the device, then the coil on the generator is working. If nothing happens on the device, then you will have to change the generator or hall sensor.
Adjusting fork softness on a bicycle
Pre-setting the travel of the suspension fork - preload - allows you to set the spring stiffness.
When in optimal condition, the damping system dampens vibrations where needed and maintains firmness on level surfaces. The adjustment consists of changing the distance between the upper “unloaded” and lower point of maximum pressure.
Let's look at a few examples:
1 – load is minimal, fork is soft; 2 – high rigidity; 3 – correct setting
In the first case, the fork travel is close to the maximum possible. On the roads this will result in constant oscillations of the springs “up and down” under the pressure of the cyclist. Interestingly, such a fork will handle obstacles in the form of bumps and potholes poorly.
The second option is high fork rigidity, stroke length less than 50% of the original. This value is not enough for the smooth passage of large obstacles.
In the third situation, the shock absorber is fully tuned, allowing it to effectively absorb impacts without compromising the dynamics of the bike. On average, the correct setting is 70% to 90% of the fork travel of the unloaded distance.
The preload method depends on the shock absorber type:
- On spring models, the compression amount is changed manually using a special regulator. When replacing a spring, a stiffer shock absorber is selected to increase the load, and vice versa.
- For spring-air forks, the stiffness is adjusted through the pressure in the chamber.
- On air shock absorbers, the fork travel is controlled by changing the pressure in the positive sector.
You can measure the load in a stationary position, sitting on a bicycle or while moving. For accurate results, adjustments are recommended to be made in small increments.
The fifth reason is alarm
If all the work done does not produce results, then the reason may be the alarm installed on the moped. It can block the spark. Checked by turning off the alarm. We pull out the alarm chip and check for the presence of a spark. If a spark appears, then we remove the alarm unit or check it.
If all of the above reasons do not produce results and a spark does not appear, then we check the wiring on the moped, the high-voltage cap and connecting points that could oxidize and lose contact.
If after the above reasons you do not have a spark, then the spark has gone to the wheel. Joke.
"Chezet"
The history of the legendary “Cezet” goes back to pre-war times, when the Czechoslovak arms factory Ceska Zbrojovka (CZ) decided to start producing motorcycles. In 1936, the plant produced prototypes of the Cheset, on the basis of which motorcycles with engines of 250 and 350 cc were later developed.
In 1960, CZ launched the Cheset motorcycles into mass production. In the USSR, CZ experienced unprecedented success. Along with the Java, this motorcycle was a success among rockers, and the black Cheset became the dream of an entire generation.
The famous cross-country Cezet was born in 1962. The motorcycle was equipped with a 250 cc single-cylinder two-stroke engine. Cheset's finest hour lasted until the end of the 60s. Racers from the USSR, Belgium and the GDR competed on it and won championships.
What is interesting to the consumer
Why are city residents interested in the Delta?
The popularity of this model should be sought in the technical characteristics of the vehicle:
- Electric starter;
- More than moderate appetite - 2.5 l/100 km;
- Four-speed semi-automatic (for Delta Racer model);
- Load capacity 100 kg;
- Easy to maintain with your own hands;
- More than reasonable price for the model itself and spare parts.
Another electrical connection diagram from the spare parts catalog for Delta
Depreciation
This process is carried out in the fork using a spring and damper. It’s easy to guess that when the wheel hits an obstacle, the spring compresses, leveling the impact. Well, the damper plays the opposite role. It is necessary so that after an impact there is no rebound - a sharp return of the spring to its original position. Both elements are named conventionally. That is, a spring, for example, is not always a metal spiral. Its functions can be performed by various substances, including air.
Depending on the type of spring and damper, bicycle forks are:
- Spring. In such bicycle forks, there is no damper. The main element here is a simple steel spring. Despite the simplicity of the design, riding with such a fork on uneven roads is much more comfortable than with a rigid analogue.
- Spring-elastomer. In these forks, a damper works in tandem with a steel spring. The latter is an elastomer - an element made of soft plastic. Such a damper performs its tasks well, but serves little purpose. Due to rapid wear, the elastomer only lasts for a season of more or less active driving.
- Airborne. In such forks, air acts as both a spring and a damper. The low weight of this design is its main advantage. Air shock absorbers also have disadvantages. Among them are air leakage in cold weather and lack of adjustment. Air is pumped into forks of this type using a high-pressure bicycle pump.
- Oil-air. This type of forks is considered the best. The role of the spring is played by air, and the role of damper is played by oil. Thanks to the smooth recovery of air after compression, oil flows from one section to another. Such forks are considered optimal in terms of weight and have a large number of settings.
- Oil-spring. As the name suggests, the spring element in these forks is a steel spring, and the damper is oil. Shock absorbers of this design have the greatest weight. They also have a significant advantage - excellent shock absorption and smooth running.