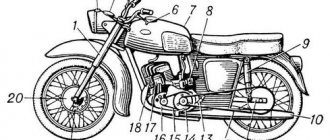
Moped inventors
The first attempts to create a motorcycle date back to 1885, when G. Daimler in Cannstadt installed a vertical gasoline engine on a specially built wooden bicycle. The design turned out to be too cumbersome and did not receive further development. However, in 1893, two other German inventors, Hildebrandt and Wolfmüller, began producing motorcycles in Munich, in which the connecting rods of a two-cylinder horizontal engine acted, like a steam locomotive, directly on the drive wheel, as a result of which the machine moved jerkily. Changing a blown tire meant having to re-adjust the engine. This design also did not leave a noticeable mark on the history of transport. Therefore, it can be argued that the first practical motorcycle, from which its modern counterparts are related, was created by Russian inventors Evgeny and Mikhail Werner.
Werner moped 1898
In 1896, in Paris, one of the brothers came up with the idea of installing a small gasoline engine on a bicycle. A horizontal four-stroke engine was placed above the rear wheel, the transmission to which was carried out using a roller chain and friction discs. But after testing, the engine (now vertical) was moved to the front fork. The result exceeded all expectations.
In 1897, 12 such bicycles were produced, and the following year, 1898, the company was founded for their production. They called their motorized bicycle "motorcycle". This is where the Russian word came from - a motorcycle, although essentially it was a moped.
The motorcycle with the "Werner Frere" ("Werner Brothers") emblem of 1898 (shown here) was equipped with a single-cylinder, four-stroke, air-cooled engine. It developed a power of 0.75 hp. With. at 1200 rpm. A large-diameter pulley with a semicircular groove was mounted on the front wheel. Rotation from the engine was transmitted to it by a round belt. To ignite the combustible mixture, it was not the spark plug of the electric ignition system that served, but the glow tube, which was heated red-hot before starting the engine. Since there was no clutch or gearbox, the motorcycle was started up using regular bicycle pedals.
The carburetor, like the ignition, was quite primitive - evaporative type. From the gasoline tank, fuel vapors flowed directly into the inlet pipe.
The advantage of the Werner machine was its simplicity and low weight - about 30 kg. Any bicycle quickly became a motorcycle (more precisely, a moped) only by installing a motor, a driven pulley and a gas tank.
The spread of Werner motorcycles in Russia in 1898-1900. It was carried out by one of the four brothers, Ippolit Antonovich, whose store was located in Moscow on Petrovka. Over the course of several years, Werner motorcycles won victories at many major competitions and received over 30 first and second prizes. In 1900, at the World Exhibition in Paris, they were awarded gold and silver medals.
The Werner's design caused numerous imitations. Light motorcycles (or mopeds) with a motor above the front wheel began to be produced, “Scheibert”, “Komet” in Germany, “Ixion” in France. And the plant that built the Wartburg cars in the German city of Eisenach even acquired a license from the Werners to produce their motorcycle.
Czech mechanic Vaclav Laurin, having visited Paris in 1898, became acquainted with the Werner invention and bought one machine. At home, using the Werner type, in 1899 he built a prototype of the first Laurin-Clement motorcycle, model 1A.
Subsequently, based on the experience gained during operation, Czech inventors began producing more advanced models, which essentially became the ancestors of today's motorcycles. On these “laurin-clements” the engine was already located in the middle of the frame, which had a special design that was not borrowed from the bicycle.
By the beginning of 1901, over 3,500 Werner motorcycles had been produced. At the same time, the brothers created a new design with an open frame (here they had already taken into account experience). The engine of this motorcycle was located in the middle (like modern ones), and its crankcase served as one of the frame links. Since 1902, many motorcycle companies in different countries began to build similar structures. Since 1906, it began producing cars, which was discontinued in 1914 due to the war.
Who are they, the Werner brothers? Here the automobile historian unwittingly intrudes into another area - the history of Russian journalism and publishing.
One of the brothers, Mikhail Antonovich, in addition to articles and essays, wrote novels, and the youngest, Evgeniy, was a poet.
In 1885, they acquired a printing house on Arbat and resumed publishing the magazine Around the World. Some time later, the Werners began publishing the magazines “Friend of Children” and “Cricket”, in which M.P. and A.P. Chekhov collaborated. An interesting review by Anton Pavlovich about the Werner brothers in a letter to the publisher I. A. Leikin: “Around the World” has more than 20 thousand subscribers, and “Cricket” for 5 thousand. What are these guys like?.. Energetic as hell...”
Mikhail Pavlovich Chekhov, who collaborated in “Children’s Friend,” describes the work of the brothers in their printing house this way: “Business was in full swing, the machines thundered, the gas engine flared and puffed, and the Werners themselves did not sit in bars, idly wait for profits, but both workers dressed in blue blouses worked right there, tirelessly. The main thing is that they themselves were up to their necks in the most menial work.”
Having settled in Paris, the Werners first tried to get into journalism. But things didn't work out for them. Then they organized a small workshop to repair binoculars, cameras, typewriters and gramophones. And here the idea of a “motorcycle” arose, the fate of which turned out to be more successful than all the other undertakings of the brothers.
It should be noted that light mopeds with an engine above the front wheel have survived to this day. One of the large French companies producing mopeds, Velosolex, has been producing mopeds with this arrangement for many decades (“Behind the Wheel,” 1985, No. 1). Therefore, we can rightfully call the Werner brothers the inventors of the moped in the most modern sense of the word.
V. DUBOVSKAYA
1987N12P24
Specifications
Almost all Carpathian models had the same dimensions, weight and other technical characteristics. Therefore, this information will be presented in the form of a list:
- moped dimensions (DShV) in millimeters – 18207201100;
- maximum load – no more than 100 kg;
- the maximum speed that he could reach when accelerating in a straight line was 50 km/h;
- tire sizes – 2.75-16;
- engine type: carburetor, air cooling;
- volume - 49 cubic centimeters;
- fuel consumption – 2 liters per 100 km;
- engine power – 1.5 hp;
- moped weight – 55 kg.
The production period of the Karpaty moped begins in 1981 and ends in 1992. The line was finally discontinued in 1997. Among his competitors, he took first place. There was no better car in the country than the Karpaty with an engine capacity of up to fifty cubic meters. He was a legend of the USSR.
In the early nineties, a new engine was designed with a reed valve on the intake. However, they did not have time to install it on the Karpaty. The collapse of the Soviet Union led to a decline in demand for mopeds. The Lvov Motorcycle Plant died along with the collapse of the country. There were attempts by small firms to revive the production of these mopeds, but they failed, and the demand has already gone to completely different models and brands of mopeds.
Five random articles about motorcycles:
Three improvements to the Java 634 for motorcycle tourists
Three proposals On the YAVA-634 motorcycle, for more convenient maintenance, I introduced a number of improvements that may be of interest to motorcycle tourists.
Here are three of them: 1. To prevent dirt from clogging the gap between the wheel and the shield when traveling on dirt roads, I raised the shield by installing an extension (photo 1) made of sheet steel. 1. This is what the shield bracket extension looks like. 2. I secured the panel under the saddle (photo 2). on which I placed a ground switch 2 (toggle switch), a block 3 with a fuse, two sockets 4 for connecting the battery, a socket 5 for connecting a lamp mounted in the base of the saddle (it illuminates the seat space), and two sockets 6 from which you can take power supply for a portable lamp, receiver, vulcanizer, etc. 2. Underseat space: 1 - panel: 2 - toggle switch; 3 — block with fuse; 4 — sockets for connecting the battery; 5 - socket for connecting a lamp embedded in the base of the saddle... Read more >>
Java 680 Trial (250 cc)
Jawa-680 250 cc for trial Among fans of motorcycle sports, there are more and more people who are fond of trials.
Accordingly, the share of trial machines in the global production of sports motorcycles is growing. Now they are made by such factories as the Italian "Aprilia", "Beta", "Garelli", the Japanese "Honda", "Simson" - in the GDR, ChZ and JAVA - in Czechoslovakia. One of the largest manufacturers of sports motorcycles, Italian, annually produces 5,000 machines specially designed for such competitions. On the scale of Western Europe, this is a rather impressive figure. YAVA-680 is a special motorcycle of the 1987 model. The engine with a displacement of 246 cm3 with a cylinder diameter of 70 mm and a piston stroke of 64 mm is a further modification of the YAVA-125 engine. When creating it, the goal was to ensure minimal external dimensions and weight. The cylinder is made of an alloy of light metals, the mixture in it is... Read more >>
After boring the cylinder and installing new piston and rings, knocking noises appeared in the engine of the IZH motorcycle
".
the reason for which is unclear to me. What can be wrong?" - asks K. Simakov from Khabarovsk. It is most likely that the rings make a knock when they meet the edges of the windows, into which they fall slightly during the movement of the piston. This phenomenon, characteristic of two-stroke engines, leads to intense wear of the cylinder at the location of the windows, and sometimes to breakage of the rings. To eliminate their interference, remove the cylinder and rings. Remove the chamfers from the lower and upper edges of the windows using a file and sandpaper, as shown in the figure, and carefully remove the processing products. Blunt the outer edges of the rings on a lathe (in a arbor) or by hand with a file and sandpaper. After assembling the engine, if the work is done correctly, instead of knocking you should hear a slight rustling sound made by the rings when moving in the piston grooves and passing through the windows, indicating the normal operation of these parts.1974N03P18 Read more >>
IZH Jupiter 5-01 K (IZH-6.114-01)
The youngest Jupiter On average, every two to two and a half years, the Izhmash motorcycle production plant produces either a new model or one of the modifications of “planets” and “Jupiters”.
General view of the IZH Jupiter-5-01 motorcycle. The fairing, new tank, seat, tool boxes changed the appearance of the motorcycle and modernized its shape. When we visited Izhevsk in May and walked along the thread of the largest motorcycle conveyor in the country, from which up to 400 thousand cars a year already roll off, we immediately noted for ourselves: the main place in the plant’s production program is occupied by the new IZH Planeta-5 models. and "IZH Jupiter-5-01". True, between them one could see small inclusions of “Planet-4” with two mufflers and an old crew part. But, as it turned out, they were intended for sale in some countries of Asia and Latin America, where they had proven themselves well and where demand for them remained. For us... Read more >>
Ural M-67. Electrical diagram
Rice.
Electrical circuit diagram of the Ural M-671 motorcycle - left turn signal lamp 2 - lamp A12-21; 3 - headlight; - 4 - lamp A12-4 side and parking light; 5 — lamp A12-45-40 high and low beam; 6 — right turn signal lamp (not connected on a motorcycle with a sidecar): 7 — speedometer; 8 — lamp A12-1 speedometer lighting; 9 — indicator lamp for direction indicators; 10 — warning lamp for emergency oil pressure; 11 — high beam warning lamp; 12 — generator warning lamp; 13 — neutral sensor warning lamp; 14 — instrument panel; 15 - central switch; 16 — direction indicator switch; 17 — turn signal switch; 18 — contact plug; 19 — emergency oil pressure sensor; 20 - light switch; 21 — front light of the stroller 22 — lamp A12-21 marker... Read more >>
login registration forgot your password?
Motorcycle goods store About the store Terms and return procedure
"Izh-49"
In 1951, production of the Izh-49 model was launched in Izhevsk. As in the case of “Moskva,” they took a captured vehicle as a basis. True, the DKW NZ 350 has undergone some improvements, which only made it better - under our brand, of course.
The motorcycle turned out to be reliable, very durable and incredibly beautiful. Even today it is able to captivate a true biker with its appearance - what a fit, what precise lines... Yes, it was a car!
The plant produced versions with a sidecar, sports versions for cross-country and road racing. Not everyone can afford to own them now: the Izh-49 has collector’s value. You can buy it for no less than 100 thousand rubles. At the same time, the price tends to rise.
IZH-49. The most durable.
Reliable, durable, beautiful. The sound of its engine for the Soviet ear was akin to the sound of a Harley-Davidson engine for Americans. Their production began in 1951. At its core, it was an improved design of the German motorcycle DKW NZ 350. IZH-49 won great love among the population and was used in all corners of the vast Soviet Union.
On its basis, versions with a sidecar were produced, as well as sports motorcycles for cross-country and road racing. Now IZH-49 is a collector's item. Prices for them start from 100 thousand rubles.
9. M-1A “Moscow”. The first post-war.
After the war, the Moscow Bicycle Plant began producing a copy of the German DKW RT125 motorcycle with a 125 cc engine. M-1A "Moscow" became the first post-war motorcycle of the USSR. It was a simple and lightweight motorcycle that did not require much metal or rubber to produce.
Such motorcycles were used in huge quantities to train motorcyclists in DOSAAF schools. Perhaps your grandfather studied just like this. In 1951, production was transferred to Minsk to a bicycle factory built there. An almost identical model was produced in Kovrov under the designation K-125.
"Java"
This moped has been on its way to fame for many days. The year of birth of “Java” is 1929, and the first unit of equipment was created thanks to a license provided by the German company Wanderer. The name of the moped was formed from the first letters of the name of the owner of the plant and the German company.
“Java” gained real popularity only after the end of the war. It was at that time that models began to be produced that are still being produced today. They differ from the first copies in the cubic capacity of the engine, which is 250-350 cm3.
This brand of moped, popular in the USSR, was different from the others. This is the only foreign vehicle that has become entirely “native” to Soviet people. Its owner was considered prestigious and successful, with whom one could and should have an acquaintance. The technical side of the moped was no worse than that of American and European brands, but the price was much more affordable.
Today, the Internet is overflowing with offers for the sale of motorcycles that have simply incredible tuning. But the real value is from rare mopeds from the USSR, and proper improvement of the models only increases their individuality.