What is a starting enrichment
A starting enricher (electrovalve) is a device designed to supply an additional amount of air-fuel mixture into the combustion chamber during a cold start of the scooter engine. The fact is that when starting the scooter when cold, the engine requires an enriched mixture. The supply of such a mixture is ensured by the carburetor solenoid valve .
If the starting enrichment is in good working order and there are no breakdowns in other engine elements, the scooter engine starts easily even at temperatures around zero degrees.
Scooter starting enrichment device
There are two types of starting concentrators - manual and automatic.
The manual (mechanical) starting enrichment requires adjustment - it must be opened at startup and closed after the engine warms up using a cable on the steering wheel. But manually opening and closing the additional channel for supplying the mixture is inconvenient. An automatic starting enricher (thermoelectric valve) is installed on most modern 2t and 4t scooters. We will learn about the device of the automatic starting enrichment further.
Solenoid valve body- Ceramic heater
- Drive (powder)
- Stock
- Pusher
- Damper
- Fuel chamber
- Float chamber
- Starting fuel jet
- Spring
The scooter carburetor has a small additional fuel chamber 7, which is connected to the main float chamber 8 through the start nozzle 9. The tube from chamber 7 leads to the mixing chamber into which air is supplied and from which the air-gasoline mixture goes into the engine. A valve 6 can move in the mixing chamber, similar to a carburetor throttle valve, only much smaller in size. Just like the throttle valve, the starting valve contains a spring-loaded needle that closes the fuel channel when the valve is lowered. Valve body 1 is wrapped in thermal insulation (polyethylene foam) and covered with a rubber boot. This enricher design is used on almost all modern scooters.
Older models may use a design without an electric heater, heat is transferred to the drive through a copper heat-conducting cylinder directly from the scooter's engine cylinder, and a membrane .
One cavity of the flask, where it is located, is connected through a thermal valve to the intake manifold, which is mounted on the cylinder head.
The principle of operation of the scooter carburetor solenoid valve
When the engine is cold, the valve with the spool needle 6 is raised as high as possible (open). The needle opens the fuel supply channel, and the flap opens the air supply hole. At the first engine revolutions, a vacuum is created in the emulsion channel and gasoline located in chamber 7 is sucked into the engine through channel A, causing a strong enrichment of the mixture and facilitating the first flashes in the engine. After the engine has started, but has not yet warmed up, it still needs a rich mixture. The enricher works like a parallel carburetor - gasoline enters it through jet 9, mixes with air and enters the engine.
When the engine is running, alternating current from its generator is always supplied to the contacts of the ceramic heater 2 of the thermoelectric valve of the starting system. Heater 2 warms up drive 3. As the engine and drive warm up, the rod gradually extends by 3 ... 4 mm and drives the damper through pusher 5. Thus, the engine warms up along with the thermoelectric valve, the spool with the needle drops and closes the air and fuel channels, and the mixture gradually becomes leaner. After 3...5 minutes, the damper closes completely and the degree of enrichment of the mixture on a hot engine is regulated only by the carburetor idle system .
When the engine stops heating of the valve stops , the damper drive cools down (the powder is compressed) and under the action of spring 10, pusher 5, rod 4 and damper 6 return to their original position, opening the channels for subsequent start-up. Cooling down and returning to its original position also occurs within a few minutes.
The disadvantage of this type of enrichment is that it operates separately from the engine. For example, very often, especially in warm weather, while the engine is still hot and there is no need to enrich the mixture, the thermoelement is already cooling down. We start the engine and it gets a rich mixture.
Operating principle of the second type of starting enrichment (with a membrane)
When cold, the valve is open . After starting the engine, a vacuum occurs in the manifold and is supplied to the membrane through a thermal valve. As a result of low pressure, the membrane rises and opens a channel for additional air supply. As the cylinder head warms up, the valve closes and the valve with the needle is lowered under the action of a spring, cutting off the additional fuel supply.
With this design principle, the connection with the actual engine temperature is maintained, and fuel dosage is carried out more correctly.
Why do valves burn out?
Valves burnout occurs for various reasons. For engines that require periodic valve adjustment, valve burnout often occurs due to untimely adjustment of the valve thermal clearance. On engines with automatic adjustment of the specified gap, failure of hydraulic compensators also often leads to the valve burning out.
The main causes of engine valve burnout are:
- valves are tightly clamped;
- the valve guide is worn;
- the valve stem itself is worn out;
- the engine runs on a lean mixture (especially with LPG);
A burnt-out valve can collapse at one moment, after which fragments of the valve fall into the engine cylinder. As a result, serious damage to the piston, cylinder head or cylinder head defects may occur. In the latter case, there is a risk that a large piece of the burnt valve will pierce the engine cylinder block, which is the actual destruction of not only the cylinder head and piston group, but also the cylinder block. In such a situation, prolonged operation of the engine with a burnt-out valve may lead to the need to replace the entire engine.
How to check the solenoid valve and starting enrichment on a 4t scooter?
Many owners of Honda scooters and owners of mopeds of other brands have to independently repair and maintain their equipment, as well as perform tuning. Sometimes situations arise when it is problematic to start a cold moped due to the fact that the fuel does not fill the required volume of the float chamber, or the gasoline is mixed with air in insufficient concentration. Having figured out how to check the solenoid valve on a scooter, you can solve these problems yourself and quickly warm up the engine in the morning. Let's look at this in more detail.
Starting enrichment on a 4t scooter - description and purpose
Not all motorcycle enthusiasts know what an electric valve on a scooter is for. This device is also called a starting enricher. It is responsible for the volume of the air-fuel mixture, which fills the cylinder chamber through a nozzle when starting a cooled scooter engine. A feature of small-capacity motorcycles is the engine’s need for a rich mixture during a cold start of the scooter engine. The fuel entering through the carburetor is mixed with air in a certain concentration thanks to an electric valve connected to the carburetor.
The starting enricher is responsible for the volume of the air-fuel mixture
If the starting enrichment is functioning and there are no breakdowns of the power unit, starting the engine is not a problem even in the cold season. There is no doubt about the importance of the electric valve in ensuring trouble-free starting of the engines of modern mopeds and scooters. However, if difficulties arise with starting the engine, interruptions in operation and excessive power consumption of the engine, it can be assumed that problems have arisen with the starting enrichment. That is why it is important to know its structure and be able to check its functionality.
Causes of burnout
Valves burn out for various reasons, including:
- factory defects or low-quality spare parts;
- incorrect valve adjustment or malfunction of hydraulic compensators;
- valve wear (valve stem or guide bushing);
- early or late ignition;
- lean mixture.
No one is immune from purchasing defective and low-quality spare parts, so buy spare parts from trusted sellers who value their reputation. If the valves are adjusted incorrectly (they are tightly clamped), the engine operation will be noticeable by the characteristic “tractor” sound. In this case, due to non-compliance with the thermal clearance, the valve overheats, which will invariably lead to its burnout.
If the ignition is set incorrectly, combustion of the combustible mixture occurs when the valve is open and leads to its malfunction. A lean mixture is dangerous because the combustion temperature of the combustible mixture increases, which leads to overheating and burnout.
How does an electric valve work on a scooter?
To enrich the fuel-air mixture, a fuel enrichment device with a mechanical drive and an automatic control system is used. Let us consider the operating principle and features of each of these enrichment systems.
Manual
The manual enrichment system, which requires precise adjustment, is inconvenient to use. To start the scooter engine after parking overnight, you need to press the lever on the steering wheel, which transmits force through the cable to the pusher. After the power unit starts, warms up and reaches operating temperature, it is necessary to return the manual enrichment lever so that the volume control flap and needle return to their original position. As experience in operating scooters shows, such a system has a number of inconveniences.
How to determine for yourself that the timing valve has burnt out
Valve burnout is a common problem in gasoline and diesel engines. This malfunction occurs both on relatively “fresh” engines and on power units with an impressive mileage. At the initial stage, it is extremely important to accurately determine the nature of the malfunction, since further operation of the engine with burnt valves greatly aggravates the consequences of such a breakdown and leads to expensive repairs.
How does a scooter carburetor solenoid valve work?
The starting enrichment on a 2t scooter and on a four-stroke moped works according to a fairly simple algorithm. On a cold power unit, the spool needle occupies the upper position. It is responsible for opening the fuel channel, and the position of the damper affects the volume of supplied air. The first revolutions when starting the engine cause a vacuum inside the emulsion channel, and gasoline is sucked into the engine.
The result is a highly enriched mixture, making it easier to start a cold engine. Before reaching operating temperature, the power unit needs to be fed with an enriched mixture.
The enricher in this mode performs the function of a parallel carburetor - fuel entering through the nozzle is mixed with air and directed to the engine.
The current generated by the generator of the running engine is supplied to the contacts of the heater that controls the thermoelectric valve of the intake system. Due to heating, the temperature of the powder drive increases, which causes the rod to gradually extend up to 4 mm. The force is transmitted to the pusher, which ensures the movement of the damper.
The starter enricher on a scooter works according to a fairly simple algorithm.
As the engine warms up, the spool with the needle lowers, followed by the air-fuel channel closing. After five minutes, the damper closes completely and the mixture becomes lean. Now the gasoline enrichment system on a warm engine is regulated by the carburetor.
After stopping the engine, the valve stops heating, and as a result of powder compression, the damper drive using a pusher and rod returns it to its original position. The system is ready for subsequent startup. The cooling and return process takes no more than two minutes. The enricher has a drawback - it works separately from the motor.
As a result, in the warm season, on a hot engine that does not need a rich mixture, the engine, when the thermoelement has cooled, is powered by a rich mixture.
Determining valve burnout without removing the cylinder head
The first step is to determine which cylinder is not working. The testing methods are in many ways similar to diagnosing faulty spark plugs. To check, you should start the engine, after which, with the engine running at idle speed, you will need to remove the caps from the spark plugs one by one.
Then you need to unscrew the spark plug on the inoperative cylinder and replace it with a known good one, and also check the high-voltage armored wire of this cylinder for functionality. It would also be a good idea to check the ignition coil, etc. Subsequent starting of the engine will show whether the problem lies in the elements of the vehicle’s ignition system or whether further diagnostics are necessary.
If the nature of the engine’s operation does not change after installing the working spark plug, replacing the high-voltage wire and checking other components of the ignition system (the engine continues to rev), then there is a high probability of more serious breakdowns:
- timing valve burnout;
- CPG malfunctions;
Burnout of the valves means that compression in the cylinder is reduced due to a violation of the tightness of the combustion chamber (leakage during the fit of the intake or exhaust valve, destruction of the disc and/or valve seat). Wear of the cylinder-piston group and piston breakage also lead to low compression in the problem cylinder. Also, the cylinder may not work due to stuck or broken piston rings.
Low compression clearly indicates a malfunction, but one caveat should be taken into account. It will not be possible to establish a burnt-out valve and rule out problems with the CPG only based on the compression indicator. The fact is that compression in the engine can decrease both as a result of a burnt-out valve, and due to broken piston rings, as well as a number of other defects. For this reason, in parallel with the compression measurement, additional engine diagnostics should be carried out.
- The easiest way to determine valve burnout after you have measured the compression in the cylinders is to pour several “cubes” of engine oil through the spark plug well. Then the compression must be measured again. An increase in compression in the cylinder after adding oil will indicate that an oil film has formed, acting as a “seal”. This phenomenon is typical in the case of piston wear. If the compression indicator has not changed, it means that the valve has burned out, since the oil in the cylinder in this case will not affect the compression in any way.
- Also, to determine whether the valves are burned out, you should inspect the spark plug on the problem cylinder. A clear sign of valve burnout is that the spark plug is completely dry, that is, it does not have a characteristic oil deposit. There may also be smoke or air coming out of the engine breather. The intensity of smoke production directly depends on the degree of wear of the CPG.
As for breakdowns that are associated with the piston, in this case the spark plug is covered with oil, and the appearance of bluish smoke can be observed from the breather. Note that oil on a candle is an indirect sign. Even if the spark plug is dry or covered with a slight soot, but smoke comes from the breather, then this symptom indicates problems with the piston or piston rings. On new engines with low mileage, there is a high probability that the piston rings are stuck.
Let us add that the appearance of engine oil that comes out through the breather also indicates a malfunction of the partitions between the piston rings. Taking into account the above, you can accurately determine why the compression in the engine has decreased, identify problems with the cylinder-piston group, or determine burnout of the timing valves.
Operating principle of a membrane enricher
The membrane starting enrichment works on a different principle. When the engine is not warmed up, the valve is in the open position. Starting the engine causes a vacuum in the area of the intake manifold, which is transferred to the membrane thanks to the thermal valve. Under the influence of reduced pressure, the membrane tries to rise, opening a channel responsible for supplying additional air volume.
Further heating of the cylinder to operating temperature causes the valve to close and lower the spring-loaded valve associated with the needle. As a result, the supply of additional fuel is cut off. Such a system with a membrane functions in a clear connection with the engine temperature, which ensures a more correct dosage of fuel.
The membrane starting enrichment works on a different principle.
Consequences
In the best case, burnt valves lead to increased fuel consumption and reduced vehicle power. However, this can quickly move on to more complex problems:
- damage to the cylinder head, cylinder, piston from fragments of a burnt out valve;
- breakdown of the cylinder block with large fragments;
- burnout of the valve seat, which leads to the need to replace the cylinder head.
In addition, fire from an ignited combustible mixture with an unburned valve can enter both the intake manifold and the exhaust system, reducing their service life.
Signs that a check is needed
If difficulties arise with starting the engine and in a number of other situations, it is necessary to be able to check the functionality of the starting enrichment. Thoughts about a malfunction of the solenoid valve may arise in different cases.
Let's take a closer look at the main reasons:
- the first morning start of a cold scooter engine is problematic;
- it is difficult to start a cooled scooter engine after a long stay;
- fuel consumption significantly exceeds the consumption indicated in the passport;
- The scooter's power unit is quite unstable at idle;
- a warm engine does not maintain speed, and a cold engine functions intermittently.
Any of these problems should make the scooter owner think about a possible malfunction of the solenoid valve.
A faulty enrichment device can be in two positions:
- with the solenoid valve needle constantly extended;
- in the initial state, when the needle does not protrude.
It is necessary to be able to check the functionality of the starting enrichment if difficulties arise with starting the engine.
Each case has a different effect on the operation of the motor. The first situation makes it difficult to start the engine of a cold scooter. An attempt to start the engine by pressing the kickstarter, as well as starting with an electric starter, are unsuccessful. In the second case, the engine starts without problems, but during operation it consumes an increased amount of gasoline. Increased fuel consumption is associated with engine operation on a highly enriched mixture.
Signs of burnt valves
One of the main signs of a burnt-out valve is the engine tripping, which also indicates other problems not related to the valves, the elimination of which is cheaper and easier to repair. In addition to engine tripping, engine power decreases and fuel consumption increases.
The main indicator of the presence of a malfunction in the engine is its tripping in all operating modes (for example, with a faulty spark plug, tripping of a warmed-up engine operating at high speeds may not be noticeable).
How to check the solenoid valve on a scooter
Let's try to figure out how to check the solenoid valve on a scooter or moped.
This is a simple operation. Let's start in order:
- You should check whether the enrichment channel is closed by the solenoid valve needle. Start the cold engine and observe the change in idle speed. At first they are increased and then decreased to the desired frequency. In this case, you can make a conclusion about the serviceability of the starting enrichment and not search for its faults;
- If the scooter starts without problems, but the engine speed does not decrease after reaching operating temperature and remains high, there is a high probability that the starting enrichment is faulty. In this case, it is necessary to check the functionality of the solenoid valve;
Checking the solenoid valve on a scooter
- If the power unit can be started only after long and exhausting presses on the kickstarter, the carburetor is not clogged, the gasoline level in the float chamber is set correctly, and the compression has not dropped, then most likely there are problems with the operation of the starting enrichment, and it needs to be checked.
So, we have come close to testing the scooter's starting enrichment for operability. To perform this operation, it is necessary to disconnect the wires connecting the solenoid valve to the scooter's electrical network. Then you should unscrew the fastening of the solenoid valve to the carburetor body and remove it. Next, you will need to prepare a pair of insulated wires, the length of which will allow you to connect the terminals of the starting enrichment to the battery.
When connecting, there is no need to observe polarity, since the solenoid valve is powered from an alternating voltage network. It is important to pay attention that the ends of the wires freed from insulation do not touch each other. All that remains is to connect the wires to the chips and supply 12 volts from the battery to the enrichment unit.
With a working enrichment device, after a couple of minutes you can see the needle gradually moving out of the device body. The amount of stroke can be determined by measuring the extension of the rod before applying voltage and after turning off the power. For a faulty solenoid valve, five minutes after connecting to the battery, the needle will remain in the same position. If there are no defects in the wiring, then we can conclude that the enrichment unit is faulty.
Don’t be upset and try to repair the solenoid valve - the cost of a new one, depending on the model of the moped, varies between 5-7 dollars. When purchasing, it is advisable to have an old starting enrichment with you or clearly find out from the seller whether the spare parts he offers correspond to the brand of the scooter.
Fix a malfunction of the solenoid valve on a Chinese scooter
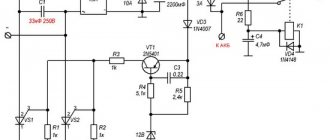
How to fix a carburetor solenoid valve malfunction (139QMB engine) with your own hands using the example of the Chinese Super Sport Acar scooter
The solenoid valve on the scooter's carburetor is used for cold starting of the engine. And it so happened that the previous owner had big problems Super Sport Acar To do this, in the removed state, I connected it to a 12-volt charger. There was no movement of the needle either after 5 minutes (as it should be approximately) or after 10 minutes. The verdict is harsh - faulty, but since there were no shops with spare parts for the scooter within a radius of tens of kilometers, I had to make do on my own.
I took a sharp knife and cut off the top part where the wires fit. The plastic turned out to be relatively soft and this procedure did not take much time. I disconnected both parts and the solenoid valve was easily disassembled into the following parts.
I looked carefully and saw that the heating element (in the form of a tablet) had oxidized from the sides to the contacts. I cleaned both the element and contacts with fine sandpaper. I pressed the heating element between the contacts with my fingers and connected the device. After 10-15 seconds I felt that the element was heating up. Next, I took the part to which the heating element is adjacent and, using a lighter with a weak flame, heated up the copper part a little - the thin rod on the other side began to extend. Everything works... Next, I cut out a strip of soft aluminum, made a hole in the middle into which the cylindrical part of the solenoid valve fit, and crimped the assembled body. In the future, for reliability, I plan to put a screw with a nut in the upper part. And it is advisable to initially coat the cut site with cold welding for plastic or some other adhesive.
Electrics and electrical equipment of a scooter
Dedicated to all owners of Chinese scooters...
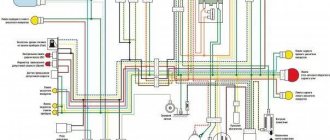
To begin with, I would like to present a wiring diagram for a Chinese scooter.
Since all Chinese scooters are very similar, like Siamese twins, their electrical circuits are practically no different.
The diagram was found on the Internet and is, in my opinion, one of the most successful, since it shows the color of the connecting conductors. This greatly simplifies the diagram and makes it more comfortable to read.
(Click on the image to enlarge. The image will open in a new window).
It is worth noting that in the electrical circuit of a scooter, just like in any electronic circuit, there is a common wire . On a scooter, the common wire is the minus ( - ). In the diagram, the common wire is shown in green . If you look more closely, you will notice that it is connected to all the electrical equipment of the scooter: headlight ( 16 ), turn relay ( 24 ), instrument panel backlight lamp ( 15 ), indicator lamps ( 20 , 36 , 22 , 17 ), tachometer ( 18 ), fuel level sensor ( 14 ), horn ( 31 ), tail light/brake light ( 13 ), start relay ( 10 ) and other devices.
First, let's go over the main elements of the Chinese scooter circuit.
Egnition lock.
Ignition switch ( 12 ) or “Main switch”. The ignition switch is nothing more than a regular multi-position switch. Even though the ignition switch has 3 positions, the electrical circuit uses only 2.
When the key is in the first position, the red and black wires are connected. In this case, the voltage from the battery enters the electric circuit of the scooter, the scooter is ready to start. The fuel level indicator, tachometer, sound signal, turn relay, and ignition circuit are also ready for operation. They are supplied with power from the battery.
If the ignition switch malfunctions, it can be safely replaced with some kind of switch like a toggle switch. The toggle switch must be powerful enough, because the entire electrical circuit of the scooter is, in fact, switched through the ignition switch. Of course, you can do without a toggle switch if you limit yourself to short-circuiting the red and black wires, as the heroes of Hollywood action films once did
.
1 is shorted to the housing (common wire). In this case, engine operation is blocked . Some scooter models have an engine stop button ( 27 ) to block the engine, which, like the ignition switch, connects the white- black and green (common, body) wires.
Generator.
The generator ( 4 ) produces alternating electric current to power all current consumers and charge the battery ( 6 ).
There are 5 wires coming from the generator. One of them is connected to a common wire (frame). The alternating voltage is removed from the white wire and supplied to the relay regulator for subsequent straightening and stabilization. The yellow wire removes voltage, which is used to power the low/high beam lamp, which is installed in the front fairing of the scooter.
Also in the design of the generator there is a so-called hall sensor . It is not electrically connected to the generator and there are 2 wires coming from it: white- green and red - black . The hall sensor is connected to the CDI ignition module ( 1 ).
Relay regulator.
Regulator relay ( 5 ). People may call it a “stabilizer”, “transistor”, “regulator”, “voltage regulator” or simply “relay”. All these definitions refer to one piece of hardware. This is what the relay regulator looks like.
The relay regulator on Chinese scooters is installed in the front part under a plastic fairing. The relay-regulator itself is attached to the metal base of the scooter in order to reduce the heating of the relay radiator during operation. This is what the relay regulator looks like on a scooter.
In the operation of a scooter, the relay regulator plays a very important role. The task of the relay regulator is to convert the alternating voltage from the generator into direct voltage and limit it to 13.5 - 14.8 volts. This is the voltage required to charge the battery.
The diagram and photo show that there are 4 wires coming from the relay-regulator. Green is the common wire. We have already talked about it. Red is the output of positive DC voltage 13.5 -14.8 volts.
The regulator receives alternating voltage from the generator through the white wire to the relay. Also connected to the regulator is yellow wire coming from the generator. It supplies the regulator with alternating voltage from the generator. Due to the electronic circuit of the regulator, the voltage on this wire is converted into a pulsating one, and is supplied to powerful current consumers - the low and high beam lamps, as well as the dashboard backlight lamps (there may be several of them).
The supply voltage of the lamps is not stabilized, but is limited by the relay regulator at a certain level (about 12V), since at high speeds the alternating voltage supplied from the generator exceeds the permissible limit. I think those who have had their dimensions burned out due to malfunctions of the relay-regulator know this.
Despite all its importance, the device of the relay regulator is quite primitive. If you pick apart the compound with which the printed circuit board is filled, you will find that the main relay is an electronic circuit consisting of a thyristor BT151-650R , a diode bridge on 1N4007 , a powerful diode 1N5408 , as well as several wiring elements: electrolytic capacitors, low-power SMD transistors, resistors and a zener diode.
Due to its primitive circuitry, the relay-regulator often fails. Read about how to check the voltage regulator here.
How to determine
Valve failure can be determined by several methods:
- Diagnostics by disassembling the engine. This method is reliable and accurate, but to do this it is necessary to disassemble the engine - remove the cylinder head. Due to the fact that this process is labor-intensive, time-consuming and requires certain skills and tools, it is worth moving on to it if all other causes of engine tripping have been excluded.
- Diagnostics using special tools. This method is the most preferable, because using it, you can quickly and with a higher probability determine the cause of the tripping without disassembling the engine, however, this will require a special device - a compression gauge. A decrease in cylinder compression leads to a loss of power and indicates that the car engine requires disassembly and repair.
- Engine tripping and reduced compression of cylinders 3 and 4 occur as a result of a malfunction of the vacuum brake booster. Low compression indicates a malfunction of the valves and problems of the cylinder-piston group - malfunctions of the piston rings, wear of the cylinder and piston. To eliminate problems with the CPG, you need to pour oil into the idle cylinder and crank the engine. If at the same time the compression increases, then the problem is the CPG is worn out, otherwise the valves are burnt out.
- Diagnostics without the use of special tools. Valve failure can be determined with high probability and without tools by following certain steps, which we will discuss in the instructions below.
Video: Signs of valve burnout
Something else useful for you:
Instructions
How to determine valve burnout without special tools? In this manual, we will look at how to determine burnout without resorting to special tools and disassembling the engine (provided that the ignition and power systems are adjusted in accordance with the requirements and are not the cause of the trip).
- We determine the faulty cylinder. To do this, the engine must be running and safety precautions must be observed. We disconnect the high-voltage wires from the distributor or from the spark plugs one by one and listen to the engine. If the sound of the running engine has changed and the tripping has become noticeable, then this cylinder is working. When you disconnect the faulty cylinder, the engine will operate the same as before it was disconnected.
- We determine the serviceability of high-voltage wires. We determine the serviceability of the wires in the same way as the serviceability of the spark plugs - by moving from a serviceable cylinder to a faulty one. In a dark room, if the wires are faulty, sparking can be observed.
- Checking the distributor and ignition coil. To check the serviceability of the distributor, capacitor and ignition coil, remove the spark plug, connect it to a high-voltage wire and crank the engine with the starter. In this case, the electrode of the spark plug is located at a distance of 1-2 cm from the vehicle’s mass. If a bright and blue spark appears as a result, this indicates their serviceability.
- Checking the vacuum brake booster. A faulty brake booster affects compression in cylinders 3 and 4. To diagnose its serviceability, disconnect the hose going from the vacuum pump to the motor and plug it. If the engine runs smoothly, replace the brake booster. If the elements of the electrical equipment and brake systems are in good condition, then you will have to disassemble the engine and repair it.
- Malfunction of the cylinder-piston group. A CPG malfunction differs from valve burnout by the presence of exhaust gases in the engine crankcase, which can be noticed by disconnecting the breather hose from the air filter. And the presence of oil on the spark plug electrode indicates a malfunction of the CPG.
- If, as a result of the diagnostics, no deficiencies are identified, then we can talk about burnout and the need for repairs.
- We determine the serviceability of the spark plug. The easiest way, which does not require knowledge, is to replace the spark plug. To do this, at the diagnostic stage it is not necessary to buy new spark plugs; swap spark plugs from the working and non-working cylinders. If at the same time the cylinder with the spark plug from the faulty cylinder stops working, then this indicates a malfunction of this spark plug, and if it works, then the problem is not in the spark plug.
In addition, you can determine a non-working spark plug by inspection. A faulty spark plug has the following external defects:
- spark plug electrodes with soot, soot and “wet”;
- the body has cracks;
- There are black dots and stripes on the body (the spark plug is broken). The electrodes of a serviceable spark plug are light or slightly brown in color, the body is without damage or black marks.
Having sufficient skills and tools, you can replace the valves yourself, but since this procedure is very responsible, complex and requires special tools and devices, it is better to entrust it to specialists.
If the engine fails, do not put off diagnosing the cause until later, even if the budget does not allow for repairs in the near future. It is necessary to identify the reason why the engine is unstable. And if this reason is not related to burnout of valves and wear of the cylinder-piston group, then the car can be operated in a gentle mode, which will lead to increased fuel consumption and the possibility of stalling at the wrong moment. But otherwise, it is better to stop using it to avoid higher repair costs.
Ignition circuit elements.
One of the most important electrical circuits in a scooter is the ignition circuit. It includes the CDI ignition module ( 1 ), ignition coil ( 2 ), spark plug ( 3 ).
CDI ignition module.
The CDI ignition module ( 1 ) is made in the form of a small box filled with compound. This makes it difficult to disassemble the CDI unit if it malfunctions. Although the modular design of this unit simplifies the process of replacing it.
There are 5 wires connected to the CDI module. The CDI module itself is located in the bottom of the scooter body near the battery compartment and is secured to the frame with a rubber clamp. Access to the CDI block is made difficult by the fact that it is located in the bottom part and is covered with decorative plastic, which has to be completely removed.
Ignition coil.
Ignition coil ( 2 ). The ignition coil itself is located on the right side of the scooter and is mounted on the frame. It is a kind of plastic barrel with two connectors for connection and a high-voltage wire output that goes to the spark plug.
Structurally, the ignition coil is located next to the start relay. To protect against dust, dirt and accidental short circuits, the coil is covered with a rubber cover.
Spark plug.
A7TC spark plug ( 3 ).
The spark plug turned out to be cleverly hidden on the scooter, and it can take quite a long time to find it the first time. But if we “walk” along the high-voltage wire from the ignition coil, the wire will lead us straight to the spark plug cap.
The cap is removed from the candle with a little effort. It is fixed to the spark plug contact with an elastic metal latch.
It is worth noting that the high-voltage wire is connected to the cap without soldering. The insulated stranded wire is simply screwed onto the screw contact built into the cap. Therefore, you should not pull the wire too hard, otherwise you can pull the wire out of the cap. This can be easily fixed, but the wire will have to be shortened by 0.5 - 1 cm.
It's not so easy to get to the spark plug itself. To dismantle it, a socket wrench is required. With its help, the candle is simply unscrewed from its seat.
Starter.
Starter ( 8 ). The starter is used to start the engine. It is located in the middle part of the scooter next to the engine. It's not easy to get to.
The starting of the starter is controlled by the starting relay (10).
The start relay is located on the right side of the scooter frame. The starting relay receives a thick red wire from the positive terminal of the battery. This is how the start relay is energized.