Disassembly
For disassembly it is necessary to remove: — the clutch release rod with the release bearing parts; — starting lever; — a disk with two fingers of an elastic coupling of the cardan transmission from the secondary shaft; — right crankcase cover with manual speed control lever; - fork guide shaft; - shift forks; — unscrew the screws of the front cover; - after this, alternately hitting the primary and secondary shafts with a copper hammer; — remove the front cover with shafts and gears.
If necessary, disassemble the mechanisms: - disengaging the clutch; — foot switch; — manual switching; — gear shift forks; - launcher; - a cover with shafts and gears of constant mesh.
When disassembling the clutch release assembly, you should pay attention to whether there are any traces of crushing or twisting of the square end of the rod, whether the felt seal of the rod is damaged, whether the cylindrical end of the rod rotates freely and without jamming in the tip, whether the thrust bearing balls are falling out of the separator, whether the rubber ring (clutch slider seal).
Pay attention when disassembling the foot switch. For wear, crushing and breaking off the working edges of the pawls and the teeth of the selector sector. For jamming of the spring when compressed in the countersinks of the pawls. To loosen the return spring thrust screws, and also check whether the lever or the axis of the foot shift lever is bent and whether its finger is worn out, and whether the seals are in good condition.
When disassembling the manual speed control. It is necessary to make sure that there are no cracks in the place where the sector is welded to the roller and that there are no scuffs on the working surfaces, and also check whether the shift sector oil seal is in good condition and whether the shift lock ball is not stuck.
It is not recommended to disassemble the cover with rollers and constant-mesh gears unless clearly necessary, but you should only make sure that the gear teeth are in good condition, that the movable couplings are reliably engaged with the constant-mesh gears, that the movable couplings are easy to move and that the gearbox bearings are in good condition.
Return to contents — ↑
Technical characteristics of modern models [edit | edit code]
Tourist, Tourist 2WD, Gear-UP, Troika Lux
| Tourist | Tourist-2WD | Gear-UP | Troika Lux | |
| Model: | IMZ-8.1037 Tourist | IMZ-8.1037 Tourist-2WD | IMZ-8.1037 Gear-UP | IMZ-8.1037 Troika Lux |
| Dimensions L×W×H, mm: | 2580×1700×1100 | 2580×1700×780 | 2580×1700×1100 | |
| Ground clearance, mm: | 125 | |||
| Dry weight, kg: | 350 | |||
| Total weight, kg: | up | |||
| Fuel tank, l: | 19 | |||
| Maximum speed, km/h: | 105 | |||
| Fuel consumption in the city, l/100 km: | 6-7 | |||
| Fuel consumption on the highway, l/100 km: | 4-5 | |||
| Engine: | 745 cm³, 42 l. p., 4-stroke, 2 cylinders, opposed OHV | |||
| Launch: | electric starter and kickstarter | |||
| Electrical system: | 12 V, generator 500 W | |||
| Ignition system: | contact | |||
| Checkpoint: | 4-speed, with reverse | |||
| Main gear: | gimbal | |||
| Gear ratios: | I - 3.6; II - 2.62; III - 1.61; IV - 1.3; Rear: 4.2 | |||
| Main gear ratio: | 4,62 | |||
| Tires: | 4.00x - 19″ | |||
| Wheels: | knitted, painted, 19″ | spoked, chrome-plated, 19″ | knitted, painted, 19″ | spoked, chrome-plated, 19″ |
| Brakes: | front - hydraulic, disc; rear - drums | |||
| Suspension: | front - lever with spring-hydraulic shock absorbers; rear - pendulum with spring-hydraulic shock absorbers, adjustable for load | front - telescopic; rear - pendulum with spring-hydraulic shock absorbers, adjustable for load | ||
| Seat: | separate, double adjustable | solid | separate, double adjustable | solid |
| The package includes additional equipment: | Painted stroller wheel rack, driver's mudguards, passenger handles, parking brake | Chrome-plated rack for the stroller wheel, searchlight, driver's mudguards, stroller glass, shovel, canister, chrome-plated driver's protective bar, chrome-plated stroller protective bar | Stroller wheel rack, searchlight, shovel, canister, driver's mudguards, passenger handles, parking brake, driver's protective bar, stroller's protective bar | Chrome-plated luggage rack on the stroller wheel, chrome-plated passenger handles, velor upholstery of the stroller, leather passenger seat in the stroller, stroller glass, parking brake, driver's roll bar |
Retro, Retro-Solo, Wolf, Solo-sT
| Retro | Retro Solo | Wolf | Solo-sT | |
| Model: | RETRO | RETRO SOLO | WOLF | Solo-sT |
| Dimensions L×W×H, mm: | 2224×1630×1020 | 2224×840×1060 | 2530×850×1300 | n/a |
| Ground clearance, mm: | 140 | 115 | 125 | |
| Dry weight, kg: | 343 | 220 | 260 | 198 |
| Total weight, kg: | 610 | 400 | 430 | n/a |
| Fuel tank, l: | 19 | |||
| Maximum speed, km/h: | 120 | 150 | ||
| Fuel consumption in the city, l/100 km: | 6-7 | 5-6 | ||
| Fuel consumption on the highway, l/100 km: | 4-5 | |||
| Engine: | 745 cm³, 42 l. p., 4-stroke, 2 cylinders, opposed OHV | |||
| Launch: | electric starter and kickstarter | |||
| Electrical system: | 12 V, generator 500 W | |||
| Ignition system: | microprocessor | |||
| Checkpoint: | 4-speed, with reverse | |||
| Main gear: | gimbal | |||
| Gear ratios: | I - 3.6; II - 2.28; III - 1.56; IV - 1.19; Rear: 4.36 | |||
| Main gear ratio: | 4,62 | 3,89 | ||
| Tires: | 110/90-18″ | front 90/90-18″ rear 130/90-16″ | front 3.50-18″ rear 4.00-18″ | |
| Wheels: | spoked, chrome-plated, 18″ | spoked, chrome-plated, 18″ | spoked, chrome plated | spoked, chrome-plated, 18″ |
| Brakes: | front - hydraulic, disc; rear - drums | front - hydraulic, disc; rear - hydraulic, disc | front - hydraulic, disc; rear - hydraulic, disc | |
| Suspension: | front - telescopic; rear - pendulum with spring-hydraulic shock absorbers, adjustable for load | front - telescopic; rear - pendulum with spring-hydraulic shock absorbers, adjustable for load | ||
| Seat: | separate, double adjustable | separate, double adjustable | separate | separate |
| The package includes additional equipment: | Velor upholstery of the stroller, leather passenger seat in the stroller, stroller glass, parking brake, driver's roll bar | Driver safety bars |
Fault Inspection
When inspecting the parts, you should check the ease of movement of the forks along the rod. Condition of fork stays and ring grooves in movable couplings. The amount of axial movement of the forks in the groove of the engagement couplings.
The following malfunctions may occur in the trigger mechanism: - wear, crushing or chipping of the pawl; — jamming of the pawl pusher; — breakage of the pawl spring; — bending the ends of the return spring of the starting pedal; — damage to the working end of the buffer pin; — cracks in the starting lever; - wear of the oil seal.
Return to contents — ↑
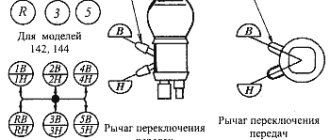
How to change speeds
I add hell for example!
I already opened it, but it’s only about repairs and installation.
in this case it is better not to buy.
From a scooter straight to the Urals, you’re desperate. My advice is to take with you someone who at least understands a little about them and has ridden them of course. In principle, there is nothing complicated, but there are some nuances, it’s better not to risk your life. Do you have a license? If not (most likely, otherwise I don’t think there would be such questions), it’s better not to go on public roads. Practice somewhere in the village, in garages, etc.
Where does a 16 year old pioneer get his license? ))
I also switched from a scooter to the Dnieper, however, then it almost didn’t go)
the first all the way down, then up in order neutral, second, third, and fourth. Down, respectively, you press not the front shoulder of the pedal up to the rear.
My pleasure. It’s better not to risk it yourself, let someone who knows how and with a license overtake it. Then you yourself will master driving in a large open area; the difference between a Ural and a scooter is big.
Congratulations on your decision to buy a Urals! A lot of new and wonderful things await you) in addition to everything said above, yes, it’s better to ask someone who knows how to drive to drive. you'll learn on your own later. When I bought my first IZH (I still didn’t have a license), I had to drive more than 100 km, and miraculously I didn’t fly under a car at the first intersection. but the miracle might not have happened. but he was a friend with rights)
CLUTCH. Don't forget to squeeze the clutch (lever on the left of the steering wheel) when changing gears)))
Yes, I know that, I just didn’t understand where to switch the foot (and without a clutch it would have been funny)))
The best way to change gears is with your foot.
and press the clutch by hand...
and most importantly, think with your head.
Find the instructions for the Ural 67-36 motorcycle and everything will be indicated there in detail - which gear corresponds to which speed. If you don’t find it, remind me, I’ll tell you then. I'm at work right now and don't have the instructions at hand.
Thank you, I already understood everything in principle.
So you can’t really tell a newbie what he’s asking for, he’ll take it and crash into you. There’ll be no one to blame. It’s my own fault for not prompting him in time. You need to be more attentive to newcomers.
Before you try to ride (if it's a solo ride), put the bike on the ground and try to lift it off the ground. Otherwise, God forbid, you fall and then you won’t pick him up
And with a stroller, even more so, you need to be more experienced in driving, since a single driver and a stroller are slightly different in control and behavior on the road.
hmm. driving license as I remember on cat. A can be opened from the age of 16.
FIRE is simple. No comments.
Don't forget to take with you a supply of motor oil, spare spark plugs, some tools, a helmet and a motorcycle license. And as much money as possible.
Kherivoznait, but for the first time in a wheelchair for me it was hellish torment. It was somehow easier on the Wolf the first time.
By the way, what are you going to do with the motorcycle later?
Maybe I’ll repair it and go to the dacha.
No, I was just hoping for a chopper.
O my young friend. Just because you're studying doesn't mean you already have them. So, first get a license, then say what you have. And it’s not a fact that you’ll get it. Z.Y. In general, you don’t have a license yet, and you definitely won’t for two years)))
Remind me about the clutch.
Finding neutral is very simple, you put it in first, and if there is a reverse gear, turn it on and off, that's all)))
Gearbox assembly
Reassembling the gearbox follows the reverse order of disassembly. First, the trigger shaft assembly with gear is installed into the hole in the rear wall of the crankcase. Then place the crankcase with the front hole up; after that, placing a paper gasket, insert the primary and secondary shafts assembled with a cover and bearings into it and press them into the rear wall of the crankcase with light blows of a hammer. Then the trigger shaft is put in place.
When installing the front bearing sleeve of the trigger shaft, it must be turned counterclockwise so that the spring is sufficiently wrapped and the starting pedal is sharply thrown back to its original position until it stops against the spring-loaded buffer rod.
After this, the parts of the gear shift forks, manual and foot shift, thrust bearing and rod are installed. After assembling the box, it is necessary to adjust the operation of the foot switch.
Similar articles:
- Adjusting the K-52 carburetor of the Ural motorcycle
- Carburetor repair
Return to contents — ↑
List of models [edit | edit code]
Road motorcycles
- IMZ M-72 (1940-1961) - the first motorcycle of the Irbit plant, a copy of the BMW R71, was modernized throughout its production, the latest model even received a short-lever fork and aluminum wheel hubs;
- IMZ M-52 (single) (1950-1957) - a model with the chassis of the M-72 and a 500 cm³ engine. Only a limited edition of 678 motorcycles was produced;
- IMZ M-61 (1957-1963) - a transitional model with the chassis from the M-72 and a new engine (650 cm³), the travel of the front fork and rear suspension has been increased. The front fork has been changed. The crew section has been lightened;
- “Ural” M-62 (1961-1965) - new gearbox, increased suspension travel, automatic ignition timing introduced, camshaft cam profile changed to reduce wear. The steering has been changed (chain throttle and duralumin clutch and brake levers);
- “Ural-2” M-63 (1963-1971) - a frame with a pendulum suspension of the rear wheel on spring-hydraulic shock absorbers (later a similar suspension was introduced on the sidecar wheel), ground clearance was significantly increased due to the introduction of a new exhaust system.
- “Ural-3” M-66 (1971-1975) - the engine was significantly modernized, the power increased to 32 hp. With. Engine durability has been increased due to full-flow oil purification and the use of a new crankshaft design. The motorcycle has direction indicators and new lights;
- "Ural" M-67 (1973-1976) - twelve-volt electrical equipment was used. The design of the motorcycle frame has been changed;
- “Ural” M-67-36 (1976-1984) - due to changes in the design of the cylinder heads, the use of K-301G carburetors with an increased diffuser diameter and an increase in the diameter of the exhaust system, the engine power was increased from 23.5 to 26.5 kW. (36 hp). The right turn signal on the motorcycle itself has been removed.
- “Ural” IMZ-8.103-30 (1985-1986 [ source not specified 2336 days
]) - the frame and rear suspension, optics, electrical equipment were modernized, a brake was installed on the sidecar wheel, instead of two mufflers, one was installed on the right side; - “Ural” IMZ-8.103-10 (1987-1994) - differed from the previous model by the presence of reverse gear, slightly lighter weight, noise and fuel consumption;
- “Ural” IMZ-8.103-40 Tourist - equipped with a lever front fork;
- “Ural” IMZ-8.123 Solo - a single unit based on the IMZ-8.103-10, engine power 40 hp. pp., 18-inch wheels;
- "Ural" IMZ-8.1037 GEAR-UP;
- "Ural" IMZ-8.1243 Voyage;
- "Ural" IMZ-8.1024 Cobra;
- "Ural" IMZ-8.1238 Wolf (1999-2011) - a motorcycle in the chopper style;
- "Ural" IMZ-8.1036 Retro
Sports motorcycles
- M-35;
- M-52S for road racing;
- M-52K for cross-country competitions;
- M-61K for cross-country competitions;
- M-62K for cross-country competitions;
- M-75M;
- M-76;
- M-77 for road racing.
- M-80;
- K-1000 for cross-country competitions;
- “Cross” IMZ-8-201 for cross-country competitions.
Special equipment
- "Ural" IMZ-8.1233 Solo-DPS - patrol motorcycle;
- "Ural" IMZ-8.1037 Gear-UP - a military motorcycle equipped with a 7.62 mm PKMB machine gun on a standard turret;
- "Ural" IMZ-8.1037 Gear-UP-ATGM - a military motorcycle, carrier of the Konkurs-M ATGM. The launcher with a thermal imaging sight is mounted on a motorcycle sidecar on a special turret. An ammunition load of two ATGMs is transported in the ammo rack of the stroller. In the stowed position, the launcher and thermal imaging sight are placed in the trunk of the stroller. The weight of the container with a guided missile (without launcher and thermal imaging sight) is 26.5 kg; the firing range of the complex is 4000 m during the day and 3500 m at night; armor penetration - 200-250 mm (solid steel).
Limited editions
It has become a tradition to make limited editions of Urals. Among them:
- Gzhel Sugar (2009) - painted like Gzhel. Released in a single copy.
- Yamal (2012) - theme of the icebreaker "Yamal" with an oar. 50 copies were produced.
- Gaucho Rambler LE (2013) - cowboy theme with warm materials and tea set.
- World (2014) - Shuttle Theme. Powered by solar battery. 20 copies were released.
- Dark Force (2015) - Star Wars theme with lightsaber. 25 copies were produced.
- Ambassador (2017) - presented in honor of the 75th anniversary of the plant. With a standard bottle of vodka and sardines. 20 copies were released.
Repair and service
One of the main advantages of the gearbox on a Ural motorcycle is its high maintainability. Each owner can carry out a major overhaul of the gearbox in just a few days, provided that the necessary parts, spare parts, other consumables and tools are available.
To remove the unit from the motorcycle you need to do the following:
- remove the rear wheel;
- remove the cardan drive;
- unscrew the bolt and nuts securing the gearbox to the motorcycle engine;
- remove the gearbox from the motorcycle frame.
Typically, transmission repair involves replacing worn gears and adjusting the gear shift mechanism. Monitor the condition of the seals, since loss of lubricant will lead to unfavorable operating conditions of the unit, which will ultimately cause premature failure.
The need for repairs can be eliminated through high-quality and timely maintenance. While operating the motorcycle, be sure to periodically check the oil level and, if necessary, add the missing amount. If you have to top up frequently, you need to establish the cause of the loss of technical fluid.
If an oil leak is detected, tighten the mounting bolts or replace unsuitable seals and gaskets. Do not forget to change the oil in the box in a timely manner; the recommended maintenance intervals can be found in the user manual. If possible, change the oil even more often than the motorcycle manufacturer recommends.
Valve adjustment for Ural M-67, IMZ
On this engine the recommended clearance is 0.05mm.
Therefore, you will need a probe with exactly this thickness. It also has slightly different saddles, but this does not affect the adjustment process. The motorcycle should also be tilted before starting work. The process occurs as follows: This is how you can easily and quickly adjust the valves. This work is not difficult, but it will avoid many problems with the engine. Also, with properly adjusted valves, flow is reduced.
Source
Total information
Motorcycle type: with sidecar. Wheelbase, mm – 1430. Ground clearance, mm – 130. Track, mm – 1100
Dimensions, mm: – length – 2420; – width – 1650.
Height (by ignition key) – 1000
Motorcycle weight, kg: – dry – 335; – worker – 380.
Fuel consumption on the highway, l/100 km – 7. Fuel reserve on the highway, km – 310. Highest speed, km/h – 85.
Capacity (oil), l: – engine crankcase – 2.0; – gearbox housing – 0.8; – reverse gear housing – 0.150; – air purifier – 0.2.
Fuel tank capacity, l – 22.
Engine
Engine type – four-stroke two-cylinder. Brand – M-72M. Cylinder diameter, mm – 78. Piston stroke, mm – 78. Working volume, cm³ – 746. Compression ratio – 5.5 ± 0.2. Maximum power, l. With. – 22. Maximum torque, kg m – 4.0. The block head material is aluminum alloy. Head gasket – asbestos metal 0.6 mm. The piston material is aluminum alloy.
Valve distribution phases (according to the angle of rotation of the crank), degrees: – beginning of intake to c. m.t. – 76; – end of inlet after n. m.t. – 92; – beginning of release BC m.t. – 116; – end of release after c. m.t. – 52.