The contactless ignition system of the VAZ 2109 includes a switch, as well as spark plugs, a distributor (distributor), a coil and an ignition switch. The system is designed to supply a spark that ignites the air-fuel mixture into the combustion chamber. It is very important to supply the spark at exactly the right moment in the compression phase of the mixture.
Switch design and malfunctions
The VAZ 2109 switch is one of the key elements of the car’s ignition system. The device is designed to switch current pulses of the required amplitude and duration in the primary winding of the ignition coil, depending on the control pulses of the Hall sensor. It also stabilizes the current from 6 to 18 V, protects semiconductors from overloads and ensures that the ignition system is turned off when the engine is stopped.
The housing provides a connection to ground through a radiator. When the device operates, a significant amount of heat is generated through its radiator. During operation, the radiator should be regularly cleaned of all kinds of contaminants to maintain heat transfer.
Signs of a faulty switch may include the following:
- when the starter is turned on, the engine does not start, there is no spark at the spark plugs;
- the engine starts, but soon stalls at idle;
- The engine runs unsteadily and the spark sometimes disappears.
A malfunction of the VAZ switch is not the only possible reason for the appearance of such symptoms. Such signs can be observed when the distributor fails or contact is lost.
To carry out repairs correctly, a thorough diagnosis is necessary.
Recommendations
Malfunctions of the non-contact ignition system - It is not allowed to disconnect the high voltage wires while the engine is running and check the functionality of the ignition system elements “for spark”, as this can lead to injuries (due to high energy), as well as burnout of high-voltage insulation and failure of the system devices ignition
To avoid damaging the switch, do not disconnect the wires from the battery terminals while the engine is running.
When troubleshooting, as well as when performing preventative work on the distributor sensor, be sure to turn off the ignition.
In a contactless ignition system, low and high voltage wires are not allowed to be laid in the same harness.
Let us consider in detail some of the reasons characteristic of a contactless ignition system that make it difficult to start the engine.
Malfunctions of the contactless ignition system – There are no current pulses to the ignition coil, the operation of the switch is impaired. The switch is designed to convert sensor pulses into current pulses in the primary winding of the ignition coil, i.e. it opens and closes the low voltage circuit by locking and unlocking the output transistor.
| Rice. 15. Diagram of a non-contact ignition system: 1 – spark plug; 2 – sensor-distributor; 3 – ignition coil; 4 – switch; 5 – ignition switch; 6 – resistor; 7 – LED; 8 – terminal block on the sensor-distributor |
If the engine does not start when the fuel supply system to the carburetor is working properly, then a faulty switch may be the likely cause. Typically, an accurate check of the technical condition of the switch (basic pulse parameters) is carried out on a bench using an oscilloscope and a rectangular pulse generator. However, you can evaluate the performance of the switch, i.e., make sure whether it produces current pulses to the ignition coil or not, in a simple way using an A12, 3 W lamp. To do this, it is necessary, for example, in the ignition system of a VAZ-2108 car, to disconnect the brown wire with red stripes from the ignition coil, coming from terminal 1 of the switch, and connect the tip of the wire to the control lamp. Connect the other terminal of the lamp to terminal B of the ignition coil. Then turn on the ignition and crank the engine with the starter. If the control lamp flashes when the engine crankshaft is rotated by the starter, then the switch produces current pulses to the ignition coil, i.e. the low voltage circuit is working.
In cases where the control lamp does not blink, the switch does not output current pulses to the ignition coil. Therefore, it is faulty and requires replacement. It should be recalled that due to a malfunction of the commutator, the engine may not develop full power or may have interruptions in operation at all crankshaft speeds.
There is a break in the switch's power wires. The absence of current pulses on the primary winding of the ignition coil may be due to a break in the wires connecting the switch to the ignition switch or to the ignition coil, or due to their unreliable connection.
In this case, you need to carefully check the condition of the wires and the reliability of their connections. Replace any damaged wires found and tighten any loose connections.
The ignition switch is damaged. Often the reason for the lack of current pulses to the ignition coil can be a malfunction of the ignition switch. When the ignition is turned on, contacts 15/1 and 30/1 do not close. To eliminate this malfunction, you need to check the serviceability of the ignition switch using the method discussed earlier. Replace the faulty contact part of the ignition switch with a spare one.
There are no voltage pulses to the switch from the sensor, the contactless sensor is faulty. A non-contact sensor is installed instead of the breaker contacts, provides control pulses to the switch and is located in the ignition distributor sensor (Fig. 17).
The functionality of the contactless sensor can be checked as follows (Fig. 16). An adapter connector with a voltmeter must be connected between the plug connector of the ignition sensor-distributor and the connector of the wire bundle. Turning on the ignition and slowly turning the crankshaft with a special key, use a voltmeter to measure the voltage at the output of the sensor. If the contactless sensor is working properly, the voltage at its output should change sharply from the minimum (no more than 0.4 V) to the maximum - no more than 3 V less than the supply voltage. The supply voltage is usually 8 - 14 V.
If the test reveals that the cause of the voltage pulses generated by the sensor does not correspond to the above limits, then the faulty sensor must be replaced.
A break in the wires between the sensor and the switch. In the practice of operating passenger cars, most often voltage pulses from a contactless sensor may not arrive at the switch due to a break in the wires between the ignition distributor sensor and the switch. It is necessary to check the condition of the wires and the reliability of their connections by external inspection. Replace any damaged wires found, and securely secure weak connections between wires and devices.
Diagnostics of device health
It is recommended to carry out in-depth diagnostics of the device at a specialized service. A professional stand will allow you to evaluate the condition of the unit in various engine operating modes in the range from 0 to 8000 rpm. The manufacturer categorically does not recommend diagnosing using artisanal methods. This is dangerous not only for the car’s electrical system, but also for the person trying to carry out such diagnostics.
If the car’s dashboard is equipped with a voltmeter, and the car owner knows how to check the VAZ switch, then a simple way is available to him to preliminary assess the performance of the device. One of the functions of the switch is to turn off the power to the ignition coil when the engine is not running but the ignition is on. With such a shutdown, the voltage in the on-board network increases noticeably. This means that to check the functionality of the device, you should insert the key into the lock, turn it to the ignition position, but do not turn the starter. At this time, you must carefully monitor the readings on the voltmeter.
In the first seconds, the arrow will freeze approximately in the middle of the scale, and after 8-10 seconds it will noticeably move to the right. Since the device worked, the coil turned off, the voltage increased, and the voltmeter responded, then everything is in order. If a switch fails, it usually happens entirely. It is unlikely that the secondary function remained operational, but the basic one failed. So, with a high probability, the device can be considered working.
Checking the power supply of a DC CDI switch
If you have the wire of the high-voltage coil of the generator hanging idle (provided that everything was like this from the factory, and not after the intervention of some “guru”) - switch the tester to the DC measurement mode in the 20 V range. Look for the wire on the switch nutrition. Usually this is a black or gray wire; we touch the ground with one probe and the power wire with the other:
- If the display shows zeros, look for an open circuit in the power wiring.
- If the voltage is significantly less than 12v, look for oxidation or check if your battery is charged
- If the voltage is 12v or a little more, then everything is in order with the power supply and you can check further
The power supply to this switch is in perfect order.
Alternative diagnostic methods
When there is no voltmeter on the dashboard, you can get out of the situation by doing everything yourself. To do this, you will need a 12 V light bulb and two meter wires with stripped ends. The diagnostic work flow diagram is as follows:
- disconnect the battery, de-energize the electrical system;
- using a size 8 wrench, unscrew the nut and remove the wire from the ignition coil terminal marked “K”, this wire is brown and goes to the clamp marked “1” on the switch;
- connect this wire to one of the test lamp wires;
- Connect the other wire of the control lamp to terminal “K” on the ignition coil;
- connect the battery;
- Turn on the engine starter and observe the condition of the lamp. If the lamp is flashing, the device is working properly. If the lamp does not light, the device is faulty.
There is another simple and reliable way to identify a device malfunction. To do this, you need to install a known-good switch, start the car and check the functionality of the system in all modes. If the system is working normally, then the problem was precisely the failure of this device, and when the same failures occur, the switch has nothing to do with it.
The disadvantage of this method is that you need to have a spare working switch with you. While this is reasonable for long journeys in uncrowded areas, it is exotic for regular city trips.
Common Network Switch Failures
Therefore, the questions that need to be answered are the same: what happened? who did it? what will be the damage? The fundamental difference is that in a dial-up environment, responses must be port-specific, which means the following factors must be taken into account:
- how intensively each port is used;
- how the source of errors is identified and traced;
- what is the source of the broadcast storm;
- whether the forwarding tables are working correctly;
- which workstations are connected to a specific port;
- whether the switch imposes speed limits on any protocols or ports;
- does the port belong to a VLAN, and if so, does the server or service belong to the same VLAN?
Where should you start when you receive a message that your dial-up network has a problem? Typically, the main difficulty is the inability to “look” inside the switch. The source of problems should be sought first of all at the second level of the OSI network model when the switch organizes a bridge, while the use of virtual VLANs and other functions of the third and higher levels, as well as traffic forwarding rules, can further complicate the situation. If the network implements “advanced” switching functions, for example, routing at the fourth level and higher, coupled with load balancing, then diagnostics should be carried out by a specialist who is well versed in all the intricacies of configuring switches.
By installing a switch on the network, you actually create a separate collision domain on each port - this is exactly the principle of operation of switches. If a hub is connected to the port, the resources of which are shared, then the collision domain can increase to the maximum size allowed for a given Ethernet option. Switching equipment is constantly becoming cheaper, so in most modern networks only one workstation is connected to each port, and in this case the collision domain consists of a single cable segment.
The switch, in turn, is part of a separate broadcast domain, and sometimes the domain includes several switches, cascaded or connected in parallel. When using the functions of the third layer of the OSI model, a large number of broadcast domains are created in the network - according to the number of VLANs. In the extreme case, if the switch allows it, of course, each port can be configured as a separate broadcast domain. This configuration, with good reason, is called direct routing to the user's workplace.
If each port creates its own broadcast domain, then diagnostic capabilities are severely limited. In addition, establishing a separate broadcast domain on each port requires the switch to dedicate a significant portion of its CPU resources to forwarding all network traffic. In real life, it is very difficult to imagine a network where it would be necessary to process and redirect each request and response separately. Unless there is a very compelling reason, this particular network structure should be avoided.
Unfortunately, a very common configuration is where all servers are placed on one subnet or broadcast domain, and the users are distributed across a number of other subnets or broadcast domains. In this case, almost all requests must be routed. If, for ease of maintenance, it is necessary to place all servers in one room (server room), then it is recommended to distribute them over several virtual VLANs. Users who access a specific server should be assigned to the same virtual network. In this configuration, the switch fabric can bridge normal traffic to Layer 2 of the OSI model, so only unusual or infrequent requests will be routed. If the server serves more than one user community, then install additional network cards in it so that communication is carried out at the second level of the OSI model.
ACCURATELY IDENTIFYING THE PROBLEM
Almost the only truly effective method for diagnosing switched networks is to request information about the behavior of the network from the switch itself. Such data is usually requested using the SNMP protocol, or through the console port of the switch. Of course, connecting directly to the console port is less convenient, since the administrator will have to go to every switch on the network. To avoid such inconveniences, you can, of course, install terminal servers and connect them to the console ports, but it is still preferable to use the SNMP protocol, since it allows you to send requests from anywhere on the network and does not require installing additional equipment.
If you have a network management system in place, the switch can be configured to send an unsolicited response—an SNMP trap notification—every time usage, errors, or some other parameter exceeds a configured threshold. The reason can be found out later using a network management system or monitoring tools. Many problems can be successfully resolved by querying the switch, but there are some for which this method is not suitable. The request can be used both as a preventive measure and for monitoring in case of failure.
Another strategy is to wait until users start complaining. Many networks use exactly this approach, which should not be underestimated due to its apparent simplicity - in fact, it is very effective. Users are sensitive to the state of the network, despite the fact that the idea of its operation is based more on subconscious perception than on logical conclusions. Noticing the slightest deterioration in network performance, the user usually immediately complains to the IT department or system administrator. So you can start troubleshooting work from his workplace. This approach is called reactive because it involves responding to a failure that has already occurred.
On the contrary, preventative, proactive methods are aimed at preventing failure from occurring. To do this, regular polling of switches is carried out, monitoring the quality of traffic on each switch port and in each segment. When a problem has already appeared (a complaint has been received, or you have discovered a failure yourself), you can diagnose it using different methods, each of which has its own pros and cons.
SWITCH DIAGNOSIS METHODS
There are at least ten main ways to obtain information about the operation of the switch. Each one has its own course of action and has its own positive and negative sides. As usual, there is no single recipe for all occasions. Selecting a suitable solution from different options should be based, first of all, on the availability of resources, the experience of the specialist carrying out the work, and an assessment of the consequences for the functioning of the network (suspension, interruptions in work) when using one or another method.
However, even a combination of all methods does not allow you to monitor a switched network in such detail as could be done in hub-based networks. It is almost impossible to see and track absolutely all traffic and all errors related to the switch. Most diagnostic procedures assume that traffic flows between the workstation and the corresponding server or is directed to the trunk port. If two workstations communicate directly through a peer-to-peer connection, then traffic does not go through the trunk port or through any other port on the switch. Such compounds are rarely found unless specifically looked for. Typically, errors do not propagate beyond the switch port, but for some types and certain switch settings, further propagation is possible.
For simplicity, let's imagine a minimal network segment: a server connected to a switch. In some cases we will assume that the users experiencing problems are connected to the same switch, in others we will assume that they will be trying to access the server through a trunk port leading to either another switch or router. Diagnostics begins in response to a complaint about slow network operation when accessing the server. Unfortunately, this description of the problem does not tell the IT specialist anything. If this is not a simple failure, but a breach of the security system, and legal consequences are expected, then additional measures must be taken to ensure the reliability and legal validity of the collected data.
Information related to several methods at once will be given in the description of the method in which it is most fully disclosed. Most of the descriptions also refer to methods other than the one addressed in a particular section, and this can have both trivial and fundamental consequences for the final result.
METHOD 1: CONSOLE ACCESS TO THE SWITCH
You can access switch settings in a variety of ways, including the following:
- log in using a TELNET session;
- login using an SSH session;
- login via Web session;
- connect through the serial port of the switch.
Some switches have a number of built-in diagnostic tools that you can use, but be aware that their functionality varies significantly depending on the manufacturer and model of the switch. Advanced operating system commands allow for a more in-depth analysis of the broadcast traffic, but the existing interface cannot be called user-friendly. To successfully apply such functions, you must have considerable experience and deep knowledge of network theory.
Pros. Console access is a very effective diagnostic method; it is widespread and used more often than others. Many different problems on the network are caused precisely by incorrect settings of switches and actions performed in accordance with these settings.
You can always access the switch management console using one of the above methods. The almost universal availability of wireless and data services provided by mobile communications makes it possible to manage the network from anywhere in the world. By setting up your network management system to send notifications to mobile devices, you will immediately know when an outage occurs.
If the failure is indeed caused by the settings, then the console access method will certainly resolve it.
Minuses. Senior system administrators and other senior IT staff who have passwords to access switch configurations pay so much attention to the configuration when performing diagnostics that no other options even cross their minds until this method has completely exhausted itself. Meanwhile, abandoning other approaches can significantly delay the elimination of the failure and further complicate the situation. Using console access alone, only some network problems can be identified and resolved.
Typical console commands provide average usage levels, but do not provide information about specific network activity or the root cause of a particular protocol failure. Moreover, the data obtained through console access indicates how the network should work rather than reporting the actual state of affairs, so it will be of little help if, for example, part of the switch is not functioning correctly. Reviewing the configuration does not reveal software errors in the operating system or inaccuracies and omissions in the settings. Sometimes, by displaying a configuration dump on the screen, you won't be able to see the default settings because it only shows changes from the default settings. Meanwhile, these settings may well be the reason for the decrease in network performance.
Configuration data is useful for generally determining whether the switch is performing as it should. However, to check the configuration and performance of the network, you need to use other methods for diagnosing switches - perhaps not even one, but several.
If we are talking about critical network segments, then console access from remote points can either be prohibited or allowed only from a specific group of strictly fixed addresses. Typically, passwords to access switches are not known to ordinary IT and help desk personnel, so they are unable to use console access. Higher-level engineers who have passwords are typically not involved in the day-to-day work of troubleshooting network failures. Now imagine how a specialist whose direct responsibilities include constantly maintaining network performance can work effectively if console access is denied to him?
We will talk about other methods for diagnosing switches in the following issues of the section.
Igor Panov is a regional product and partner support manager for Fluke Networks in Russia and the CIS. He can be contacted at
Features of repairing the VAZ 2109 switch
Repairing a switch most often comes down to replacing it. Fine-tuning the device is intended only to improve the efficiency of the system. If the device breaks down, the procedure for replacing it is as follows:
- de-energize the vehicle's electrical system, remove the main terminal from the battery;
- disconnect the brown wire from the negative terminal of the battery;
- Use a screwdriver to press out the spring bracket and disconnect the block with wires from the switch;
- unscrew the two radiator mounting nuts and remove the device together with the radiator;
- install a new switch with a radiator;
- connect the connector block;
- place the brown wire under the left nut;
- secure the switch to the VAZ 2109 with nuts;
- connect the battery.
Examination
The easiest way to test a switch is to try replacing it with a known good one. But this can only be done if a working switch is at hand. It is not advisable to buy a new unit just to test the operation of the old one. There is a cheaper and not particularly complicated way. To test the switch, you only need a standard set of keys and a test lamp. This is enough to verify the presence or absence of pulses supplied to the ignition coil. Before checking the switch, make sure that “plus” is supplied to it and the ignition coil. Also check the connection contacts of the Hall sensor and the functionality of the sensor itself. Checking the VAZ 2107 ignition switch is performed as follows:
- turn off the ignition;
- unscrew the nut on the ignition coil and disconnect the brown wire marked “K” (the wire goes to connector “1” on the switch);
- connect a test lamp to the gap between the wire terminal and the coil terminal;
- turn on the ignition;
- turn the key and start the starter.
A flashing light indicates a working switch. If the lamp does not light, the switch needs to be replaced.
Replacing a VAZ 2107 switch
To replace the switch, you must complete the following steps:
- turn off the ignition;
- disconnect the wire block from the switch connector;
- unscrew the fastening nuts;
- remove the old switch and put a new one in its place;
- tighten the fastening nuts;
- connect the wire block to the connector.
At this point, the replacement of the VAZ 2107 switch is completed and you can check the operation of the ignition by trying to start the engine.
Source: semerkavaz.ru
What is and what is the principle of operation of the ignition switch
Even on the very first cars, battery ignition systems were used to ignite the combustible mixture, the functional diagram of which is shown in the figure.
This figure allows you to understand that its work is based on the principle of self-induction. When the current flow circuit in the winding of bobbin 3 is broken, a high-voltage EMF is induced in the secondary, causing a spark to appear on the contacts of spark plug 2. The circuit break is caused by the opening of the contacts of breaker 6.
Without touching on the advantages or disadvantages, it should be noted that this scheme worked on the car for a long time. And only the emergence of a new element base gave impetus to the further development of such a device, preserving the original principle of its operation.
Auto help:
80% of road problems are corrected on site
Wide range of services: more than 50 types of on-site repair work
24/7 technical assistance
Efficiency: time of arrival of a technical assistance specialist is 30 minutes within St. Petersburg
Equipping technical assistance vehicles with all necessary professional equipment and tools
You can see the cost of services here – prices.
Contacts
Address: St. Petersburg, Evdokima Ogneva st., 12
Telephone
Manager's email
Call or make an appointment at a time convenient for you.
We are always happy to help you.
Published: June 3, 2017admin
Add a comment Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Source: pomoshch-na-dorogakh.ru
What could the ignition system switch look like?
The above switch circuit is just one of the options for how the ignition device can be implemented. This is done using:
- transistors;
- thyristors:
- hybrid elements;
- contactless sensors.
The transistor circuit of the switch is discussed above; the thyristor circuit uses energy accumulation in the capacitor, and not in the electromagnetic field of the ignition coil. During operation of the thyristor system, when control signals are received, the circuit connects a charged capacitor to the windings of the coil, through which it is discharged, causing a spark to appear. Without touching on the advantages and disadvantages that this or that circuit has, suffice it to say that any such device provides a significant improvement in all parameters of the ignition system, and the switch over time has replaced conventional battery ignition.
However, it is necessary to note one more stage in the development of the system, and the switch in particular. The use of electronic components and the introduction of a switch into the design of the car made it possible over time to abandon the contact voltage breaker and replace it with a contactless sensor. Such a system, in domestic cars, was first used in VAZ cars, in particular the VAZ 2108. A similar operating principle, when the switch receives signals from a special unit, is implemented on the VAZ 2108 using a Hall sensor.
When considering the options for what the switch device could be, one cannot ignore the development of the ignition system itself. The main principle that is implemented during its construction is to increase the reliability and efficiency of the entire system. This is achieved by using microprocessor systems that use the readings of numerous sensors. To work with such systems, you need at least a two-channel switch, and recently a separate coil and switch for each spark plug. This approach – a two-channel switch (later also multi-channel) allows you to provide:
- more powerful spark;
- elimination of losses in the distributor;
- stable idle;
- improved starting at low temperatures;
- reduction in fuel consumption.
Checking and replacing the ignition switch VAZ 2107
The task of the VAZ 2107 ignition system is to generate a spark that ignites the air-fuel mixture in the cylinders. In older “classic” models, this works based on the “breaker-ignition coil” connection. On more modern cars, a contactless ignition system is installed, where the VAZ 2107 ignition switch is responsible for sparking.
Switch malfunctions affect the efficiency and performance of the entire ignition system and the vehicle as a whole. Therefore, it will not be superfluous to learn how to check the VAZ 2107 switch and replace it, if necessary.
How to determine if the ignition switch is faulty
The introduction of an ignition switch into the design of a car, especially on domestic cars of the VAZ family, made it possible to increase their reliability. And although the first production car with an electronic ignition system was the VAZ 2108, similar devices began to be installed on many other cars, primarily classics. However, the use of such a rather complex product has led to the fact that finding a malfunction, as well as checking and repairing the switch, has become possible for the most part only in specialized centers. External signs indicating that a malfunction has occurred may include:
- the engine does not start, there is no spark at the spark plugs;
- the engine starts but stalls after a few minutes;
- The motor is unstable; if the switch is replaced with a known good one, the defect is eliminated.
The easiest way to identify a malfunction and test a switch, as already noted, is to install a known-good one. Due to the rather low quality of the switches supplied for the VAZ family of cars, including the VAZ 2108, drivers have to carry additional switches with them to replace the failed one. However, there is also an indirect evaluation principle that allows you to check the performance of the product and identify its malfunction.
To do this, you can use the readings of the voltmeter in the instrument cluster. You need to turn on the ignition, and the needle will be in the middle of the scale, and a little later it will swing to the right (due to the power supply to the coil being turned off when the engine is not running). This arrow behavior indicates that there is no fault in the switch. In the event that there is no voltmeter, a test lamp is required to check the ignition. One end of it is connected to ground, the other to the output of the coil connected to terminal 1 of the switch. If you turn on the ignition, then if the switch is working properly, after a while the lamp will burn brighter.
However, in some cases, the ignition malfunction is not related to a switch failure. It is necessary to check the condition of the wires, first of all, contact with ground and the condition of the connectors. It is also necessary to check the Hall sensor.
The appearance of a voltage switch in the design of a car, including the domestic VAZ 2108, was a natural result of the development of the ignition system. Its further improvement was the use of first dual-channel and then multi-channel switches to improve operating efficiency. » alt=»»>
Checking the 2109 switch yourself on a VAZ, or simply “nine” car is something that sooner or later every owner of this domestic car may encounter.
This small electrical device, if it fails, makes operating the car difficult or even impossible.
In our material we will analyze in detail: what is this switch, why is it needed and how to determine whether it is working?
Content:
Car switch repair
How to check and repair the switch yourself?
If with some malfunctions in the car you can somehow get to the repair point, then with a faulty switch the engine will not start at all. Some drivers often carry a spare switch with them. In this article we will look at the principle of operation, some malfunctions of the car switch and methods for repairing it.
Possible reasons for switch failure
- Often the switch fails due to water getting into it. As a result, the Kr1055xp4 microcircuit (analogous to L497B) fails,
- Due to overvoltage or time, the output transistor type KT8231A1, KT8225A, KT8232A1, KTD8252A, KTD8264A, KTD8267, KT898A, KT8127A1 (analogous to BU941ZP) often fails.
Characteristics of some high-power transistors used in switches.
| Name | Type of shell | Analogue | Structure | Pk max, W | Ukb max, V | Uke max, V | Ueb max, V | Ik max (imp), A | h21е |
| KT8127A1 | TO-218 (KT-43) | BU941ZT(ZP) | NPN | 100 | 1500 | 700 | 5 | 5(7,5) | 35 |
| KT8231A1 | TO-218 (KT-43) | BU941ZT(ZP) | NPN | 155 | 350-450 | 350-500 | 5 | 15 | 300 |
| KT898A | TO-218 (KT-43) | BU931ZP/BU941ZT(ZP) | NPN | 125 | 350 | 350 | 15 | 5 | 400 |
| BU941ZT(ZP) | TO-218 (KT-43) | — | NPN | 155 | 350 | 350 | 15 | 15(30) | 400 |
Excerpt from car diagram
Automotive switch test bench
To test the switch, we assemble such a simple stand as in the figure below. We connect a 12 V light bulb instead of the coil.
Normal Switch Operation
When we turn the axis of the distributor with the DH (hall sensor), the light comes on. When we don’t turn it, the light doesn’t light up.
A little about the Hall sensor
A Hall sensor is a magnetoelectric device that takes its name from the name of the physicist Hall, who discovered the principle on the basis of which this sensor was subsequently created. Simply put, it is a magnetic field sensor. There are two types of Hall sensors: analog and digital.
Analog Hall sensors
Analog Hall sensors - convert field induction into voltage, the value shown by the sensor depends on the polarity of the field and its strength. But again, you need to consider the distance at which the sensor is installed.
The switch is the basis for uninterrupted engine operation
The VAZ 2109 car is equipped with a contactless ignition system.
The system includes spark plugs, four high-voltage wires (one for each spark plug), a Hall sensor, a distributor, an ignition coil and, in fact, a switch.
Rice. 1 Ignition circuit of VAZ 2109 Schematic illustration.
The ignition system generates an electrical impulse (spark), thereby igniting the mixture of fuel and air in the combustion chambers necessary for engine operation.
The switch is responsible for the cyclic supply of pulses to the ignition coil, this is necessary for the proper operation of the entire system as a whole.
Thus, if the switch is faulty, the spark will supply intermittently or be completely absent. It is not possible to drive such a car.
The VAZ 2109 switch itself consists of an aluminum case and a microcircuit installed on it. The device is mounted in the engine compartment and connected by wires to the ignition coil.
Rice. 2 Appearance of the VAZ 2109 switch.
The design of the housing and the mounting method allow the switch to successfully withstand vibrations that occur when the car is moving.
The VAZ 2109 contactless ignition system switch has the following performance characteristics:
- Voltage range 6–16 Volts.
- Operating voltage 13.5 Volts.
- Switching current 7.5–8.5 Amperes.
- A switch in good condition ensures an uninterrupted supply of spark to the cylinders with a crankshaft speed of up to 7000 rpm.
How to test the switch yourself
Author: Sochi Auto Repair
The purpose of an automobile ignition system is to create a spark, which in turn ignites the fuel assembly and ensures efficient engine operation. The ignition system includes several rather complex components and the switch is one of them. How to check the car switch yourself?
Let's look at why it is needed, how it is checked and when it needs to be changed.
Device and principle of operation
Switch – Refers to the vehicle's electrical system. It is designed to ensure that the ignition system performs its functions normally.
This device is mounted inside the space under the hood. It is quite reliable and can work in conditions with high loads and strong vibrations. This is important because the switch contains electronic components inside that are sensitive to external influences.
The switch is based on a conventional L 497 circuit that controls an “NPN” transistor. The driver has the opportunity to set the desired delay time in this diagram, the correctness of which directly affects the quality of the cold start of the power unit.
Precise tuning allows you to increase the frequency at which the crankshaft rotates, eliminate dips and ensure good traction.
The main characteristics of the switch are as follows:
- supported voltage range 6-16 V;
- voltage – 13.5 V;
- constant creation of a spark when the crankshaft rotates at 20-7000 rpm;
- current 7.5-8.5 A.
What are the signs of a broken switch?
How to check the switch yourself? The disappearance of the spark is the most basic sign indicating that the switch has failed. In this case, problems arise when starting the engine; it begins to periodically stall and operates intermittently.
However, you should not rush to change it right away. You need to make sure that the reason for the loss of spark is due to problems with the switch, and not to other faults.
If the diagnostics show that the switch is the culprit of the failure, you need to check its operation. This is precisely where many people have problems, since the switch has a complex design.
How to test the switch yourself
Many car owners do not want to check the switch and replace the faulty unit with a new one. This option has certain advantages. First of all, you need to spend your time on diagnostics; you just need to install a new device. In addition, it helps to immediately find out whether the cause of the bad spark is actually related to it.
In fact, it only takes 2-3 minutes to check the switch and you can do it yourself, right in the garage. To do this, you only need a control lamp (12 V) and standard keys. To test the switch, you need to do the following:
- The first step is to disconnect the battery to avoid accidental short-circuiting of the unscrewed wires.
- Using a key set to “8”, unscrew the nut and disconnect the wire marked with the symbol “K” from the coil. It is easy to recognize, it is colored brown and fits into the clamp on the switch marked “1”;
- The disconnected wire should be connected using a test lamp to the ignition coil terminal marked “K”, then connect the battery;
- Now you should turn on the starter and monitor the behavior of the light bulb. The switch is working properly if it starts blinking. If the light does not light up, then the device should be replaced.
We told you how to check the switch yourself. If you have doubts about the operation of this unit, it is better to check it at a car service center using a specialized stand. This will help not only to find out whether the device is working or not, but also to find out the duration of the pulses.
Good luck!
Did you like the article? Share with your friends on social networks!
Signs of a broken switch
During the operation of the car, unpleasant symptoms may occur, indicating a malfunction of the ignition system.
A possible reason for this may be incorrect operation of the switch. Here are the most common symptoms that should suggest a possible breakdown of this device:
- Can't start the engine. There is no spark when the starter is running.
- The engine starts and runs normally at low and medium speeds, but cannot be revved up at high speeds. The engine is not running at full power.
- The car stalls when moving away, although it idles stable.
- The engine starts, but does not run for a long time and immediately stalls.
- The engine begins to operate unstably - “triple”, reaching a certain speed level. When cold it can start quite normally.
- The engine may periodically, without any pattern, stall, then work normally again. The battery discharge indicator lights up. The tachometer needle shows sharp changes in the number of revolutions.
Malfunctions of the contactless ignition system in which the engine does not start
Malfunctions of the contactless ignition system - The main reasons that impede starting, as well as normal operation of the engine, and methods for eliminating them in the contactless ignition system (Fig. 15) are similar to the reasons and elimination methods characteristic of the contact ignition system, which were discussed earlier.
At the same time, the design features of some elements of the contactless ignition system, methods for detecting and eliminating basic faults require compliance with the following recommendations.
Verifying switch operation
Every car enthusiast with a sufficient level of desire and minimal technical skills can check the operation of the switch.
The easiest way to check is to replace the unit with a new one that is known to be good. If after this the problems in the engine operation have disappeared, then we can conclude that the old switch has already served its purpose.
Every car enthusiast can replace the switch independently. First of all, you need to find it under the hood of the car.
The switch is located in the area of the left (driver's) pillar. It is connected by wires to the coil.
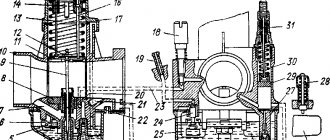
Rice. 3 Engine and organization of the engine compartment of the VAZ 2109.
1 – front glass of the shock-absorbing strut; 2 – water tank; 3 – air filter; 4 – fuel pump; 5 – steering rack; 6 – camshaft sensor; 7 – vacuum brake booster device; 8 – master cylinder of the brake system and its barrel; 9 – switch; 10 – fuses; 11 – engine cooling system tank; 12 – battery; 13 – hood fastening; 14 – ignition coil; 15 – starter; 16 – high-voltage wires; 17 – neck for oil; 18 – engine; 19 – candles; 20 – windshield washer system.
Next, disconnect the negative terminal from the battery. Then you should carefully disconnect the plastic bracket with wires from the switch. To do this, you need to release the spring clip.
Then we unscrew the nuts that secure the aluminum switch housing to the car body. Under the left nut there will be a ground terminal.
Remove the switch from the studs and replace it with a new one. The new one is installed in the reverse order.
Den242 › Blog › Identifying faults in the ignition system
Determining malfunctions in the ignition system
Malfunctions in the ignition system lead to the fact that either the engine does not start, or runs intermittently at idle or in all modes, or does not develop full power.
Due to the fault of the ignition system, the engine may not start for the following reasons:
open or short circuit in the low voltage circuit;
malfunction of spark plugs, distributor, coil or ignition switch;
incorrect connection of wires to spark plugs;
contamination or breakage of high-voltage wires;
incorrect setting of ignition timing;
damage to the runner and distributor cap.
Unstable engine idling may be caused by an increased gap between the spark plug electrodes or incorrect ignition timing. The reasons why the engine operates unstably in all modes may be damage or unreliable connection of high-voltage wires, oily or faulty spark plugs, faulty switch, slider or distributor cap.
The reason why the engine runs unstably at high speeds may be a faulty ignition distributor.
The engine does not develop full power due to a faulty ignition switch or distributor or incorrect ignition timing.
When the ignition switch operates, a large amount of heat is generated.
In order not to damage the electronic devices of the ignition system, as well as to avoid possible injuries, follow these rules:
1. Do not touch high-voltage wires and system components (coil, switch, etc.) with your hands while the engine is running, since the non-contact ignition system has a higher voltage compared to the contact system.
2. Do not check the operation of the system “for a spark” by holding the tip of a spark plug or a high-voltage wire in your hands. To check, use a special spark gap.
3. It is prohibited to lay low and high voltage wires of the ignition system in the same harness.
4. Do not disconnect the wires from the battery terminals with the ignition on: this will damage the electronic components of the ignition system.
5. It is forbidden to disconnect the block with wires from the switch when the ignition is on: the switch will be damaged.
6. Do not loosen the screws that secure the switch: through these screws it is connected to ground.
During the check, do not touch the wires and devices of the ignition system while the engine is running.
Disconnect and connect the ignition system wires only when the ignition is turned off.
To check for a “spark” you need to use a special spark gap with a gap between the electrodes of 5–7 mm. If the gap is more than 10 mm, the electronic devices of the ignition system may fail. You can use old working spark plugs as a spark gap. The gap between the spark plug electrodes should be 0.7–0.8 mm.
Malfunctions in the ignition system lead to unstable engine operation, and starting problems are also possible.
Before you start troubleshooting the ignition system, make sure that the fuel system is working properly. If gasoline does not enter the carburetor, the engine will not start. To check, remove the hose from the carburetor coming from the fuel pump and pump fuel with the manual pumping lever, while fuel should splash out of the hose. The engine may run rough due to a high fuel level in the carburetor float chamber, a faulty brake booster vacuum, or a leaky connection between the booster vacuum hose and the engine intake pipe or the booster check valve.
3.10.1. Reasons for unstable engine operation:
1. Dirty or damaged high-voltage wires. This is especially true in wet, rainy weather.
2. High-voltage wires are not fully inserted into the sockets of the ignition distributor cap or ignition coil, as well as into the tips of the spark plugs.
3. The spark plugs are faulty or the gaps between the spark plug electrodes are not adjusted.
4. The ignition timing is incorrectly adjusted.
5. Malfunction of the slider or its resistor.
6. Damage to the ignition distributor cap (especially noticeable in damp and rainy weather).
7. Malfunction of the ignition switch.
8. Malfunction of the ignition coil.
Periodically clean high-voltage wires, spark plug tips, ignition coil, distributor cap and switch with base from dust and dirt.
3.10.2. Engine won't start
1. Check if voltage is supplied to the spark plugs. To do this, remove the high-voltage wire from the central socket of the distributor cover and connect it to the arrester. Turn on the starter for a few seconds, while a spark should periodically jump between the electrodes of the spark gap. If there is no spark, then voltage is not supplied to the spark plugs. If there is a spark, check the operation of the spark plugs in the same way, removing the tips with wires from them one by one. If any spark plug does not spark, replace its wire. If there is a spark on all wires, but the engine does not start, replace the spark plugs.
2. If voltage is not supplied to the spark plugs (no spark on all four spark plugs), replace the distributor slider. Sometimes the slider resistor fails. You can check its performance using an ohmmeter: the resistor resistance should be 0.9–1.1 kOhm. If the resistance is different from the specified value, replace the slider. If, after replacing the slider, voltage is not supplied to the spark plugs, replace the ignition distributor cap. If after this the engine does not start, replace the ignition coil, switch and ignition distributor in sequence.
3.10.3. The engine is running erratically
1. Clean the high-voltage wires and check their condition. Damage to the insulation of high-voltage wires and the ignition distributor cap can be detected in the dark. To do this, start the engine and inspect the engine compartment. A characteristic glow will be visible in the damaged area.
2. To determine which spark plug is faulty, disconnect the wire from it with the engine off, and then start the engine. If interruptions in engine operation increase, then the spark plug is working. After this, stop the engine and connect the wire to the spark plug. Remove the wire from the other spark plug and start the engine again. If the nature of the vibrations has not changed, this spark plug is faulty and must be replaced. If the engine continues to run rough, replace the spark plug wire.
3. If all spark plugs and wires are in good condition, and the engine continues to run unstably, replace the slider and ignition distributor cap.
4. If, after replacing the cover and slider, interruptions in engine operation continue, replace the ignition switch.
Connecting the switch
Cases vary, and it is possible that you will have to change the wiring. Therefore, you will need to take into account the purpose of all pins on the switch plug. This will allow the connection to be made correctly, and there will be no risk of damaging it. The first pin of the switch is the output. In other words, the amplified signal is removed from it. It must be connected to the terminal of the “K” coil. The second contact is connected to ground - the negative of the battery.
All three wires from the Hall sensor go to the VAZ switch. Moreover, the signal wire is connected to the sixth terminal of the switch. The fifth is the power output (the voltage on it is stable 12 Volts). The third output of the switch is ground (minus power). The third is connected inside the block to the second. But between the fourth, which is supplied with power from the battery, and the fifth there is a constant resistance and a voltage stabilizer.