Scooters are very popular due to their economical fuel consumption, the ability to ride without a license on certain models, and excellent maneuverability in urban conditions. You can easily get to your place of study, work or recreation on it, it’s nice to just ride with friends, or go fishing. Thanks to their narrow dimensions, scooter drivers never get stuck in traffic jams. Servicing a small “iron horse” is much cheaper than a motorcycle or car. But how not to get confused in the various characteristics of this equipment and choose a device that suits the user’s weight, height and terrain preferences? A detailed answer to this question is provided here.
Scooter controls
All main scooter controls are located on the handlebars (except for models with a foot brake). They are distributed as follows:
On the left side of the handlebar: - Rear brake or clutch lever (lever is not available on scooters with a semi-automatic transmission) - Turn signal switch - Low/high beam switch - High beam switch (on some models)
On the right side of the steering wheel: — Front brake lever — Engine start button (electric starter) — External lighting switch off/dimensions/headlights (Not on all models. Often this switch is missing, because by design the light is always on) — Emergency stop button or “hazard light” (on some models) - Engine stop button (on some models)
Depending on the make and model of the scooter, the scooter's instrument panel may contain: - Speedometer - Odometer - Tachometer - Fuel gauge - Coolant temperature gauge (for liquid-cooled models) - Turn signal indicator - And low oil level indicator - Gear indicator
The scooter's ignition switch performs the following functions: - Turning on the ignition - Locking the steering wheel - Opening the underseat luggage compartment "pit" (on some models)
The first thing we will need to do:
- Remove the muffler
- Remove cooling shrouds
- Remove the generator
- Remove the variator
- Clean and blow out connectors
Removing the muffler is very easy and simple: unscrew the two nuts and two bolts on the cylinder head that secure the muffler to the frame (139QMB) or the rear wheel booster (157 QMJ)
Cooling shrouds are even easier to remove: unscrew all the bolts and screws that secure the shrouds to the engine and remove them.
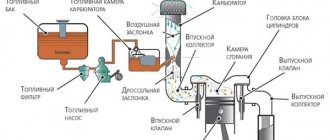
Scooter power system
The power supply system refers to the fuel supply system.
Main elements: - Gas tank - Fuel line - Carburetor - Intake manifold - Air and fuel filters
Chinese scooters
They are produced by a huge number of Chinese enterprises, representing local processing of relatively old Japanese models. Notable is the predominance of four-stroke engines on them, similar in design among most manufacturers, as well as the greatly varying quality of assembly and components among different brands that produce outwardly indistinguishable models. The big disadvantage of Chinese scooters is the extremely fragile plastic, which results in a lot of minor breakdowns.
The scooter has become a very popular means of transportation in large cities and metropolises, thanks to its economical operation and maneuverability. It does not have gears, levers or taps; to control it, just press the big red button, and then everything is done automatically. Moving from a place is not difficult: you just need to grab the gas handle. Even a computer game of cars can be somewhat more difficult than driving a scooter.
A scooter is a very useful thing. It's great to take a breeze in the evenings like this.
Engine displacement
This is one of the main characteristics of the scooter
, which divides this transport into three categories:
- small or compact - engine displacement does not exceed 50 cubic meters;
- medium - with an engine volume ranging from 50 to 250 cubic meters.
- maxi scooters are the closest to motorcycles and are equipped with powerful engines, the volume of which ranges from 250 to 500 cubic meters.
On the Russian market, scooters are presented in all three categories. The choice of engine size depends on the goals and tasks that you assign to it. For novice drivers, women and teenagers, the most preferable are compact models that can successfully move both on city roads and country paths. Medium and large scooters are designed for experienced riders who want to switch to a motorcycle.
Number of engine strokes
According to this technical specification, scooters
are divided into:
- two-stroke;
- four-stroke.
The first option is suitable for lovers of excellent traction and dynamic acceleration. Thanks to the simple design of the two-stroke engine, a driver who has at least a little knowledge of technology can independently increase its power, thereby increasing the speed of the unit. The disadvantages of a two-stroke engine include a large amount of smoke produced and noisy operation.
Recently, more and more scooters are being launched with four-stroke engines, which are prized for their quiet operation and smooth traction. One of the main advantages of such engines is minimizing oil and fuel consumption.
Variable speed drive
It is possible to increase the efficiency of a standard scooter variator and use its full potential only after installing an enlarged belt. At the same time, a set of new weights is purchased - they should all differ in weight. For a CVT, the required weight of the weights is selected extremely carefully and painstakingly, since the maximum speed of the motor vehicle and the dynamics of its acceleration depend on them.
Engine cooling type
There is a liquid and air type of engine cooling. The first option is 30% more effective than the second.
Engine power
This characteristic directly depends on the engine displacement. Small-capacity scooters are available with a power of 1-8 hp. Medium-cubic engines (50-250 cubic meters) - offer power in the range of 8-25 hp. The best performance is found in maxi scooters; in some models it reaches 50-60 horsepower.
Don't rush to buy a scooter with maximum horsepower. For daily trips around the city, 5-6 hp will be enough. with average fuel consumption: 2.5 liters per 100 km. For long country trips, you will need a more powerful car (10-20 hp). At the same time, remember that as fashion increases, traction, dynamics and gasoline consumption also increase.
Relay regulator
This is the same rectifier that converts alternating voltage to direct voltage, with a range of 13.5-14.9 V. C
.
The regulator is located under the plastic cover of the scooter at the front. It is attached to a metal backing for better heat dissipation.
The main circuits of the relay circuit are:
- The green wire is common.
- Red – output of converted and stabilized voltage within the established limits.
- White and yellow – AC input to the regulator. Due to electronics, the voltage is converted into powerful impulses. The yellow wire supplies power to a heavy load on the on-board network - headlights and instrument panel lighting.
The current for lamps is not stabilized, but is limited to acceptable values. At high generator speeds, the voltage goes beyond the operating ranges of the lamps, which leads to their burnout. The situation is very familiar to those who have encountered faulty relay regulators.
Because of one unit, you can lose all the light bulbs in a matter of seconds, so you should monitor the on-board voltage regularly.
The maximum speed at which the scooter can accelerate
An important technical characteristic that interests every buyer. Here you can estimate at a glance: compact scooters can reach speeds of up to 50 km/h; average up to 80-140 km/h; Maxi models can accelerate to 150-180 km/h.
Transmission
Today there are three types of transmission. Which one is installed on the scooter you have chosen?
Good budget cars are equipped with a single-stage
transmission, which has a simple and reliable design.
On modern European, Japanese and Taiwanese models, a belt-driven variator is often found, which ensures uniform and smooth shifting. The semi-automatic
transmission allows the driver to change gears independently.
Removing the piston
We clean and blow off the cylinder connectors, cylinder heads and valve covers. Unscrew the bolts on the valve cover and remove it from the head
Removing the timing chain tensioner
Unscrew the nuts and bolts on the cylinder head
Remove the camshaft bed. The camshaft bed is practically not subject to wear. After removing it, just wash it and check for cracks.
We remove the chain from the camshaft and take it out of bed. The camshaft has two problematic points that are worth paying attention to: wear of the support bearings and the working surfaces of the cams
The cylinder, head and camshaft bed are centered relative to each other using guide bushings. These bushings tend to fall out of their sockets and then try to find it. To avoid this, immediately remove the bushings and put them somewhere away. Here and below, the bushings will be indicated by arrows.
Remove the cylinder head. The cylinder head is the most vulnerable part of the engine and the operating parameters of the engine directly depend on its condition. To avoid problems later: the head must be completely disassembled, inspected for cracks, the valve seats cut, new valves installed, the valves ground into the seats, new oil seals installed and the plane ground in on a plate or milled
Remove the cylinder. Immediately after removal, we check the cylinder for wear of the liner and the presence of burrs on the mirror
We remove the retaining ring from the piston boss, push the pin out of the upper head of the connecting rod, and remove the piston. We check the piston for cracks and wear, paying special attention to the condition of the ring grooves and the rings themselves
More elegant motorcycle schemes
In the list of unusual pictures, where a motorcycle is schematically depicted, you can also find a drawing of a cross-shaped bike.
This brainchild of modern science and technology is replete with an abundance of unusual things, from the design of its entire structure to the shape of the engine and the number of its cylinders. The X-shaped engine looks cool and is capable of producing a lot of power. Unfortunately, few people have yet been able to verify in practice the superiority of this model of the iron horse, since these days mainly steel horses with boxer, in-line and v-shaped engines are produced en masse.
To assemble such a miracle of technology yourself, you need a lot of money and a lot of free time. And the main thing you need to stock up on is the desire to create something original in motorcycle mechanics. Still, the decisive role in the design process for creating motorcycles remains with finance.
Be that as it may, the rest of the design of such a motorcycle remained virtually unchanged. Same chain drive, same pair of wheels. The X-shaped engine is located where other types of motors are installed - under the frame and between two wheels. Perhaps the only thing missing from the bike diagram is the fuel tank and a normal seat. Still, the designers left the place for both to your discretion and imagination.
Motorcycle electronics circuit
Well, the picture indicated at the bottom of this section describes in detail the electronic system of the bike. It clearly indicates the main components that generate current and the main consumers of the latter. In addition, this picture demonstrates in a clear perspective the connection between the above parts of the motorcycle.