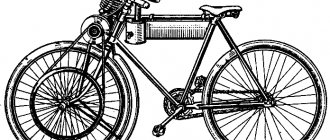
Motorcycle diagram
Hi, bikers, bikers, and just lovers of two-, three-, and four-wheeled vehicles! This portal is filled with data that is sometimes missing for many lovers of freedom-bearing transport and motorcycle restoration. If you are directly looking for electrical equipment or engine diagrams of domestic motorcycles, you need to follow this link. The same article contains information regarding the general principles of the structure of iron horses. We will give confidence to those who have just begun to study bikes, and brighten the mood by describing unusual motorcycles for those who have already gained a foothold in the biker movement.
This section is intended to describe the scheme of motorcycle equipment for beginner lovers of two-wheeled horses. The following brief visual information will help you understand the simplest steel horses. This is exactly what the bikes of the 1960s looked like. from the world's leading manufacturers of similar products. Moreover, this applies to former motorcycle legends and modern brands of iron horses. Using this picture you can study the history of the structure of motorcycles.
The first number in the diagram shows the front shock absorber fork. However, you will not see the springs themselves in the front part of the motorcycle, since the latter are hidden under an iron casing called pants. Number 2 indicates the dashboard light indicator lamps. In older bike models they were installed directly on the top of the headlight. The third number is the speedometer.
Number 4 is represented by the front brake drive handle. 5 is a (gas) handle that changes the fuel supply level using the throttle. Number six indicates the clutch lever. 7 - gas tank. 8 - air purifier. This is exactly what his old samples looked like. Number 9 in the picture is represented by the rear shock absorbers. 10 — exhaust pipe (namely “muffler”).
Number 11 will show you the rear fork (swingarm). 12 is a chain (chain drive). Number 13 indicates the engine (its crankcases). 14 is represented by a leading star. 15 is the motor chain. Number 16 indicates the left crankcase (motor) cover. 17 - piston. 18 - cylinder (popularly referred to as “piston”). Number 19 on the motorcycle diagram shows the brake pads of the front wheel drum. Well, 20 is the front wheel drum itself.
Two stroke engine
The engine capacity of this type of motorcycle is usually smaller, and the working cycle takes one revolution. In addition, it does not have intake or exhaust valves. This work is performed by the piston itself, which opens and closes the channels and windows on the cylindrical mirror. A crankcase is also used for gas exchange.
The advantages of this engine are:
- with the same cylinder volume, it has a power that is 1.5-1.8 times greater than a four-stroke;
- does not have a camshaft and valve system;
- production is cheaper.
More elegant motorcycle schemes
In the list of unusual pictures, where a motorcycle is schematically depicted, you can also find a drawing of a cross-shaped bike. This brainchild of modern science and technology is replete with an abundance of unusual things, from the design of its entire structure to the shape of the engine and the number of its cylinders.
The X-shaped engine looks cool and is capable of producing a lot of power. Unfortunately, few people have yet been able to verify in practice the superiority of this model of the iron horse, since these days mainly steel horses with boxer, in-line and v-shaped engines are produced en masse.
To assemble such a miracle of technology yourself, you need a lot of money and a lot of free time. And the main thing you need to stock up on is the desire to create something original in motorcycle mechanics. Still, the decisive role in the design process for creating motorcycles remains with finance.
Be that as it may, the rest of the design of such a motorcycle remained virtually unchanged. Same chain drive, same pair of wheels. The X-shaped engine is located where other types of motors are installed - under the frame and between two wheels. Perhaps the only thing missing from the bike diagram is the fuel tank and a normal seat. Still, the designers left the place for both to your discretion and imagination.
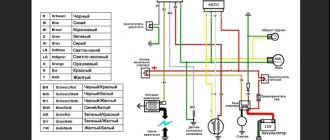
Motorcycle electronics circuit
Well, the picture indicated at the bottom of this section describes in detail the electronic system of the bike. It clearly indicates the main components that generate current and the main consumers of the latter. In addition, this picture demonstrates in a clear perspective the connection between the above parts of the motorcycle.
We think all of you have already guessed that these are electronics drawings for a single-cylinder motorcycle model. In addition, everyone can probably see that this is an old domestic bike that has been out of production a long time ago. However, fans of such transport have not sunk into oblivion. They need diagrams that make it easier to restore motorcycles, which is why such pictures from the Internet will probably never disappear, despite progress and the gradual improvement in the quality of life.
- Back
- Forward
Four stroke engine
Such engines have a duty cycle of four piston strokes and two crankshaft revolutions. The engine diagram clearly shows the structure of a piston internal combustion engine and its working process.
- On intake, the piston moves down from top dead center, drawing mixture through the open valve.
- During compression, the piston rising from bottom dead center compresses the mixture.
- During the working stroke, the mixture, ignited by an electric spark plug, burns, and the gases move the piston down.
- When exhausting, the piston, rising, pushes the exhaust gases through the open exhaust valve. When it reaches top dead center again, the exhaust valve closes and the whole process repeats.
The advantages of four strokes are:
- reliability;
- efficiency;
- less harmful exhaust;
- little noise;
- Oil and gasoline are not pre-mixed.
The design of this type can be depicted by the following engine diagram.
Tires
You've probably heard thousands of recommendations more than once that you need to regularly check the tire pressure in cars. And before every trip. But let's be honest with ourselves. You are probably unlikely to do this.
But when it comes to a motorcycle, checking the pressure in the wheels of the bike should become a commandment for you. Remember that checking your bike's tire pressure before riding will not only prevent disaster from unexpected wheel damage while riding, but will also allow you to be more confident on the road. The fact is that even the slightest deviations in the pressure in the tires of a bike can affect the handling of the motorcycle, even at low speed.
So if you start to feel that your bike has become wobbly, less controllable, etc. and you no longer feel confident behind the wheel, then it’s time to check the tire pressure of your motorcycle. Most likely it is low.
See also: Pros and cons of run-flat tires
Including you should be more strict about the condition of your motorcycle tires. For example, a worn tire on a car can sometimes amuse the driver and passengers. For example, drifting on wet asphalt. But slipping on a bike leads to an accident.
Therefore, if your motorcycle tires are worn out, you should immediately install new tires. To quickly notice the wear of your motorcycle tires, purchase tires with a wear indicator.
Filter
We all know from school that fire requires oxygen. Without oxygen, any fire will go out. We also know that any internal combustion engine works by igniting fuel, which requires oxygen for combustion. More than one vehicle and motorcycle equipped with internal combustion engines cannot do without it.
Automotive turbochargers: All the most important facts
In order for the correct mixture to form in the combustion chamber, you need to monitor the condition of the filters, just like in a car. Just like in cars, fuel filters have different designs depending on the make and model of the bike. On many motorcycles, the fuel filter is part of the fuel pump. In this case, you do not need to constantly change the filter. Some motorcycles use consumable fuel filters that need to be changed periodically. This is very easy to do as they are easy to get to and the whole process does not present any difficulties.
Like motor vehicles, motorcycles have an air filter. True, in some motorcycles it is more difficult to access than the fuel filter. For example, on an SV Suzuki bike the air filter is located under the gas tank. In order to change the air filter on this bike model, you first need to turn it upside down, and then remove a number of components to gain access to the place where the filter is installed. This is about as difficult as replacing a motorcycle drive chain.
Engine oil
Lubrication is necessary to ensure that excessive friction does not occur between engine parts. It is implemented using motor oils that have a stable structure against high temperatures and low viscosity at low levels. In addition, they do not form carbon deposits and are not aggressive to plastic and rubber parts.
Oils are mineral, semi-synthetic and synthetic. Semi-synthetics and synthetics are more expensive, but these types are preferred more, as they are believed to be healthier for the engine. Different types of oils are used for two-stroke and four-stroke engines. They also differ in the degree of forcing.
Liquid cooling system
The option is similar to what is installed on cars. The coolant here is antifreeze, which is low-freezing (from minus forty to minus sixty degrees Celsius) and high-boiling (from one hundred twenty to one hundred and thirty degrees Celsius). In addition, antifreeze achieves an anti-corrosion and lubricating effect. Pure water cannot be used in this capacity.
Overheating of the cooling system can be caused by overload or contamination of the surfaces that dissipate heat. Also, individual elements in it may break, causing liquid to leak out. Therefore, the cooling operation must be constantly monitored.
Exhaust system
The exhaust system consists of a cylindrical exhaust channel, a pipe and a muffler. In two-stroke engines, efficiency and power directly depend on the size and shape of the system parts. Therefore, they use exhaust systems on each cylinder separately. They have a resonator, a pipe and a muffling nozzle.
In four-stroke engines, the exhaust is controlled by valves in the gas distribution system, so resonance does not play a special role in them. In them, usually all pipes are reduced to a single muffler.
On some motorcycles, the exhausts are equipped with catalytic converters that reduce the toxicity of emissions (they are installed, for example, on engines from Honda and other Japanese manufacturers). Such devices were developed as a result of increasingly stringent exhaust gas requirements in the European Union, the USA and Japan. In order to prevent the backflow of mixture from the cylinders at idle and low crankshaft rotation, the exhaust systems of many motorcycles are equipped with special power valves.