Motors of new IZhs
Responding to numerous letters from readers interested in more detailed information about the new Izhevsk motorcycles “Jupiter-Z” and “Planet-3” (“Behind the Wheel”, 1970, No. 4), workers of the Izhevsk plant L. KISELEV and N. ZAROZHEVSKY talk today about engines of these machines and ways to increase the power of previous models.
Rice. 1. New IZH engines: Jupiter-3 (left) and Planet-3 (right). At first glance, they can be distinguished by the modified left crankcase cover (IZH-Planet 3) and the “oblique” arrangement of ribs on the head (IZH-Jupiter 3).
When designing new, more powerful engines for the IZH Jupiter Z and IZH Planet Z motorcycles, we sought to ensure the maximum possible interchangeability of their components and parts not only with each other, but also with previous models. Therefore, the recently produced IZH-P2 engines, which had boost capabilities, were taken as a basis. As a result of extensive design, research and technological work, it was possible to create Jupiter-3 power units with a capacity of 25 hp. With. at 5200-6000 rpm and “Planet-3” with a power of 18 hp. With. at 4600-5200 rpm (Fig. 1). To do this, it was necessary to change the cylinders with heads, intake and exhaust tracts. Let's take a closer look at the innovations.
Engine IZH Jupiter
Relatively recently, motorcyclists became acquainted with the new road motorcycle “IZH Jupiter”.
Quite comfortable, easy to operate, reliable, and most importantly, with high dynamic and performance qualities, it is superior to its predecessor, the IZH-56. Take, for example, such an important indicator as maximum speed. At full load (driver and two passengers), the IZH Jupiter’s speed is 85-90 km/h, while the old model’s speed is 70 km/h. This speed, combined with good throttle response, is achieved mainly because the Jupiter has a more advanced engine than the IZH-56. Having the same working volume as the single-cylinder IZH-56 (346 cm3), the two-cylinder two-stroke IZH Jupiter develops significantly more power (by 5 hp), namely 18 hp. With. at 4900-5100 crankshaft revolutions per minute.
What are the design features of the new engine?
Compared to previously produced engines of this class, it is “short-stroke”, that is, it has a reduced ratio of the piston stroke (58 mm) to the cylinder diameter (61.75 mm). Thanks to this, it was possible to increase power by increasing the maximum number of revolutions at lower average piston speeds. Here is a typical example. If at maximum power mode the IZH-56 engine has an average piston speed of 12.2 m/sec at 4300 rpm, then the IZH Jupiter engine has an average piston speed of 5100 rpm. it is 9.85 m/sec. This reduction made it possible to reduce wear on pistons and cylinders, reduce friction losses, etc.
An increase in the compression ratio to 6.7–7.0 had a beneficial effect on improving power and economic indicators. This was also made possible due to the smaller cylinder diameter. As a result, the average effective pressure increased and fuel consumption decreased.
The IZH Jupiter engine is equipped with a plastic contact-oil air filter, which provides good air purification from dust, and therefore increases the service life of cylinders, pistons and piston rings. It is also a good muffler for intake noise. Less noise during operation, easier and faster starting of the IZ Jupiter engine increase the performance of the motorcycle.
A cross section of the IZH Jupiter engine is shown in the figure. Let us dwell on those components and parts that differ in design from the corresponding components and parts of the IZH-56.
The cylinder head is made of aluminum alloy. The presence of a large number of fins provides sufficient cooling surface. The spark plug is located in its central part. There is no gasket between the head and the cylinder.
The cylinder consists of an aluminum jacket and a pearlitic cast iron liner pressed into it. The shirt, which has a developed ribbed surface, is made by injection molding. There is one exhaust, four bypass and one inlet port located on the cylinder mirror. Two purge channels ensure the outlet of the working mixture at an angle of 45°, and the other two at an angle of 30°.
The plant produces three groups of cylinders, differing in internal diameter by 0.01 mm. The group number is located on the top outside of the cylinder outlet. The latter does not have plugs in the purge channels. A sealing gasket is installed between the cylinder and the crankcase. The inlet pipe is common to both cylinders.
The piston is made of KS-740 aluminum alloy with a high silicon content (16 to 22 percent), which provides a low linear expansion coefficient. Thanks to this, the thermal gaps between the cylinder and the piston are kept constant under different engine operating conditions.
There are two cast iron piston compression rings. The gap in the grooves between the piston and the ring ranges from 0.075 to 0.102 mm. Depending on the size, the pistons are also divided into three groups, according to which they are matched to the cylinders.
For better heat removal from the ring area, the piston walls opposite the grooves are thickened. This allows you to reduce the temperature in the groove area and almost eliminates burning and coking of the rings. On IZ Jupiter you can use pistons from Kovrovets-175 motorcycle engines.
The hollow piston pin with a diameter of 14 mm is made of 15X steel. Its seating in the piston bosses is floating when the engine is running, axial movement is limited by two retaining rings.
The design of the connecting rod ensures its durability. It is stamped from steel 12ХН2, has an I-section. A bronze bushing is pressed into the upper head. Two holes with a diameter of 6 mm are used to lubricate the piston pin. The connecting rod lower head bearing consists of 32 rollers measuring 4X6 mm, located in a brass cage.
The crankshaft consists of two separate shafts connected to each other by an external flywheel. Their relative position is determined using keys on the axle shafts. During assembly, the remote flywheel - a steel disk with a cut - is tightened with a bolt. The shaft of each cylinder is non-separable and has two steel cheeks with axle shafts. The axle shafts are connected to each other by a crank pin pressed into them.
The crankshaft rotates in four ball bearings, of which three are 205 series, and one, on the side of the drive motor sprocket, is 304 series. The 205 series bearings are lubricated from the crank chamber through holes in the crankcase, and the 304 series bearing is lubricated with oil directly from the gearbox. Yes .
The crankshaft is held against axial movement by retaining rings in the engine crankcase. The G-36M2 generator is attached to the right end of the crankshaft, and the driving motor sprocket is mounted to the left.
Engine torque is transmitted from the crankshaft to the clutch drive drum using a double-row bushing chain. The gear ratio of the motor transmission is 2.57.
The connecting rod and crank mechanism and all other units and components of the engine, the gearbox are located in an aluminum crankcase, consisting of two halves, with a connector along the longitudinal axis. During assembly, both halves are fixed with mounting sleeves and fastened with screws. On the side of the remote flywheel, aluminum crank chamber covers are attached to each half with screws. Rubber rings are placed between them to seal
A clutch cover with a hatch is attached to the left half of the crankcase. Through it, if necessary, you can tighten the clutch springs, as well as pour oil into the gearbox. The generator cover, which also has a hatch, is attached to the right half of the crankcase. It provides access to the generator for adjustments.
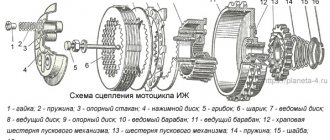
The clutch design is basically the same as on the IZH-56 motorcycle. The difference is that the outer drive drum is mounted on a ball bearing. This allows you to reduce its backlash and distortions during operation, increase the reliability and service life of the clutch drive discs.
The IZH Jupiter motorcycle uses an automatic clutch release device. At the end of the shift mechanism shaft there is a machine cam, which has two bevels, along which the lever moves, located on the bracket (it is attached to the right crankcase cover). When you press the pedal, the shaft of the shift mechanism rotates together with the cam of the machine and, thanks to the existing bevels, moves the lever. The latter presses the pusher: the clutch is disengaged and then the corresponding gear is engaged.
You can engage the clutch with a lever located on the steering wheel, as on the IZH-56, or with the gear shift pedal.
Great convenience is created by the double-shouldered lever, which allows you to change gears with both the toe and heel of the foot. The gearbox has the following gear ratios: I gear - 3.17, II - 1.71, III - 1.26, IV - 1.0.
The IZH-56 and IZH Jupiter gearboxes are identical in design, they differ only in the switching mechanism. After the clutch is disengaged, when changing gears on the IZH Jupiter motorcycle, the sector fixed to the mechanism shaft uses an anchor to rotate the worm shaft. The latter has shaped grooves into which the projections of the shift forks fit. When the worm shaft rotates, the forks move axially. They move gears. As a result, the corresponding gear is switched on or off.
The IZH Jupiter engine is equipped with a K-28Zh carburetor, which has a main fuel jet with a capacity of 270 cm3/min. The ignition timing is set within 2.2-2.6 mm before TDC. The engine is mounted on the motorcycle frame at three points, two at the front and one at the rear.
The IZH Jupiter motorcycle is produced with a side trailer, but can be used without it. In the first case, a sprocket with 16 teeth must be installed on the secondary shaft of the engine, and in the second - with 18 teeth.
Many parts and components of the IZH Jupiter and IZH-56 engines, for example the secondary shaft, drive and driven clutch discs, some gearbox gears, and the starting mechanism, are unified. It is very convenient to use.
These are the main design features of the IZH Jupiter engine. An article in one of the next issues of the magazine will be devoted to its care and operation.
V. ABRAMYAN,
engineer, public correspondent for the magazine “Behind the Wheel” at the Izhevsk Machine-Building Plant.
Cylinders
In order to improve the filling of the cylinders in both engines, the flow sections of the windows have been changed and the valve timing has been increased. This is clearly visible in Fig. 2. where the cylinder developments are presented. The IZH-Jupiter 3 engine uses a two-jet purge scheme, rather than a four-jet one. as it was on IZH-Yu2.
Rice. 2. Cylinder scans: on the left 2a - IZH Jupiter 3, on the right 2b - IZH Planet 3. The dotted line shows the windows of the IZH-Yu2 and IZH-P2 engines, respectively.
The thermal regime of engines of previous models, especially IZH-Yu2, was quite intense. Because of this, if the ignition or carburetor adjustments were violated, detonation sometimes occurred, the piston jammed, and the exhaust pipes darkened. To reduce the thermal stress of new engines and eliminate unpleasant consequences, the cylinders and heads were equipped with more developed fins, and on the Jupiter 3 model, in addition, the length of the exhaust channel in the cylinder was increased. Now the exhaust gases entering the exhaust pipe have a lower temperature.
Cylinder heads
In both new models, the combustion chambers located in the heads are formed by two concentric spheres (Fig. 3) with a central location of the spark plug. This form, despite increasing the compression ratio (up to 8.5-9 for IZ Jupiter Z and up to 8 for IZ Planet 3), ensures normal engine operation on the same grade of gasoline - A-72. This. certainly very beneficial to car owners.
Rice. 3. Combustion chamber of new IZH engines.
Retro review: Motorcycle IZH Jupiter 1964 (first generation)
In the 60s, motorcycles were very popular in the USSR. The domestic industry produced light, medium and heavy class equipment, some models were equipped with a sidecar.
This transport was in great demand, especially in rural areas. For many, it was an alternative to a more expensive and less accessible car. There were several factories for the production of motorcycles, and one of them was Izhmash.
In our retro review, IZH Jupiter-1 with a stroller is the founder of the next series of Jupiters. SKB motorcycle manufacturing began its design in 1958. Production of the model began in the second half of 1961.
The appearance of the motorcycle was quite modern for those years. The front wing is positioned high for off-road use. The gas tank is drop-shaped with a capacity of 15 liters.
The telescopic fork and rear pendulum suspension are equipped with hydraulic shock absorbers. Wheels are interchangeable, 19 inches. A chain drive goes to the rear wheel from the engine, and a cable rises from the front wheel to the headlight, where the speedometer is located.
A two-seater seat was a novelty then; before that, they had made do with separate saddles. Below it, on the left and right, there are 2 glove compartments: one for the 6-volt battery, the other for tools and small items.
The volume of the 2-cylinder, 2-stroke engine is 347 cc, compression ratio is 6.8, power is 18 horsepower. When properly tuned, this short-stroke engine is much faster and more resourceful than its 1-cylinder counterpart of the same volume.
Electricity is produced by a DC generator. There is only one carburetor - K28Zh. To reach the float release button, there is a hole in the aluminum casing with a hatch. In general, a 4-speed foot-shift transmission is located in the engine crankcase.
The motor starts with half a turn. The gearbox pedal is 2-arm, comfortable. It is enough to squeeze the clutch once when starting off and then you don’t have to use the lever anymore. After all, Jupiter-1 used semi-automatic gear shifting for the first time.
When moving, the engine is very responsive to the throttle. Mechanically driven drum brakes are sluggish by today's standards, but they suited everyone then. In a straight line, with proper adjustment, the motorcycle goes smoothly.
IZ Jupiter-1 was produced until 1966. In total, a little less than 0.5 million of these motorcycles were manufactured. Reasons for popularity: unpretentiousness to fuel, lack of spare parts and ease of repair.
For many years, these hard-working motorcycles were passed down from generation to generation. And you can still find them on our roads, with some examples in excellent condition.
Carburetor
Both motorcycles use a new K-36D carburetor with a diffuser with a diameter of 27 mm and a main jet with a flow rate of 260 cm3/min. It is a combination of parts from the famous K-36I and K-Z6Zh carburetors. The body was borrowed from the first, the atomizer and throttle needle were borrowed from the second.
Due to the new dimensions of the cylinder inlet ports, the pipes connecting the carburetor to the cylinder have also undergone changes.
The air purifier on IZ Jupiter Z and IZ Planet Z is the same with an outlet with a diameter of 57 mm (previously both models had 47 mm).
On IZH-Jupiter 3 (unlike IZH Planet 3), an additional rubber pipe with a diameter (clear) of 42 mm was introduced. It is connected to the air cleaner by an adapter flange. This was done because with a pipe with a diameter of 57 mm, the IZH-Jupiter 3 has insufficient power.
The new air cleaner replaces the two latches that secured the pan with four screws, which improve the tightness of the connection.