When any mechanism operates, a characteristic noise is created, and when it comes to a gasoline internal combustion engine, the “sound effects” are distinguished by increased volume, which causes a lot of discomfort both to the driver himself and to other road users, as well as pedestrians. As you know, the role of a noise absorber is played by a standard muffler, which is part of the exhaust system, but few people know why a resonator is needed, which is also an important component of this unit.
From the name it is obvious that this part is responsible for resonating the sound streams that arise during the operation of the car engine. Simply put, the resonator dampens sound vibrations as exhaust gases exit the combustion chamber. Let's take a closer look at the device and features of this element.
What is a resonator?
One of the main parts of the combustion exhaust system is the muffler resonator. What it is?
The resonator is an important part of the exhaust gas exhaust system of any vehicle, which in appearance is similar to a small muffler. As a result, this part is sometimes called an additional muffler.
This unit itself reduces the noise level of the operating power unit, but this is only a secondary effect of performing its most important function - to ensure an even flow of burnt gases throughout the exhaust system of the vehicle.
During operation of a car engine, regardless of the number of revolutions, intermittent levels of gas pressure appear in the manifold. Their frequency largely depends on the number of cylinders used in the engine and its crankshaft speed. The resonator is precisely designed to eliminate these intermittent levels.
What is it for?
In a system that ensures the removal of burnt gases, the resonator ensures the timely removal of the gaseous mixture from the motor chamber.
A significant part of automotive specialists are confident that the level of useful power provided by the power unit largely depends on the quality of this part.
That is why sports cars are always amenable to modernization: the standard model of the resonator, which is included in the basic package, is replaced with a more advanced version.
In order for the main flow of the exhaust mixture from the engine to fall directly on this part, it is placed immediately behind the forward flow. As a result of this, the better quality and functionality the spare part is, the higher the overall driving performance of the vehicle will be.
In addition, the presence of such a spare part significantly reduces the level of emissions of harmful gases into the environment.
Resonator device
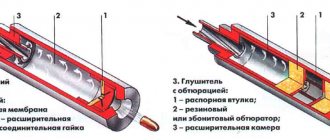
Structurally, the resonator consists of a perforated (drilled along the entire length within the device) pipe placed in a metal casing. The design also has a throttle hole designed to increase the efficiency of damping wave vibrations in the pipe. The internal cavity of the resonator is divided into two or more unequal parts by partitions located in a transverse plane to the pipe. Also, more modern exhaust resonators are designed with thermal insulation and/or sound insulation (often the same material) located under the housing and designed to reduce its temperature and/or sounds emanating from the device.
Internal structure of the resonator
The internal cavities have an unequal volume in order to ensure periodic narrowing and expansion of the flow of exhaust gases, which in turn equalizes their uneven pulsation. That is, each chamber has its own resonant frequency. In addition, they have a slight offset relative to the axis of the body. This is necessary to achieve a change in the direction of the exhaust flow. And internal perforation on the pipe is needed to dampen the large amplitude of sound waves that produce gases.
The efficiency of the resonator is influenced by the following factors:
- the degree of its wear, tightness;
- level of contamination from soot (the cleaner, the more effective);
- diameter (the larger the diameter of the device, the greater its efficiency).
The process of installing a direct-flow muffler
There are several ways to install direct flow with your own hands. We will tell you about the features of each of them right now.
“Reshaping” the standard muffler
You will need:
• muffler removed from your car;
• metal pipe with a diameter of 52 mm;
• grinder and 2-3 spare discs for it;
• iron brushes (the same ones used to clean frying pans from carbon deposits) – 50 pieces.
Let's get started...
1. Use a grinder to cut out a hole in the resonator to its full length;
2. The exposed insides of the muffler must also be cut off with a grinder, leaving 3-4 cm on each side of the pipe, to which we will weld a new pipe in the future;
3. Cut a piece from the prepared pipe of the same length as the distance between the ends of the cut pipes in the resonator;
4. On top of the pipe, using the same grinder, we make cuts every couple of centimeters, so that in the end a pattern resembling a herringbone appears. If you wish, you can make a lot of holes in the pipe, but this will require a drill and a lot of time;
5. We weld the pipe to the pipe scraps in the resonator, and fill all the free space with metal brushes. We weld the “lid”, that is, the piece that was cut down at the very beginning of the work;
TYPES OF RESONATORS
Like many parts, resonators are divided into types that depend directly on the vehicle engines. These parts must fit either a 2-stroke or a 4-stroke engine. With the help of tests, the following results were summed up:
- if the part interacts with the 4-stroke, the engine speed is reduced;
- When the part is removed, the engine speed increases.
In the case of a 2-stroke engine, the opposite happens. If you remove this element, the engine power decreases, which means fuel consumption increases. This waste is groundless; the vehicle owner will be forced to overpay at a lower vehicle speed.
Signs of a malfunctioning muffler resonator
Any malfunction of the resonator can lead to a decrease in motor power and also affect the noise level. Most often, car enthusiasts encounter the following signs of deterioration in the performance of the additional muffler:
- The volume of the exhaust system sound has increased.
- A metallic rattling noise appeared in the place where the resonator was installed. The reason for this may be that one of the internal parts of the resonator has burned through.
- Engine power began to drop. This is a consequence of the reduced capacity of the additional muffler.
If you notice one or more characteristic signs, repair or replace the resonator.
Checking the resonator
When identifying the problems listed above, every motorist should know how to check the resonator . This will not only normalize the operation of the engine and exhaust system, but also increase the comfort of using the car, including for the people around you.
To check, you will need an inspection hole (if you don’t have one, you can jack up the car). Diagnosis is made using visual inspection. During the process, it is necessary to carefully examine the integrity of both the device itself and the pipes connected to it (especially at their joints).
A clear sign of a problem is the formation of condensation in the cooling resonator, after which it begins to drip to the ground. This means that its body has lost its tightness and must be repaired, or better yet, replaced. You can check for condensation after some time, when you turn off the engine (to allow the resonator body to cool). Note! Some car enthusiasts, when making resonators on their own, specially drill a hole in its body to remove moisture . Therefore, if you bought a car with a similar resonator, then this testing method will not work for you.
Also, the integrity of the resonator body can be determined by the presence of exhaust gases leaving it. This also indicates depressurization and the need to replace it. This fact can be checked with the car engine running by looking under the bottom. To be sure, you can ask an assistant to “turn on the gas” at the same time so that more exhaust gases pass through the system. Also, suspicion of depressurization is caused by the appearance of smoke from under the bottom of the car while driving or when parked with the engine running.
Replacing a return flow muffler with a direct flow one with your own hands
When manufacturing a direct flow, it is advisable to use the positive properties of several types of structures.
Reasons for replacing a standard muffler with a direct-flow muffler
Car owners change the factory muffler to a direct flow one for several reasons:
Tools and materials for work
A direct-flow muffler is often purchased, but for lovers of tools and an insatiable thirst for creativity, we recommend making it yourself. It is preferable to make parts from stainless steel with a thickness of 0.8–2.0 mm. Select ferrous metal blanks with a thickness of 1.0–1.5 mm for the case, the rest 2.0–4.0 mm to avoid premature burnout of parts, and also use standard blanks. For the body, use a suitable size: a fire extinguisher, a thermos, an empty gas or scuba cylinder.
To fill the muffler chamber, non-flammable porous material or a combination of them is used:
How to repair a muffler
There are two ways to solve this problem. In the first case, you can buy a new muffler resonator. The price for it today is quite affordable. The cheapest option can cost about 500 rubles. But there are also mufflers that cost more than one thousand. At the same time, the choice of manufacturers and types of these system elements is quite large. If you follow the second path, you can also completely modernize the muffler resonator. In this case, it will be quite possible to carry out all the work on your own. When repairing a muffler, it is necessary to take into account the design features of the element, select the appropriate material and maintain tightness. Problems that arise with the resonator can be solved. To do this, you need to plan the work to be performed. If you have no experience in welding work, then invite a specialist.
DIY straight-through muffler
You can buy a direct-flow muffler in any specialized stores. They are usually of interest to young motorcyclists who dream of high speeds. But real bikers are not sold on stickers from famous brands. They do everything they need with their own hands.
If you want to enter the world for real men, you need to make a direct-flow muffler with your own hands. When riding at normal speed, its noise will not be different from other motorcycles. But as the speed increases, the characteristic rumble of the engine appears. What do I need to do?
Removing and installing the resonator
Many motorists are interested in a natural question - how to remove the resonator ? The answer to this question will vary depending on the brand of car. However, in general, the algorithm is simple and will be approximately as follows:
- it is necessary to disconnect the resonator pipes at the points of their connection with the exhaust gas removal system (front, on the engine or catalyst side, and at the rear, on the muffler side);
- remove the resonator from its suspensions, with the help of which it is attached to the bottom of the car;
- dismantle the resonator with its pipes.
How to replace a Renault Logan resonator
Installing a new device is done in the reverse order. When removing the resonator, it is important not to damage the O-rings that connect its pipes to the rest of the exhaust system.
As an example, we present to your attention two video instructions demonstrating the replacement of the resonator on popular Renault Logan cars and front-wheel drive VAZ 2110, VAZ 2111, VAZ 2112, VAZ 2114, VAZ 2115, Kalina, Priore, Grante.
Partial or complete failure of the car exhaust system resonator is not a critical failure . Diagnosing a resonator failure is not difficult even for an inexperienced car owner. This is indicated by a loss of power, the spread of exhaust gases under the bottom and/or into the cabin, and an increase in background noise when the engine is running. Please note that the car can be used case, however, we still recommend that you do not delay repairs, since driving with a burnt-out resonator can lead to failure of other elements of the vehicle’s exhaust system.
Features of work
If you look at the cross-section of the resonator, you will notice its similarity to a conventional muffler. The design of the exhaust system resonator is quite simple. The design includes several chambers separated by a special mesh. As a result, gas flows begin to narrow or expand, as their flow occurs unstably - in sharp jerks.
Additionally, we advise you to read the article by our specialist, which talks about how to make a flame arrester for a car with your own hands.
We also advise you to carefully study our expert’s article, from which you can learn how to choose a thermal tape for a muffler.
Thanks to the resonator, pulsation equalization begins to occur. The moving gas flows gradually become uniform.
The principle of operation of the exhaust system resonator is associated with the displacement of chambers that direct the movement of toxic gases. It changes dramatically, making the uneven pulsations smoother. To understand how the muffler resonator works, you need to know why there is a special perforation inside the pipe. It reduces noise from the acoustic exhaust.
To achieve stable operation of an additional pipe, it is necessary to constantly diagnose it. To obtain maximum performance and high efficiency of the product, several important factors must be taken into account:
- the condition of the catalyst, which reduces toxic substances in the exhaust;
- pipe diameter;
- muffler cleanliness.
The muffler resonator is one of the few that creates silence
The resonator is one of the most irreplaceable components of the exhaust system, in appearance it resembles a small additional muffler. Some side effects of its operation actually contribute to a significant reduction in the noise emitted by the engine, however, this is far from its most basic function.
Functions and principles of operation of the muffler resonator
First of all, the resonator facilitates the timely removal of spent engine exhaust, distributing it evenly throughout the exhaust system and freeing the chambers of the power unit for new gases.
Experts say that with the help of a resonator, it is possible to achieve uniform gas pressure in the exhaust system, which ensures minimal resistance and increases the productivity of both itself and the engine.
It is with its help that it is possible to achieve maximum engine efficiency, releasing all its useful power.
It is noteworthy that the resonator not only has external similarities with the muffler, the similarity is also noted in the internal structure of these parts. So, let’s note the most basic points on which the operation of the resonator and its similarity to a muffler are based:
- The resonator is divided into several different chambers, due to which periodic narrowing and expansion of gas flows is carried out, which evens out their uneven pulsation;
- These chambers have some displacement, due to which the direction of the exhaust flow changes, which also helps to dampen uneven pulsations;
- Internal perforation allows you to dampen the frequency of exhaust gases, which will provide a significant reduction in the volume of the exhaust sound.
As has already become clear, the resonator is an integral part of the muffler, located between the muffler and the neutralizer or intake manifold. Please note that depending on the vehicle model, its specific location in the exhaust system may vary. However, regardless of this, the resonator always significantly affects the driving properties of the car and the comfort of being in the cabin. Therefore, ensuring its high-quality work is one of the driver’s primary tasks.
“Symptoms” of resonator malfunctions
Since a breakdown of the resonator can negatively affect not only the sound properties of the muffler, but also the engine power, it is extremely important to identify and eliminate the malfunction before more serious problems arise. So, the main problems that will indicate a breakdown of the resonator include:
- Deterioration of the muffler - an increase in the volume of the sound of the exhaust system. If the resonator breaks down, it negatively affects the operation of the muffler, resulting in sounds when driving that are characteristic of a broken muffler.
- The presence of a rattling metallic sound in the area where the resonator is located. If such a sound occurs, then, most likely, one of the internal components of the resonator has burned out, resulting in its separation and “dangling” in one of the chambers.
- Significant drop in engine power. Due to a breakdown of the resonator, its throughput capacity is greatly reduced, as a result of which it can no longer suppress uneven exhaust pulsations, which negatively affect the operation of the power unit.
If such symptoms are detected and a malfunction is determined, it is the resonator that should be replaced, since it cannot be repaired. In order to reduce your costs as much as possible, we’ll figure out how to do it yourself.
How to replace the muffler resonator yourself
In order to replace the resonator yourself, you will need:
- Overpass or garage pit;
- New resonator;
- New gaskets for the resonator;
- New fasteners and O-ring;
- Two keys for 17;
- Anti-corrosion aerosol.
- And materials for repairing the exhaust system.
To carry out the replacement, we drive the car onto an overpass or garage pit and put it in gear, after which:
- We treat the bolts securing the resonator to the muffler with anti-corrosion aerosol, and then proceed to remove them. If problems arise, the aerosol should be applied several times per removal. Note that most often the bolts are torn off during such removal, however, perhaps you will be the one who will be able to save them.
- We disconnect the clamp securing the resonator to the muffler, then disconnect the pipes and remove the metal seal.
- We loosen the nuts securing the resonator to the neutralizer or collector, after which, lifting the resonator, remove the attached suspension cushions from the brackets.
- We finally unscrew the nuts securing the resonator to the converter or intake pipe, and then remove the resonator itself.
- Installation of the part is carried out in the reverse order.
Important! When connecting the resonator and muffler, carefully check the place where they meet, where there should be no cracks (gaps).
If they are present, the efficiency of the resonator drops significantly, and this is also fraught with the appearance of an unpleasant loud sound.
DIY straight-through muffler
You can buy a direct-flow muffler in any specialized stores. They are usually of interest to young motorcyclists who dream of high speeds. But real bikers are not sold on stickers from famous brands. They do everything they need with their own hands.
If you want to enter the world for real men, you need to make a direct-flow muffler with your own hands. When riding at normal speed, its noise will not be different from other motorcycles. But as the speed increases, the characteristic rumble of the engine appears. What do I need to do?
What is a resonator and what function does it perform in a car exhaust system?
The operation of the engine in vehicles, if we talk about internal combustion engines, is associated with the production of quite loud noise. But the driver, his passengers, and people on the street practically do not hear this noise effect.
This was not always the case. The first cars running on internal combustion engines were very noisy and created a lot of smoke, and therefore this became a real problem. But after some time they came up with a solution.
What it is
First, you need to understand what a resonator is in a modern car and what the purpose of this part of the exhaust system of a vehicle is.
A muffler resonator or simply a resonator is an integral part of the system responsible for removing exhaust gases from a running vehicle. Given the way this resonator looks, many people call it an additional muffler. It does look like a muffler, but it is not one. This is just part of the exhaust system.
Not everyone fully understands what a resonator is in a car with an internal combustion engine. It is often positioned as a unit to reduce the noise level of a running motor. But in fact, this is a secondary effect, which is achieved by performing the main function of the resonator. It consists of ensuring an even flow of exhaust gases throughout the vehicle exhaust system.
When the engine is running, regardless of the number of engine revolutions, so-called intermittent gas pressure parameters are formed in the manifold. Their frequency is largely influenced by the number of cylinders in the internal combustion engine and the revolutions made by the crankshaft. The resonator makes it possible to eliminate these intermittent parameters or pressure levels.
Why are resonators used?
Now, more specifically regarding why resonators are needed in cars. The name itself makes it clear that this element is responsible for resonating noise or sound streams that are formed during the operation of the motor.
If we talk in simple terms about why a resonator is in the exhaust system, then it is a damper of sound vibrations at the moment when the exhaust gases leave the combustion chamber. But this is not all the functionality of the component. In fact, resonators perform several tasks simultaneously, although the main one is considered to be resonating, or sound damping. Mainly low frequencies.
Experts say that the resonator in the design of the exhaust system serves not only to remove gas and reduce noise levels. Another point for which the device is used is to increase the useful power of the power plant. It’s not for nothing that sports cars undergo special modifications, where the standard resonator is changed to a more efficient option. In such cases, the element is placed directly behind the forward flow.
Direct exhaust system
An extremely important functional feature of the resonator is its ability to reduce the temperature of the exhaust gases. This significantly extends the service life of the entire system and the muffler in particular.
As an addition, we can note the fact of reducing the level of harmful emissions due to the participation of resonators in the operation of the automobile exhaust system.
Considering the functions and purpose of this element, questions arise as to whether it is possible to remove the resonator from the car, what will happen and what consequences are possible. Some people think that removing such an element is stupid. But there is far more than one such driver who removed the structure.
To answer this question, you should consider what will happen when operating a car without a resonator. The following will happen:
- The sound of the exhaust system will increase significantly. Sometimes it exceeds all permissible limits and becomes extremely unpleasant and noisy. In many ways, the noise level depends on the engine power and its speed;
- The increase in noise will be especially noticeable in the low frequency range. It is the resonator that dampens low sounds;
- the temperature of the exiting exhaust gas, which passes through the vehicle muffler, will increase. This significantly reduces its service life. The muffler will have to be replaced soon;
- the normal distribution of shock waves in the gas environment will be disrupted. At the same time, the vacuum zones will change. All this leads to noticeable engine power losses;
- Fuel consumption settings will also be disrupted. This will lead to increased fuel consumption.
It is possible to completely abandon the use of a resonator only in certain situations, when a comprehensive tuning of the exhaust system is carried out with the installation of additional elements and special tuning. If you simply remove the resonator from the exhaust and continue to operate the car in this condition, this will not give anything except increased noise and accelerated wear with all the ensuing consequences.
Calculation of the exhaust resonator for a two-stroke engine (GP Blair)
Speed of sound in a gas (pressure wave speed) One of the main parameters is the speed of sound, this determines the speed of the pressure waves that we use in the resonator.
Where: Tk - exhaust gas temperature (in Kelvin) R = 287 γ = 1.4, a0 - Speed of sound in gas (m/s)
The next task is to determine the temperature of the exhaust gases, in degrees Kelvin. The temperature depends on the engine mode and type, expressed in terms of BMEP . Machine-Dependent Brake Mean Effective Pressure ( BMEP ) The BMEP for a motor affects all resonator design parameters, and is calculated as shown:
Where: kW - engine power, kW (1 hp = 0.746 kW) (1 bhp = 0.746 kW) SVCC - displacement, cm. (SVCC is swept volume, cc) Rpm - revolutions per minute - engine speed (Rpm is engine speed, rpm) BMEP - pressure in bar
Average Exhaust Temperature Once the engine's BMEP is determined, the average exhaust temperature can be calculated using the formula shown below. This is an empirical formula based on measurements during testing.
Where: Tk - exhaust gas temperature in Kelvin BMEP - in bars (Bar)
This formula was calculated based on the following table:
| Motorcycle type | BMEP, bar (Bar) | Avg. exhaust temperature, °C |
| Motorcycle Grand Prix Racer | 11+ | 650 |
| Enduro | 8 | 500 |
| Roadster | 5 | 350 |
Adjusted Release Length
Blair's formulas assume that the adjusted release length is to the end of the tapering cone. Given by the formula below.
Where: Lt is the tuned length, mm a0 is the found speed of sound, in m/s Qep is the length of the release phase, degrees (exhaust duration, degrees)
Effective Exhaust Diameter (EXD) This is the diameter of the pipe whose cross-section corresponds to that of the exhaust port. (Formula for a rectangular window. P is the number "pi".)
Where EXD is the effective diameter, mm. width — window width, mm height — window height, mm If the exhaust windows are not rectangular in shape, the total area of the exhaust windows is substituted in the formula instead of width * height.
Emission coefficients. There are several coefficients used in resonator calculations - they are a function of the mode and type of engine.
These formulas are the result of interpolation of the tabular data (below), - Note that these engines use gasoline, and range from 50cc to 500cc per cylinder. This web page has been copied by someone for use with glowplug engines. It is doubtful that these formulas are suitable for such engines, since the exhaust gas temperature is much lower and the speed is much higher. If the person who copied the pages sent an email request asking my permission, I could tell it was not appropriate.
| Motorcycle class | BMEP, bar (Bar) | K | K 1 | K2 |
| Enduro | 8 | 0.7 | 1.125 1.25 | 2.25 |
| Motocross | 9-10 | 0.65 | ||
| Grand Prix (GP) motorcycle (Grand Prix Racer) | 11+ | 0.6 | 1.05 | 3.25 |
Calculation of a resonator with a two-stage diffuser.
The diagram of a typical resonant exhaust system with a two-stage diffuser is shown above. Note that the length of the straight pipe section LP01 includes the length of the outlet pipe, that is, LP01 is measured from the piston wall. The following table gives dimensions for the lengths of the exhaust system with two expansion stages.
| LP01 = 0.10LT | LP12 = 0.41LT | LP23 = 0.14LT |
| LP34 = 0.11LT | LP45 = 0.24LT | LP56 = LP45 |
Diameters of a two-stage diffuser for a resonance chamber. D1 = K1.EXD D3 = K2.EXD D4 = K.EXD
Calculation of a three-stage diffuser.
A simplified diagram of a typical three-stage diffuser resonant exhaust system is shown above. Note that the length of the straight pipe section LP01 includes the length of the outlet pipe, that is, LP01 is measured from the piston wall. Calculation of the dimensions of a three-stage diffuser. The following table gives dimensions for the lengths of the exhaust system with three expansion stages.
| LP01 = 0.10LT | LP12 = 0.275LT | LP23 = 0.183LT |
| LP34 = 0.092LT | LP45 = 0.11LT | LP56 = 0.24LT |
| LP67 = LP56 |
The following table gives the diameters of the three-stage diffuser
| D1 = K1.EXD | D4 = K2.EXD | D5 = K.EXD |
It can be seen that two additional parameters are required to calculate the diameter. They are defined like this:
Note also that an additional coefficient has appeared. This Kh coefficient is called the "horn coefficient", with typical values between one and two.
Small Kh values are best suited for GP engines with narrow power regions, large values are best for wide-range, more flexible engines.
(We are talking about engines with multi-stage gearboxes and an uneven torque characteristic (GP) - versus engines with a flat characteristic - “elastic”, with good “low-end traction”, for driving with infrequent gear changes - approx. trans.)
This document uses formulas from the books mentioned in the introduction. It is difficult to overstate the usefulness of these books for two-stroke design. All formulas are provided "as is", without warranty of suitability or correctness. The author would be interested in hearing from developers who have used the data presented here to make their own resonant systems. The author would also like to know about other formulas currently used for resonator design. The author would also like to receive constructive criticism and pointing out errors in the text of the document.
Components of the structure
As previously noted, the appearance of resonators is very similar to mufflers. Because of this, they are easy to confuse for a beginner. And more experienced motorists call resonators small or additional mufflers.
In fact, structurally this is a rather complex element, including several layers. Moreover, each of these layers is responsible for performing a specific function.
If you get acquainted with the structure of car resonators in cross-section, you can really notice a significant external resemblance to the standard standard muffler of a vehicle.
It is worth making some clarifications regarding how the muffler resonator is arranged in a car:
- the design is presented in the form of several chambers, which are separated from each other by a special mesh;
- This structure allows you to constantly narrow and expand the flow of exhaust gases. It is important to note that the gas comes out in sharp jerks. The resonator evens out these jerks, which allows you to obtain a uniform flow of exhaust gas at the output;
- the chambers inside are slightly offset, which allows you to change the direction of exhaust movement, thereby smoothing out uneven pulsation;
- Exhaust frequency damping occurs due to internal perforation. With its help, the noise level is reduced.
An automobile resonator performs its tasks thanks to a design that provides for the presence of a large number of closed cavities connected to each other using a pipeline and many perforations, that is, holes.
The holes provided by the design make it possible to cause multi-frequency vibrations that change due to friction.
As for the location, this element of the exhaust system is installed directly between the intake manifold or converter and the standard muffler.
But the location may be slightly different. This depends on the specific vehicle model and manufacturer.
It is important to understand that the gas produced in the engine during combustion of the air-fuel mixture has a high temperature. In this case, the function of the car resonator is to reduce it, reducing the thermal load on the muffler and the exhaust system elements coming after the resonator.
Now as for what temperature is at the outlet of the combustion chamber and under what thermal loads the small muffler operates. Depending on the specific vehicle system, temperatures can reach over 650 degrees Celsius. After combustion, the exhaust gas goes to the intake manifold at extremely high temperatures.
When reaching the car muffler resonator, the temperature does not drop so much. Therefore, it is extremely important that the resonator is made of high-quality and heat-resistant materials. When the resonator itself operates efficiently, it contributes to a drop in temperature, due to which the load on the muffler is significantly less. This extends its service life and preserves the integrity of the entire automotive exhaust system.
Resonators or additional mufflers are classified depending on the type of engine they are used on.
Therefore, there are 2 main types of devices.
- Designed for installation on two-stroke engines. If the vehicle is equipped with such a motor, which is not so common these days, then the resonator becomes a mandatory element of the exhaust system layout. If the resonator is missing, this will immediately lead to an increase in the amount of fuel consumed. The operation of the motor will change for the worse, speed and power will decrease. This is due to the fact that not only exhaust gas will be removed, but also incompletely burned fuel. Hence the drop in speed parallels the increase in fuel consumption.
- Resonators installed on four-stroke power plants. In the case of such engines, the resonator may not be beneficial to the car, but may create certain additional problems. Removal allows you to increase the engine power level by approximately 15%. Experienced motorists believe that on four-stroke engines the resonator only interferes with the normal operation of the engine. Yes, if you remove it, the power will actually increase. But at the same time, the environmental friendliness of the vehicle will deteriorate, and the exhaust will begin to pollute the environment. Therefore, 4-stroke engines still have resonators that allow them to achieve the required environmental standards.
Features of work
If you look at the cross-section of the resonator, you will notice its similarity to a conventional muffler. The design of the exhaust system resonator is quite simple. The design includes several chambers separated by a special mesh. As a result, gas flows begin to narrow or expand, as their flow occurs unstably - in sharp jerks.
Thanks to the resonator, pulsation equalization begins to occur. The moving gas flows gradually become uniform.
The principle of operation of the exhaust system resonator is associated with the displacement of chambers that direct the movement of toxic gases. It changes dramatically, making the uneven pulsations smoother. To understand how the muffler resonator works, you need to know why there is a special perforation inside the pipe. It reduces noise from the acoustic exhaust.
To achieve stable operation of an additional pipe, it is necessary to constantly diagnose it. To obtain maximum performance and high efficiency of the product, several important factors must be taken into account:
- the condition of the catalyst, which reduces toxic substances in the exhaust;
- pipe diameter;
- muffler cleanliness.
The principle of operation of the pipe is to use closed cavities located near the pipeline. They are connected to the product by numerous holes. Typically, the housing contains two different volumes, separated by a solid partition.
Differences between a resonator and a flame arrester
You can quite often come across stories from motorists who installed a flame arrester in the exhaust system of their vehicle. But not everyone knows what it is and how a resonator generally differs from a flame arrester.
Some argue that the only difference is the name. Others claim there is a significant difference between the two elements. It is necessary to understand the issue in more detail.
There is a device that for some reason in Russia and the CIS countries is often called a flame arrester. Let's start with the fact that the element does not extinguish the flame. This is where questions arise regarding the strange name. But the structure is actually installed in the exhaust system.
Moreover, flame arresters are placed directly behind the exhaust pipe. In fact, this design performs the tasks of an additional resonator. But here it is worth making some amendments.
In Russia, environmental standards are not nearly as strict as in Europe. Because of this, quite often on cars you can find situations where a flame arrester is installed in the rightful place of the catalytic converter, that is, the catalyst. Although the catalyst allows us to reduce the level of harmful emissions into our atmosphere.
In terms of its role in the exhaust system of a vehicle, a flame arrester really resembles a resonator in many ways. Its main functions include the implementation of the following tasks:
- partially compensates for the impulses that occur during detonation of the air-fuel mixture inside the combustion chambers;
- partially compensates for noise or sound waves in the low frequency range;
- regulates the movement of exhaust gas;
- reduces the temperature of the exhaust gas.
Now regarding the differences that directly interest us between the resonator and the so-called flame arrester.
The difference is in 2 main things:
- Flame arrestors must be made of high quality materials. This is due to its installation directly behind the exhaust pipe. Therefore, the absorber is subject to significant temperature loads and fluctuations. If the material is of poor quality, the element will quickly fail.
- A resonator compensates for sound waves more effectively than a flame arrester. After all, the direct responsibility of the resonator is precisely to compensate for peak sound waves, to organize the sound before it goes to the muffler.
Taking these factors into account, we can say that each element performs its assigned functions. The flame arrester and the resonator are not synonymous devices at all. These are slightly different elements of the exhaust system of a vehicle. But there really are similarities between them.