Modern motorcycle equipment is equipped with two types of internal combustion engines: two- and four-stroke power units. Therefore, when choosing motor oil for a scooter, you need to be guided not only by the popularity of the technical fluid manufacturer, but also take into account the performance characteristics of the model, as well as the manufacturer’s recommendations.
API classification
According to the API (American Petroleum Institute) classification, lubricants are divided into classes marked with two letters, the first of which is S (Service), the second indicates the category of vehicles for which this composition is suitable. For modern bikes, products of the SG and SH classes are most often recommended, and somewhat less frequently - SJ and SL. This is due to the fact that the latter two are capable of increasing engine power, but due to the content of anti-friction additives they can worsen the performance of the motorcycle clutch.
Troubleshooting your scooter's battery charging system
This article will focus on troubleshooting the charging system of a scooter battery. If your scooter's battery is constantly draining, this may be due to a problem with the battery power system. To test this system you will need a multimeter.
When the scooter's on-board voltage is 12 volts, the battery is simply necessary for the normal operation of the moped, since it provides electricity to its starter and carburetor starting enrichment.
The scooter's generator begins to produce electricity (alternating current) when the engine is running starting from 2000-3000 rpm. With the help of a converter-stabilizer, alternating current is converted into direct current, which is needed to charge the battery. The stabilizer ensures that the battery does not overcharge. If the battery needs charging, the stabilizer passes current to it. When the battery is fully charged, the stabilizer seems to turn off and no current is supplied to the battery.
If the power supply system is damaged and no current is supplied to the battery, it will not charge. Until the battery is completely discharged, the scooter's motor will continue to operate. When the battery is completely discharged, the engine will stall and will no longer start (either with an electric or kickstarter).
On the other hand, if the stabilizer does not turn off the current, this will lead to the battery being overcharged, it will heat up and “boil”, and the acid in the battery will leak out. As a result, the battery will fail and may burst.
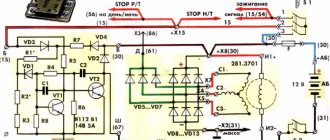
Rice. 1 Schematic diagram of the scooter battery charging system
Troubleshooting algorithm
Problem: Scooter battery is not charging.
1. Check the fuse and its contacts (clean if necessary). If the fuse is blown, it must be replaced. If the fuse is blown, the engine will not start.
2. Check the battery contacts. If necessary, clean with sandpaper and tighten the fasteners.
3. Check all wires and plugs of the battery charging system. First of all, check the ground - the blue or black (usually) wire that connects the negative terminal of the battery to the scooter frame. Sometimes cleaning the battery terminals is all it takes to get your scooter working again.
Engine lacks power
1. Start the engine and slightly increase the gas to observe.
If the speed does not increase as it should, then this may be
clogged air filter; clogged gas filter; clogged muffler; clogged carburetor; faulty starting enrichment; clogged or leaking rubber gas and air pipes leading to the gas valve and carburetor.
2. Unscrew the spark plug,
Candle color is “wrong”
faulty or dirty spark plug; over-enriched mixture; inappropriate spark plug heat rating; problems with the piston - it splashes with oil.
check spark
If there is no spark or it is weak
faulty or dirty spark plug; broken or shorted wiring; broken or “shorted” ignition coil; broken or “shorted” inductive ignition sensor; faulty ignition switch; faulty generator.
3. Check if the engine is overheating.
If yes then this could be
mixture too lean; gasoline of poor quality; heavy carbon deposits in the combustion chamber; early ignition time.
4. Check the compression in the cylinder.
If compression is absent or low (4-6 atm)
faulty reed valve - for 2t engines; leakage through the crankcase, for example through the crankshaft seals - for 2t engines; burnt or loose valves - for 4t engines; torn cylinder head gasket; burnt or worn piston and/or cylinder and/or rings; crack in the cylinder head.
5. Check the ignition timing.
If the ignition timing is incorrect
faulty switch (CDI); faulty generator; The generator rotor is installed incorrectly.
6. Accelerate quickly or continue driving at high speed.
If the engine knocks (knocks)
mixture too lean; heavy carbon deposits in the combustion chamber; gasoline of poor quality; clutch slips.
Do-it-yourself voltage regulator for a scooter
You can make a relay regulator yourself; this requires a little knowledge and a scooter voltage regulator circuit. We will make a voltage regulator for a Chinese scooter with our own hands. The cheapest option is to use a shunt voltage regulator. The caveat is that for proper operation you need to disassemble the generator and remove the wire from ground with a separate wire.
It was decided to make a voltage regulator with your own hands for the reason that the Chinese analogues are so lousy that there are simply no words. Look at the photo of the Chinese voltage regulator circuit:
We will assemble a single-phase generator according to this circuit:
In order to make a relay regulator, you must first disassemble the generator and remove the stator from the engine. Now we see this picture:
The photo shows a mass that needs to be unsoldered, and to it we need to solder a separate wire to the winding. After which it needs to be taken outside. This wire will be one end of the winding. The other end is the white wire.
After this, carefully reassemble the generator in reverse order. Why was all this going on?! We now have 2 wires coming out of the generator, which we will use (there are 3 wires in total). All the changes that have occurred can be seen in the photo below:
The voltage regulator connection is shown in this scooter voltage regulator diagram:
OK it's all over Now. Our DIY scooter voltage regulator is almost finished. Now you need to connect the yellow wire from our old relay regulator to the “+” terminal of the scooter battery.
After all the work done, we got constant voltage on our board. networks.
Another homemade voltage regulator for a scooter in the video:
Photo report: How to check the charging of a scooter?
The process of checking the charging of a scooter can be expressed in just a couple of sentences. There is nothing complicated in this matter: open the battery hatch, switch the tester to the mode for measuring direct current in the 20V range, start the engine and, without removing the terminals from the battery, give it a good gas and measure the current:
- If the current is less than 13.4V, check the wiring, generator, relay regulator
- If the current is more than 14.6V - check the relay regulator
In our case, the charge current is within the normal range, which means that everything is in order with the generator and relay regulator
In fact, there is nothing more to talk about and it could have ended there, if not for one “but”... And the “but” is what to do if the charge current is lower than normal, for example 12V or much higher, for example 16V or something else more?
In both cases, the situation cannot be left as is, especially in the second case, when the charge current is higher than normal. Since sooner or later the high current will damage the battery and burn out all the light bulbs, and even the wiring
All the reasons for high or low charging current cannot be described in this article and they are all essentially individual. Some had a short circuit, some had a burnt-out control wiring in the generator, some had a faulty relay-regulator, and some messed up the wiring themselves... If you have skills in this matter, move towards the relay. regulator, you can't go wrong.
Signs that a check is needed
If the battery on your scooter often runs out, and it is still quite new, this means that there is a problem with the operation of the relay regulator. As practice shows, it burns out quite often. If the device is faulty, the battery stops charging completely and loses its capacity. This means you won’t be able to start the scooter with a button; you’ll have to start it with a kickstarter.
Another characteristic sign of incorrect operation of the device may be the frequent burnout of incandescent light bulbs. They themselves are durable and have a good durability, but are quite sensitive to voltage changes. This happens because the optimal voltage in the scooter network is considered to be 12-13 V. Increasing this value even by 2 V reduces the service life of electronics and components by 2 times.
The greater the deviation from the norm, the greater the likelihood that something will burn out in the scooter. Therefore, when starting the scooter from the starter due to a power surge and a faulty relay, the bulbs usually burn out.
Signs of a malfunctioning regulator are identical for all models of Chinese scooters. They are especially typical for charging relays for scooters of Chinese models with an engine capacity of 50 cc. Therefore, before making a decision to replace something in electronics, testing systems and devices should begin with the relay regulator.
How to replace a faulty relay regulator on a scooter?
If the charging current is not supplied to the battery contacts when the generator is working properly, the stabilizer needs to be changed. Replacing it yourself is not difficult.
To do this you need to do the following:
- Place the scooter on the central support.
- Find the location of the device in a specific moped model. If you can’t find it right away, you can use the instruction manual.
- Dismantle the cladding. Depending on the moped model, the stabilizer may be located on the front (under the front plastic), in the rear, or under the seat. In this case, the underseat space is removed along with the seat.
- Unscrew the device from its seat while maintaining the fasteners. As a rule, the relay is attached to the scooter frame with a bolt, or less often with a self-tapping screw.
- Disconnect the connector and secure the new regulator with the fastener. The installed device must have a pinout and connector similar to the one replaced, and be suitable in terms of parameters for this particular scooter model.
- Connect the relay-regulator on the scooter to a standard connector and assemble the remaining spare parts in the reverse order of disassembly.
How to make a relay regulator with your own hands?
To make a relay regulator with your own hands, you need a diagram and a little knowledge. The model of a homemade regulator is based on the principle of disassembling the generator and outputting a separate end of the wire from ground.
As a diagram, you can take the relay-regulator connection diagram (Figure 3), and on its basis assemble a single-phase generator.
To collect the stabilizer you need:
- disassemble the generator and remove the stator from the engine;
- then you need to unsolder the ground from the generator, solder a separate additional wire for the winding to it and bring it out. This wire will be one end of the winding. The second end is the generator wire;
- After removing the wires, you need to reassemble the generator in reverse order.
With this device, the generator has 2 wires (there should be 3 in total). You can connect the stabilizer according to this scheme:
Do-it-yourself relay-regulator manufacturing diagram
At the end of the process, you need to connect the yellow wire from the old regulator to the “+” terminal in order to obtain a constant voltage on the sides of the network. Check the resulting voltage regulator on the scooter. At this point, the process of creating a homemade device can be considered complete.
The relay regulator is a very useful thing and necessary for the normal operation of the moped. However, it requires attention and constant monitoring of its work. Therefore, if the device fails or its performance is unsatisfactory, it is better to replace it with a new one, the cost of which today ranges from 300 to 500 rubles.
How to check the voltage regulator of a scooter?
To check, you need to stock up on a multimeter that has a voltmeter function. It is needed to measure the voltage at the output of the voltage regulator.
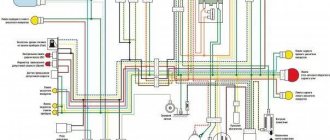
To measure the voltage, you first need to get to your destination. To do this you need to remove the front fairing. As a rule, it is fastened with several nuts and rivets (for example, Honda dio has 3 nuts and 4 rivets). We remove the fairing carefully, it is easy to damage. There we need to find a small box in which there are 4 outputs (some scooters have 5 outputs). The outputs have the following colors: green, red, yellow and white.
In order to measure the voltage, the scooter must first stabilize in operation, that is, the idle speed must be stable. You can put it on the step, start it and wait for it to stabilize. If the scooter does not start or does not hold idle, then read the article: the scooter does not hold idle. If everything is fine, then you need to measure the voltage between the red and green wires. We set our measuring device to 20V, constant voltage measurement mode. If the voltage is within 14.6 - 14.8 then this is the normal voltage of the relay regulator . If the regulator is faulty, then this value can fluctuate even by 5V or more in any direction. If the value is less than 14.5V, or exceeds 15V, then the regulator is faulty.
How to check PP with a multimeter on a moped?
The relay regulator on a Chinese scooter is checked using a multimeter with a voltmeter function. For this purpose, a simple DT-830 (or equivalent) is usually used. It is better to carry out diagnostics and measurement of output voltage with the device removed.
Verification algorithm:
- You need to unscrew the fairing with the central phase and find on the frame a device with 4 wires: red, green, yellow and white.
- Then start the scooter and check the voltage at idle: measure it between the green and red wires, setting the multimeter to the maximum value of 20 V.
- If the multimeter display shows a figure of 14.6-14.8 V, this is normal. For stabilizers on Chinese mopeds, this is the operating standard voltage. If at idle the multimeter shows a value of 15-16 V, this is a high voltage indicator. This indicates a malfunction of the relay regulator.
- Then you need to check the voltage supplied to the lighting lamps. An alternating voltage is supplied to the central low beam (high beam) lamp, so the multimeter should be switched to the alternating current measurement mode with a parameter of 20 V.
- Next, we measure the voltage between the green and yellow wires (green is the general electrical network of the moped). If the multimeter shows a network voltage of up to 12 V, then the electrical appliances are operating without additional load.
- If at idle this value is 16 V or higher, and with a sharp increase in engine speed it jumps to 25 V, the device does not stabilize the voltage and, therefore, does not work. With such readings, the device must be replaced with a new one.
Using a multimeter, the relay regulator is checked on a Chinese scooter.
On 4T scooters, the relay regulator is checked using a tester. Typically a mechanical tester is used for these purposes, although there are also electronic models.
In order to take a measurement, you need:
- switch the device to the “KiloOhm” mode and remove the regulator;
- then place the probes on the first pair of terminals (AB). The tester should show a value of no more than 18 kOhm;
- after that, we change the position of the probes on the terminals in the opposite direction (VA) and measure the voltage again - the arrow on the device should show 0;
- then we install the probes on the next pair of terminals (SD) and measure the readings on this pair;
- swap the probes (DS) and measure the indicator again;
- the remaining measurements have no contact and are not checked. The indicator when checking them should be zero.
In this way, regulators are tested on popular Japanese models with small engine volumes from brands such as Honda (Leard, Dio, Tact), Suzuki, Yamaha.
Replacing a faulty relay regulator on a scooter is not difficult.
What is a voltage regulator used for?
The relay regulator stabilizes the voltage of the scooter generator at the required level, not allowing it to increase or decrease the value above or below the norm. This prevents on-board voltage surges from going beyond the established limits (depending on the boards this is 12-14 V) and ruining the work of consumers whose service life is designed to be no more than 13 V.
That is, this part takes on the impulses that arise during the operation of the scooter (turning on the headlights, the starter button) and transfers the resulting thermal shock to itself. In this case, all the heat that could settle on the contacts is generated in it and removed through the device.
In addition to stabilizing the voltage, the relay also converts alternating current into direct current, which is necessary for charging the battery.
Moped manufacturers install charging relays with different parameters on scooters and select them individually for each. Depending on the regulator circuit, the connectors also differ. Chinese models usually have 5 terminals (male), while Japanese models have 4.
Scheme and principle of operation
The operation of the stabilizer for all models is almost the same and consists in distributing the current supplied from the generator to stabilize it and further distribute it to consumers.
The main peripheral consumers of the scooter include:
- battery;
- indicators;
- light bulbs;
- sensors;
- enrichment agent;
- other nodes;
- starting enrichment.
How does the stabilizer work? The main principle of its operation is to act as a transformer, which lowers the voltage to an optimal level acceptable for the operation of electrical appliances, and also stabilizes the network and prevents unexpected power surges.
If the relay malfunctions, the scooter’s devices fail, quickly wear out or burn out.
To avoid these problems and their undesirable consequences, you should know the basics of the correct operation of the electrical circuit and voltage components of the scooter (Figure 1).