Winter is knocking on the door... and often the first victim of the cold is your motorcycle battery. How to protect this? Here are our tips for maintaining, charging, and choosing a motorcycle battery charger.
Due to the first very cold weather conditions and the threat of snow and ice, many are choosing to store their motorcycle or scooter temporarily or for a longer period of time in a garage while temperatures rise. In this case, you must at least disconnect the battery from the motorcycle or scooter (they themselves are stored in a safe place), it is better to disassemble it in order to store it in a dry and usually heated place . Then under no circumstances allow it to discharge for too long.
How often should you charge your motorcycle battery?
The battery must be charged each time it is completely discharged. Conventional acid (in common parlance, lead) batteries, if they are not worn out, require recharging on average after 45-60 days; Old ones need to be recharged more often. But gel motorcycle batteries are more viable - 1-2 recharges per season will be enough for them.
Do not forget that the battery is characterized by a certain degree of self-discharge, even when turned off. This most often occurs in winter, when bikers park their motorcycles and batteries sit idle on racks.
It is hardly advisable to delay recharging until the time when the battery has stopped showing all signs of life during any attempts to start the motorcycle. This may ultimately result in over-discharging, which is highly undesirable and can greatly affect the health of the battery.
To eliminate undesirable consequences, it is necessary to monitor the condition of the device and regularly test it with a voltmeter.
A simple testing procedure involves the following steps: the indicator is set at 20 volts, the red probe goes to ( +) , the black probe goes to ( –) . We look at the readings (volts):
- 12.3 – position within normal limits, no recharging required;
- 11-12.2 – the battery needs to be charged;
- before 11 – critical condition, urgent recharging is needed, although it may not save the situation.
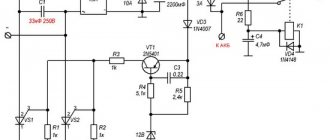
Chargers for charging a motorcycle battery at 12 volts
Chargers for this vehicle are usually divided into two main types:
- automatic;
- non-automatic.
Automatic chargers do not require owner intervention - they are simply connected, allowing the control unit to adjust the required current and maintain control throughout the entire charging cycle. This is especially convenient in winter when the battery is at home.
Non-automatic chargers require external control of the process. Usually a multimeter is used for this, and if you do not have time to stock up on one, you will have to carry out visual inspection. To do this, you need to remove the plugs from the battery and monitor the condition of the electrolyte.
Otherwise, manual chargers, which are cheaper, are no different from expensive automatic ones and charge the battery just as well.
To charge a motorcycle gel battery, take care of a special device in advance. Today you can choose the right charger without any problems - they are presented in a wide range in various online motorcycle stores. Chargers for gel motorcycle batteries are also divided into automatic and non-automatic. The price is influenced by the range of functions - the more there are, the higher the cost.
Many motorcyclists are also concerned about the question of whether it is possible to charge a motorcycle battery with a car charger. It is better, of course, to use a “native” device and resort to such substitutions in exceptional cases. This is explained by the fact that car and motorcycle batteries differ from each other in capacity: for the first batteries it is much higher and the chargers for them supply a higher current.
Unconscious use of such chargers can prematurely damage the motorcycle battery. You can use a car charger if it has a current regulator so that it is equal to 10% of the motorcycle battery capacity.
Advantages of a scooter with gel batteries
Automatic transmission, electric engine start, ease of getting on the scooter due to the absence of a gas tank in the front, affordable price and operation without a driver's license. All these are quite significant advantages when the question arises of acquiring a scooter. Having become the owner of a scooter, the first thing you should do is remain its owner. We are talking about alarm systems, of which there are sufficient quantities on the motor market today to suit every financial taste.
There are several types of scooters - city scooters, exclusively for short trips on smooth asphalt, scooters with a retro design in the style of the 50s, and cruiser scooters, designed for long rides in comfort. And to ensure constant comfort when driving and starting, it is recommended to install gel batteries on scooters . What is the difference between a gel battery and the most common acid battery?
Appearance of a gel battery for a moped
Rules and methods for charging a 12-volt motorcycle battery
General charging scheme
If a new battery is used on a motorcycle with a tuned electrical system, there will generally be no need for regular charging. In other cases, you need to perform the following algorithm of actions:
- Remove the battery from the motorcycle.
- Remove the plugs from the serviceable batteries and prepare a hydrometer (voltmeter for maintenance-free sealed batteries) to check the density of the electrolyte.
- Take in the required amount of electrolyte (the hydrometer - spindle - should float freely) and watch the charge reading: 1.28 g/cm3 - full; 1.20 kg/l – 50 percent; 1.12 g/cm3 – battery is discharged.
- Connect the charger (positive wire and battery positive terminal).
- Set the charging current (the parameters should be looked at the packaging or on the battery itself).
- When there is no marking, you need to charge with a current that is equal to 10% of the capacity (at 10A/h, the charging current is not >1A for ten hours). Charge until the electrolyte density reaches 1.26-1.27 g/cc. cm.
Maintenance-free batteries that cannot be topped up with water are charged exclusively by devices that have automatic voltage maintenance.
Charging an acid battery
They are charged with current depending on their capacity in a ratio of 1:10. The regulator sets the desired value.
The process continues until the voltage is equal to the number of battery cells when multiplied by 2.4 (the average is 14.4 for a typical battery). Visual observation of the electrolyte will show the onset of this moment by the formation of bubbles on the surface of the acid. It will be necessary to reduce the current by 2 times and continue charging for 2 hours.
Charging the gel battery
Its current-to-capacity ratio is the same as that of lead batteries. But there is a distinctive feature in the process itself - the voltage supplied to the battery should not be higher than the threshold. For most of these batteries the figure is 14.2-14.4 V.
Another feature is that there is no need to reduce the current at the second charging stage. The process will occur automatically until fully charged. Typically it will take approximately 10 hours to complete.
If the battery is excessively discharged (there is no difference - lead or gel), it must be restored using a current strength 2 times lower than usual. This will be 5% capacity. This will significantly increase the charging time.
Constant current charging
The average charging rate of acid batteries, which are used more often than alkaline ones (although the latter are less sensitive in operation), is calculated by dividing the battery capacity (see technical specifications) by 10. Therefore, it is recommended to select the battery charging current from the capacity ratios. So, at 6A/h, a current of 0.6 Ampere will be sufficient. This current is provided by a portable pulse-type charging device #171; Aida UP-12#187.
This method will require checking the temperature, electrolyte density, and voltage. In order for the process to proceed efficiently, the check must be carried out periodically, at least every 60 minutes, while simultaneously adjusting the current strength. To increase the charge level, the current strength must be reduced by half when the voltage increases to 14.4V.
The completion of charging can be judged by the level of voltage, density and gas output.
Charging at a stable voltage
With this option, the charge level is closely related to the charger voltage. This is clearly visible in the parameters of the maximum voltage at the output of the device (volts) - the first line and the battery charge level (%) with continuous 24-hour charging - the second line:
- 14,4 – 85;
- 15 – up to 90;
- 16 – up to 97.
One hundred percent charging in 24 hours is achieved only with 16.4 V output. It happens automatically, so there is no need to control the process. Complete completion can be judged by the voltage - it will be equal at the terminals of the battery and charger. If you use a device with a lower voltage - 14.4 V, then to charge the battery, for example, to 95%, it will take not a day, but a longer period.
Fast charging
The principle of operation is to use increased current parameters. In less time, you can breathe life into a dead battery.
The procedure is somewhat similar to that described above, but the difference is that a slightly higher current is required to charge the battery. Its value must be set according to the maximum capabilities. Before you start charging, you need to familiarize yourself with all the parameters and study the inscriptions on the battery case (find out whether it supports fast charging).
For the most part, companies that produce batteries do not recommend using the accelerated method, as this shortens the battery life and causes sulfation of the plates. This is explained by the fact that during the charging process, the current strength is stored in memory, and the battery is no longer able to be charged 100% by the generator.
With constant accelerated charging of the battery, the service life is significantly reduced. Exceeding the battery charging current may cause an explosion!
Since this method excludes absolute restoration of capacity, one or more subsequent charges are required, but not in an accelerated mode, but in a more gentle mode.
Charging the battery with pulse current
It involves the use of a charger of variable current or voltage, that is, when the parameters increase or decrease at certain intervals.
The pulse current can be:
- asymmetrical;
- pulsating.
Charging a battery with asymmetrical current is characterized by polarity changes in each cycle. But the electric charge is higher with direct than reverse polarity (charge-discharge - 10:1, pulse duration - 1:2). In this rhythm the battery is charged.
With pulsating current, the peculiarity is that the battery is charged due to changes in the magnitude of the current and constant polarity.
Charging using a current stabilizer
Using this device, it is possible to avoid voltage surges that can lead to negative consequences when charging the battery. This happens when a very discharged battery is connected to, for example, a ten-amp charger. The voltage on the battery rises sharply from nine to twelve volts, the current reaches the maximum value that the charger can provide.
This situation can lead to the plates being bent and the can shorting out. To avoid such breakdowns, it is recommended to use stabilizers. When charging, you need to set the current indicator, which is equal to 5% of the battery capacity, and when an acceptable voltage is reached, increase it to the optimal level - 10%. During the process, the stabilizer will reduce the current and, when the battery is fully charged, the current will be zero.
Charging a maintenance free battery
Let's consider the situation using a non-automatic charger. By connecting it to the terminals of a 12-volt sealed (maintenance-free) battery and observing the polarity on the charger, we set the minimum current. After this, the charger is plugged into the outlet.
To properly charge a battery, a current of 1/10 of its capacity is required. That is, if the capacity is 30A/h, the current required is 3 amperes. The ammeter readings need to be checked from time to time, since the current regularly changes naturally, so you will need to return it to the desired value.
The charging process should continue until a voltage of 13.8 volts is reached (measured with a voltmeter). Having reached this indicator, it is necessary to reduce the current on the charger (for example, from 3 to 2 amperes) and return the voltage again to its previous level - 13.8 volts. The same procedure with the current strength will need to be repeated, reducing it by another 2 times (in our situation - from 2 to 1 ampere). The charger is now ready to be disconnected. In most cases, it takes approximately 12 hours to fully charge a 12-volt motorcycle battery.
Watch a video on how to charge a motorcycle battery:
Pros of a gel battery:
- Thanks to the gel filling, they produce a high current when starting;
- Significant service life, of course, subject to compliance with operating rules;
- Possibility of use immediately after purchase, since it is not serviced;
- If the case is damaged, the contents do not leak, unlike its lead counterpart;
- Almost does not pay attention to changes in the position of the scooter;
- Considered one of the safest types of batteries in the world;
- Tolerates winter and frost well in general;
- Minor disadvantages:
- High voltage accuracy when charging;
- The price is several times higher than the cost of lead batteries.
How to revive a dead battery?
Before you start reviving a completely dead battery, you need to find out the possible reasons for its failure.
Electrolyte boils when charging
If this is observed in one of the sections, then in all likelihood a short circuit of the plates has occurred. In this situation, instead of charging the battery, rinse the jar with distilled water. Do the procedure until all the coal chips disappear. Then bring the electrolyte in the battery to the required density and charge it.
If this method turns out to be useless, then the battery will no longer be of any use: with a closed battery, one conversation - to the landfill. Alternatively, you can mechanically close the plate (in road conditions) to get home.
Reducing battery capacity to zero
Most likely the battery plates have become sulfated. To revive a motorcycle battery, you need to stock up on:
- distilled water;
- nominal (1.28 g/cc) electrolyte density;
- hydrometer - a device that measures the density of the electrolyte (small devices are available for motorcycles);
- a charger with adjustable current;
- to the electrolyte - a desulfating additive.
As a rule, the process of cleaning battery plates is described in the instructions, but the key points are as follows:
- Fill the battery with electrolyte.
- We add an additive to the jars (there are also those that are added before filling).
- We expect it to dissolve in the electrolyte within 48 hours.
- We carry out a cycle of running the battery: we charge and immediately discharge the battery (we use the brake light lamp for this, but not the bike starter).
The discharge process should be continued until the voltage is at 10 volts. The cycle must be repeated until the nominal density of the electrolyte in the battery is reached.
The battery being serviced must have a special tube that will facilitate the removal of gases and condensate during operation. It should extend outside the bike and not close.
Read also:
- Just not at night: experts tell us how to properly charge your smartphone
- RULink company invites you to visit the online exhibition MIMS-2020
- Rules for charging smartphones are listed
- Motorcycle batteries RDrive eXtremal reached 2nd place in Russia
- Revolution in the ROM market: waterproof RDrive StartEasy starter-chargers
- Harley-Davidson has abandoned electric motorcycles
Tags: BC-12065Z, GS Yuasa, choice of charger, charger, motor battery, motor battery, smart charger