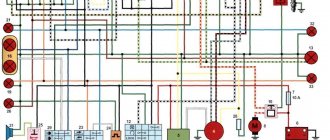
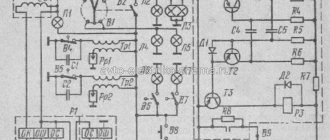
Modern scooters made in China have a similar layout. The engineers of the Celestial Empire did not bother and assembled all the critical components according to a single scheme. Even if there are differences, they are minimal.
This statement is also true for the electrical components of the moped. Any owner periodically encounters problems associated with these nodes. The electrical circuit of a Chinese 4t scooter is not a complex system; it contains only the main elements necessary for the full operation of the unit.
Knowing the main electrical wiring components and their purpose, you can quickly find the problem and fix it.
Delta moped wiring diagram china
The electrical circuit diagram of Chinese scooters is shown in the figure:
As with other electrical connections, there is a common wire on all cube mopeds. In this diagram it is the negative tire running along the entire body. The corresponding battery terminal is also connected to the scooter's frame, ensuring that each electrical component's ground is in constant contact with the power source.
Electrics and electrical equipment of a scooter
The main components in the 4t moped circuit are:
- central locking;
- battery charging source - generator;
- voltage limiter;
- spark formation and control systems;
- control elements for headlights, brake lights, turns;
- fuel level indicator in the tank.
All circuits are connected together using wiring.
Depending on the modifications and dimensions of the scooter, the instrument panel may include a tachometer - a device for monitoring the number of engine revolutions.
All of the listed nodes of the general scheme perform a strictly assigned role. Failure of at least one of them leads to the cessation of operation of the connected devices. Therefore, monitoring the serviceability of the main elements must be done every certain period for the purpose of prevention.
Factors affecting engine power
Four-stroke cycle 1=top dead center 2=bottom dead center A: intake stroke B: compression stroke C: power stroke D: exhaust stroke
The power of a piston engine depends on the volume of the cylinders, volumetric efficiency, energy losses - gas-dynamic, thermal and mechanical, the degree of compression of the fuel-air mixture, the oxygen content in the air and the rotation speed. Engine power also depends on the throughput of the intake and exhaust strokes, and therefore on their flow sections, the length and configuration of the channels, as well as on the diameters of the valves larger than the intake ones. This is true for any piston engine. The maximum power of the internal combustion engine is achieved at the highest filling of the cylinders. Crankshaft speed is ultimately limited by the strength of the materials and the properties of the lubricant. Valves, pistons and crankshafts experience high dynamic loads. At high engine speeds, physical damage to the piston rings and mechanical contact of the valves with the pistons can occur, which leads to engine destruction. The piston rings vibrate vertically in the piston grooves. These vibrations worsen the seal between the piston and liner, which leads to loss of compression, a drop in power and overall efficiency. If the crankshaft rotates too quickly, the valve springs cannot close the valves quickly enough. This can lead to contact between the pistons and the valves and cause serious damage, which is why high-speed sports engines use valve actuators without return springs. Thus, Daimler-Benz mass-produces engines with desmodromic valve control (with double cams, one opens the valve, the other presses it to the seat), BMW uses electromagnetic valve control. At high speeds, the operating conditions of the lubricant in all friction pairs deteriorate.
Together with the losses to overcome the inertia of the reciprocating moving elements of the CPG, this limits the average speed of the pistons of most production engines to 10 m/s.
Egnition lock
This component in the circuit of a 4-stroke 50cc or 150cc moped represents a switch. Moreover, it is multi-positional.
The lock performs the task of a central switch. It turns off the power to the entire scooter and turns the circuit back on when you turn the key. The larva itself is connected to a slider, which closes the corresponding contacts.
In the first position, the main wires interact - red and black. Current from the battery is supplied to the main circuits of the scooter. Since then it has been ready to launch.
The remaining positions close the black and white wire from the ignition module to the ground of the scooter. The operation of the motor is blocked by interrupting the spark supply from the coil. Depending on the modification, some models have a stop button in the electrical circuit. It performs the same function as the lock.
Compression stroke - two-stroke engine
The piston of a two-stroke engine rises from the BDC of the piston (in this position it is in Fig. 2) to the TDC of the piston (the position of the piston in Fig. 3), blocking first the purge 2 and then the exhaust 3 windows of the cylinder of a two-stroke engine. After the piston closes the outlet hole in the cylinder, compression of the previously entered fuel mixture begins. At the same time, in the crank chamber 1, due to its tightness and after the piston closes the purge windows 2, a vacuum is created under the piston, under the influence of which a combustible mixture enters the crank chamber of a two-stroke engine from the carburetor through the inlet window and the opening valve.
Generator
Owners of 50cc who are familiar with the design of the scooter will immediately understand the purpose of this device. It produces an alternating electric current that powers the moped when the engine is running. But the second main task is to charge the battery while working. That is, the battery ensures the operation of the devices when the engine is turned off, and then the generator takes on this task.
The connection is made according to the following principle. There are several wires coming from the generator. The negative tire is attached to the frame of the scooter. There is alternating voltage on the white wire, which is immediately sent for rectification and stabilization.
In the electrical circuit, the yellow wire powers the low and high beam lights. Additionally, a Hall sensor is located in the generator housing. Its task is to generate impulses to control sparking. It is not electrically connected to the generator; it is connected to a white-green and red-black wire. The sensor is connected to the CDI block.
Lubrication
Lubrication in both models is also carried out differently. In our case, it is carried out by proportionally mixing gasoline and oil. A 4-stroke engine requires the use of a special expansion tank. it is connected by a system of pipes to a plunger pump. from here the lubricant falls into the inlet pipe. Moreover, its quantity is supplied exactly in the volume that is needed.
Based on the foregoing, we can highlight the following advantages that a two-stroke engine has:
- Greater power with the same displacement;
- Simple device;
- Light weight of the unit.
All this forces designers and developers of modern technology to use this model in their new projects. Who knows, maybe over time the discharge and compression system will undergo changes, bringing the efficiency of the equipment to a new level.
Relay regulator
This is the same rectifier that converts alternating voltage to direct voltage, with a range of 13.5-14.9 V. C
.
The regulator is located under the plastic cover of the scooter at the front. It is attached to a metal backing for better heat dissipation.
The main circuits of the relay circuit are:
- The green wire is common.
- Red—the output of the converted and stabilized voltage is within the established limits.
- White and yellow - AC input to the regulator. Due to electronics, the voltage is converted into powerful impulses. The yellow wire supplies power to a heavy load on the on-board network - headlights and instrument panel lighting.
The current for lamps is not stabilized, but is limited to acceptable values. At high generator speeds, the voltage goes beyond the operating ranges of the lamps, which leads to their burnout. The situation is very familiar to those who have encountered faulty relay regulators.
Because of one unit, you can lose all the light bulbs in a matter of seconds, so you should monitor the on-board voltage regularly.
Ignition circuit components
The ignition system is an important element in the operation of the entire scooter. The formation of a spark and a precisely calculated impulse that ignites the fuel depend on it.
The scooter ignition circuit includes many components that are responsible for a specific job.
CDI ignition module
The first item in the list is the CDI module. This abbreviation stands for Capacitor Discharge Ignition - ignition from a capacitor discharge.
The switch module is made in a non-separable box, so if it fails, it is replaced with a new one. 5 wires are connected to it, distributed throughout the entire ignition circuit of the scooter.
The block is hidden inside the scooter, so getting to it is not easy. The plastic covers will have to be completely dismantled.
Ignition coil
The purpose of this component is a quick pulse of high voltage voltage based on a signal from the switch. It goes directly to the spark plug, where it is converted into a spark.
The coil is located on the right side of the Chinese scooter and is attached to its supporting structure. It is easy to recognize - it is made in the form of a plastic barrel. On the reverse side there is a thick wire connected. It is he who transfers the discharge according to the circuit from the transformer to the spark plug.
To protect against dirt and dust, the coil is placed in a rubber cover.
Spark plug
Its function is simple - to form a spark and ignite the mixture inside the cylinder. The scooter uses an A7TC spark plug.
Its position is hidden from view, but experienced owners know where to look for it. Having passed along the high-voltage wire, we reach the engine block and the spark plug cap.
The rubber seal protects the contact from accidental electrical breakdown. Remove with a little effort towards you. Do not pull the wire too hard - the cap may come off.
The spark plug is unscrewed with a socket wrench. After removal, you need to inspect the color of the contacts and their condition. An indicator of good engine performance is a brown tint without traces of soot. Deviation from the norm indicates a malfunction of the carburetor.
Starter
The device is used to make it easier to start a scooter engine, without using a kick pedal. The starter is located in the middle part of the moped, near the engine. To open it, you need to remove the decorative plastic.
The starter is connected through the starting relay, which is located on the scooter frame.
Fuel gauge and indicator
The sensor measures the amount of gasoline in the tank and signals the need to refuel. It is located in the tank itself and is connected by three wires.
The indicator is directly connected to the sensor. Both are powered by stabilized current from the rectifier. If problems are observed in the operation of the indicator, you should check the connection to the circuit.
Voltage is supplied only when the ignition switch is turned on.
Turns relay
The breaker is used to control the turn lights. When the button is closed, the relay produces current pulses with a frequency of 1 Hz.
The block is located under the instrument panel. To change the relay you need to remove the plastic protection.
Switching the circuit is not difficult. When turning right, voltage flows through the blue wire, which is responsible for the corresponding lamps. The left position of the switch shorts the gray bus to the orange one.
Duplicate lamps on the instrument panel are connected in parallel to the turns circuit lines. They signal that the lamps are on on a specific side of the scooter.
Sound signal
The purpose of the sound horn is clear to everyone. On the scooter it is located near the limiter relay.
The signal is powered by direct current through the ignition switch and is activated by a button on the handlebars of the moped. The component is non-separable, so if it fails, it is completely replaced.
How to properly repair scooter wiring?
All troubles come from ignorance. Or rather, from the reluctance of some people to receive this knowledge and apply it in practice. Sometimes a motorcycle comes in for repairs, and from the original wiring there are only three wires left in it, worn out by more than one roll of electrical tape... The illiteracy of scooter owners only benefits those who repair them; as long as there are such owners, there is enough work for everyone...
To successfully repair the wiring we will need:
- Terminals
- Heat shrink sleeve
- Soldering iron
- Terminal crimp
- Insulating tape
The most common faults in electrical wiring include the following:
- Burnout, violation of insulation integrity, breakage, oxidation of contact terminals
- Breakage, violation of insulation integrity, oxidation, combustion of wires
- Unqualified repairs, as well as installation of terminals, connectors, wires that do not meet the parameters of consumers
Malfunctions in wiring are easy to identify: just do a visual inspection of the wiring and a broken or broken wire will immediately reveal itself, as well as a terminal or connector. In particularly difficult cases, you can ring a suspicious wire for a break, but this rarely happens.
Let’s take an ordinary “Chinese” as an example. After an accident with plastic falling and breaking, all electrical appliances stopped working, including the starter.
Taking off the “face”
After a quick inspection, four broken wires were discovered.
The wires were broken for a reason: someone was repairing the wiring and laid the wires incorrectly: the harness was laid in the place where the front fork crossbar rests on the frame stop. While the scooter was driving normally, everything was fine. And as soon as the steering wheel turned sharply during the fall, the traverse broke four wires at once.
This malfunction is not serious and can be easily treated: cut the damaged wires with side cutters
Using the same side cutters, we cut small pieces of thin heat-shrinkable cambric
We put cambric on the wire
We strip 4-5 cm of insulation and do a classic twist. Classic twisting is done not in the collective farm way, but strictly according to those regulations:
Bend the wires at a distance of 1-2 cm from the insulation
We wind one core around another
We wind the second core and cut off the protruding ends
Collective farm twisting is done a little differently. In terms of the level of skill and culture of repair, such twisting is unacceptable.
According to all those regulations, the twists must be soldered with tin, crimped with sleeves, or the ends welded with a special welding machine. To deviate from those regulations is evil, so we take it and solder it.
We stretch the cambric over the twist and shrink it with a hairdryer. You can also seat it with a match, but you must follow fire safety measures. The scooter is made of plastic and also contains gasoline - it is better to use a hairdryer.
The problems with this scooter did not end there. During the course of the play, we also had to replace several terminals, insulate and re-lay the wiring.
When a wire comes off from the terminals, many people fix this problem something like this:
Such a collective farm cannot be left like this: the wires are barely holding on, and the current going to the signal is very high, and besides, the terminals are exposed - it’s closed for an hour. It needs treatment in any case.
We cut off the snot remaining from the previous repair from the wires, strip off 1 cm of insulation, and place the core in the terminal
Crimp the terminal
We cut off the cambric, put it on the terminal and seat it
A completely different look
After repairing the wiring, we put the wires in their places. If there are a lot of wires, we wrap them with electrical tape into bundles so that they move around. We turn the steering wheel from side to side and make sure that the wires are not stretched anywhere and do not rub against moving parts; we fix everything that requires fixing with zip ties.
As it was
How did it happen
Electrical circuit diagram of a scooter
Every car, motorcycle, moped, and scooter has electrical wiring - wires connecting electronic components, blocks and modules of equipment.
The correct operation of all systems, and in our case the scooter as a whole, depends on its serviceability. Today we will look at various options for schematic diagrams of the electrical wiring of a scooter.
Electrical wiring diagrams for scooters differ depending on their model. Below, the article offers various options for scooter schemes, perhaps one will suit you. If you do not have a diagram specifically for your scooter model, then you can use one of the proposed standard diagrams below:
A simple typical scooter diagram
Electrical diagram of the scooter STILET-150Z, JOKER-150Z
Electrical diagram of the DINK-125 scooter
Electrical diagram of the scooter VITALITY-50 2T
Wiring diagram for LIFAN/ZiD scooters - LIFAN LF50QT-15,
LF50QT-8A/9, Viper Booster, Race 1/2/3, Grand Prix, Phantom, Reggy Bizon
Electrical diagram of REGGY scooter
VIPER ACTIVE scooter wiring diagram
PATRON JOKER 50 scooter wiring diagram
Scooter wiring diagram. Engine 139QMB ("Poltosy")
Tags: [car]
SHARE WITH YOUR FRIENDS
Analogues - engine 1P39QMB
Chinese developers have created an analogue of the Japanese 139QMB engine - a motor labeled 1P39QMB, which in appearance completely replicates the original. Despite all the similarities, you can still find differences: the valve clearances on the 1P39QMB are not adjustable. The situation is similar with the carburetor: before direct operation it requires thorough cleaning and correct adjustment. Chinese copies of 139QMB engines, of course, cope with their task, but their main purpose was to reduce the final cost of motor vehicles. Budget versions of scooters are equipped with exactly the same versions of engines that are good only for short trips at low speeds.
Before starting operation, be sure to carry out a full run-in of the 1P39QMB engine. The optimal operating mode of the engine begins only after 2 thousand kilometers, but after 10 thousand kilometers all its technical characteristics drop, and it loses dynamics and power.
What does a scooter consist of?
Scooter variator belt sizes
Belt sizes for popular scooters (Honda, Yamaha, Kymso, etc.)
Engines on Chinese scooters
Article review of engines that are installed on Chinese scooters and mopeds, for example 139QMB or 1P39QMB engines
Scooter fuel system
The structure and main components of the fuel system of a 4T scooter.
Scooter gearbox - device
A gearbox is a mechanism that transmits and converts torque, with one or more mechanical gears. Scooter gearbox.
The working principle of a four-stroke scooter engine
The design of a four-stroke scooter engine, as well as its advantages.
Scooter carburetor design
At first glance, a carburetor looks like a complex device, but with a little theory, it will be easier for you to adjust it. The first thing you need to know is at least the basics of the principle of operation of the carburetor and its main controls and adjustments. The throttle handle on the steering wheel is directly connected to the air damper and the metering needle attached to it. Air passing through the carburetor will pick up fuel from the fuel chamber.
Scooter crankshaft - device
After tuning other engine components (piston, commutator, etc.), the crankshaft must be replaced with a stronger (tuned) one. The fact is that when tuning the engine, the power and engine speed increase, which means the load on the crankshaft increases; a large load on a standard crankshaft is unacceptable! This can lead to wear and “killing” of the bearings, connecting rod, and the shaft itself, which means a complete engine overhaul.
Scooter chain drive device
The drive transmission consists of two sprockets - driving and driven. The drive sprocket is mounted on the centrifugal clutch drum. When the scooter engine is idling, the sprocket drum is not connected to the crankshaft. When the engine crankshaft speed increases, the clutch engages and torque goes to the clutch drum and drive sprocket. The driven sprocket is rigidly fixed to the rear wheel gearbox shaft.
CVT device
Once upon a time, manual transmissions (from two to four stages) prevailed as transmissions for scooters, also called scooters. They were switched by rotating the left handlebar or, like a motorcycle, by a lever under the left foot. The main difference between a modern scooter and its predecessors and motorcycles is the absence of a manual gearbox. Its function is performed by an automatic transmission - a V-belt variator.
Automatic fuel tap
Automatic fuel tap (ATC) device
Features of a 4-stroke engine
In a two-stroke engine, lubrication of the piston and cylinder pins, crankshaft, piston, bearing and compressor rings is carried out by pouring oil into gasoline.
The crankshaft of a 4-stroke engine is located in an oil bath, which is a significant difference. That is why there is no need to mix fuel and add oil. All the car owner needs to do is fill the fuel tank with gasoline. The car owner, therefore, has no need to purchase special oil, without which a two-stroke engine cannot function. In addition, in the presence of a four-stroke engine, the amount of carbon deposits on the piston mirror and on the walls of the muffler is reduced
Another important difference is that in a two-stroke engine, a flammable mixture splashes into the exhaust pipe, which is due to its design
It should be recognized that four-stroke engines also have minor disadvantages. For example, their working moments for regulating the thermal valve clearance are not particularly high-quality.
General structure of the scooter
Any scooter owner should know how his vehicle works, because without such knowledge it is not only impossible to find out the cause of the malfunction, but also to eliminate it. Almost all equipment, no matter in which country or in which factory it was produced, has the same design for a scooter, so after examining and repairing one moped, you can easily troubleshoot any other.
Scooters are rightfully considered one of the most economical and unpretentious means of transportation. Ease of operation, low engine power and amazing maneuverability have made scooters one of the most popular types of equipment.
If we consider the general structure of a scooter, then we can say that this vehicle contains an engine, transmission, suspension, chassis, plastic parts and control systems. The functions of the main components of mopeds should be considered in detail.
- In a scooter engine (the device is often an internal combustion engine - an internal combustion engine), the energy obtained from fuel combustion is converted into mechanical energy, which sets the vehicle in motion.
- The main function of the transmission is to transfer torque from the engine to the drive wheel (in the case of scooters, this is the rear wheel). The transmission of most mopeds that were produced from the beginning of 2000 to the present day consists of an automatic variator, clutch, gearbox, and a foot start system.
| The diagram shows the general structure of the moped: 1 - front fairing; 2 — steering panel; 3 — protective steering fairing; 4 — seats for the passenger and driver; 5 — trunk located under the seat; 6 — wing; 7 — side fairing; 8 — rear wheel; 9 — power transmission; 10 — driver's floor; 11 — suspension; 12 - brake system. |
- The chassis of the moped includes both wheels, the brake system and the suspension. It is thanks to the suspension, which ensures the connection of the wheels to the frame, that vibrations during driving are dampened, and braking or speeding up are carried out smoothly and softly.
| The photo shows the structure of the moped, or rather, the “engine and transmission” unit: 1 - the place where the engine is attached to the frame; 2 — engine cylinder; 3 - the transmission itself, which includes the scooter’s variator device, as well as the clutch; 4 - place to which the shock absorber is attached; 5 - wheel. |
Basically, all mopeds have either a two-stroke or four-stroke gasoline engine and, depending on such features, the moped or scooter can be supplemented with various components - for example, an oil pump.
It should be noted that the design of the scooter’s carburetor also refers to the “engine-transmission” unit, although it is not indicated in the photo.
- The scooter's control devices include a steering wheel, a series of ignition buttons, turn signals, headlight switches, brake levers and a speed controller.
- Plastic cladding refers to all mudguards, fairings, as well as tuning such as spoilers or panels that perform an aesthetic function.
Side mirrors, trunk, saddlebags and other parts that are not included in the basic structure of the scooter are called additional components or equipment.
Despite the fact that many motorcyclists are accustomed to scooters with an automatic centrifugal clutch, on the market you can also find two-wheeled vehicles with a mechanical gear shift system (for example, with a four-speed manual gearbox with an engine capacity of 49.3 cc). Such scooters are considered rare and require great driving skills from drivers.
Engine Features
The official manufacturer of the 139QMB scooter engine is Hongling Corporation, which equips motorcycles not only of its own brand, but also of other brands with this engine.
The corporation sells power units to other manufacturers. The motor itself is very recognizable: the design features of the 139QMB engine and its markings on the left side of the crankcase immediately make it clear what kind of heart beats the scooter.
The motor has no flaws, does not require special treatment and calmly tolerates minor negligence and negligence. The manufacturer provides a guarantee for its products that covers the first 5 thousand kilometers. This mileage is enough for the new 139QMB 4t scooter engine to fully run in and grind in all elements and components of the systems.
The total service life of the engine is about 20 thousand kilometers, with the exception of 5 thousand running-in at an average driving speed of 90 km/h. The technical characteristics of the 139QMB engine are not bad: its power is enough for a two-seater full-size scooter.